Contents
- 1 Exploring Advanced Optical Concepts
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Modes of Multimode Fiber
- 1.3 Modulating a Light Beam
- 1.4 Understanding Broadband Light Sources
- 1.5 Nonlinear Scattering Phenomena
- 1.6 Frequency Combs in Precision Measurement
- 1.7 Focusing a Laser Beam
- 1.8 Amplifying Ultrashort Pulses
- 1.9 Rotating Polarization
- 1.10 Compressing Femtosecond Pulses
- 1.11 Adjusting Laser Wavelength
- 1.12 Conclusion

Source: YouTube
Exploring Advanced Optical Concepts
Introduction
In the realm of photonics, understanding the behavior and manipulation of light is crucial. This blog post delves into various advanced optical concepts, providing insights into their applications and significance in modern technology.
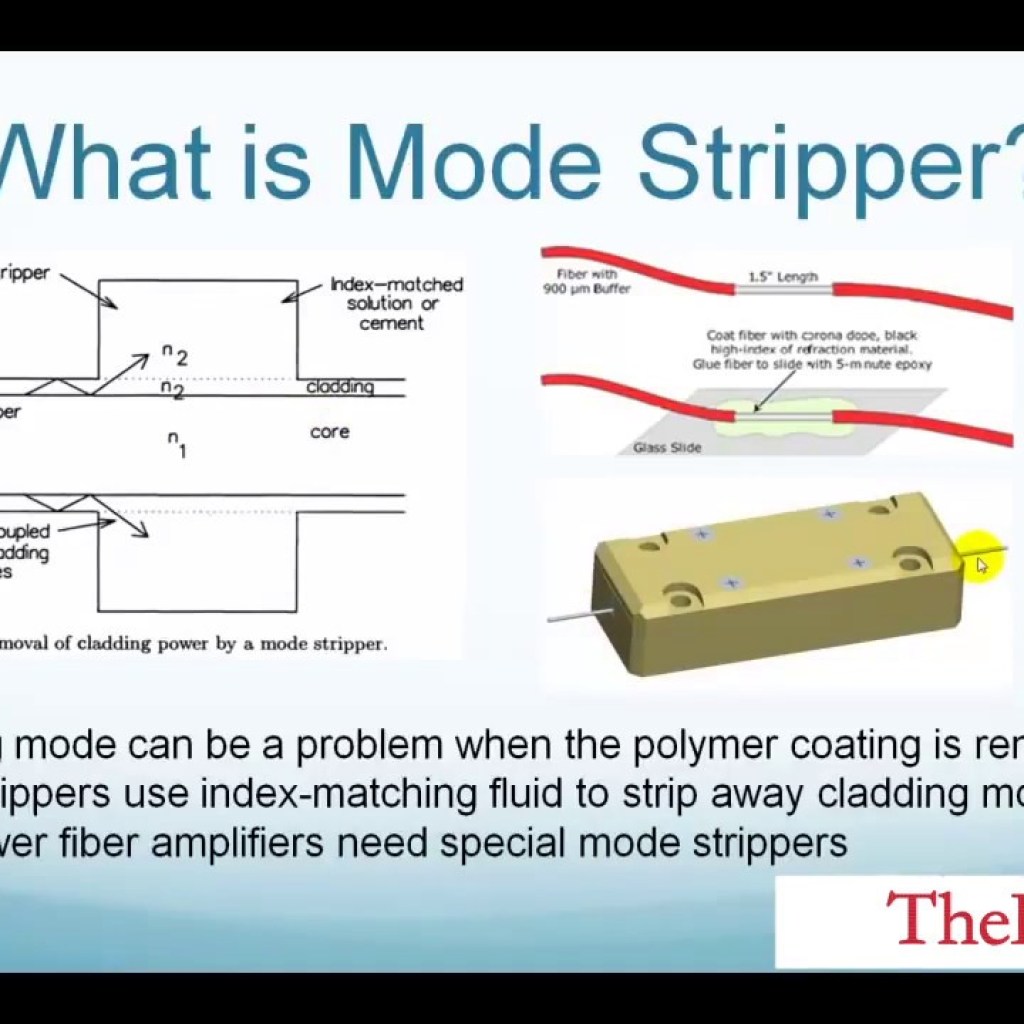
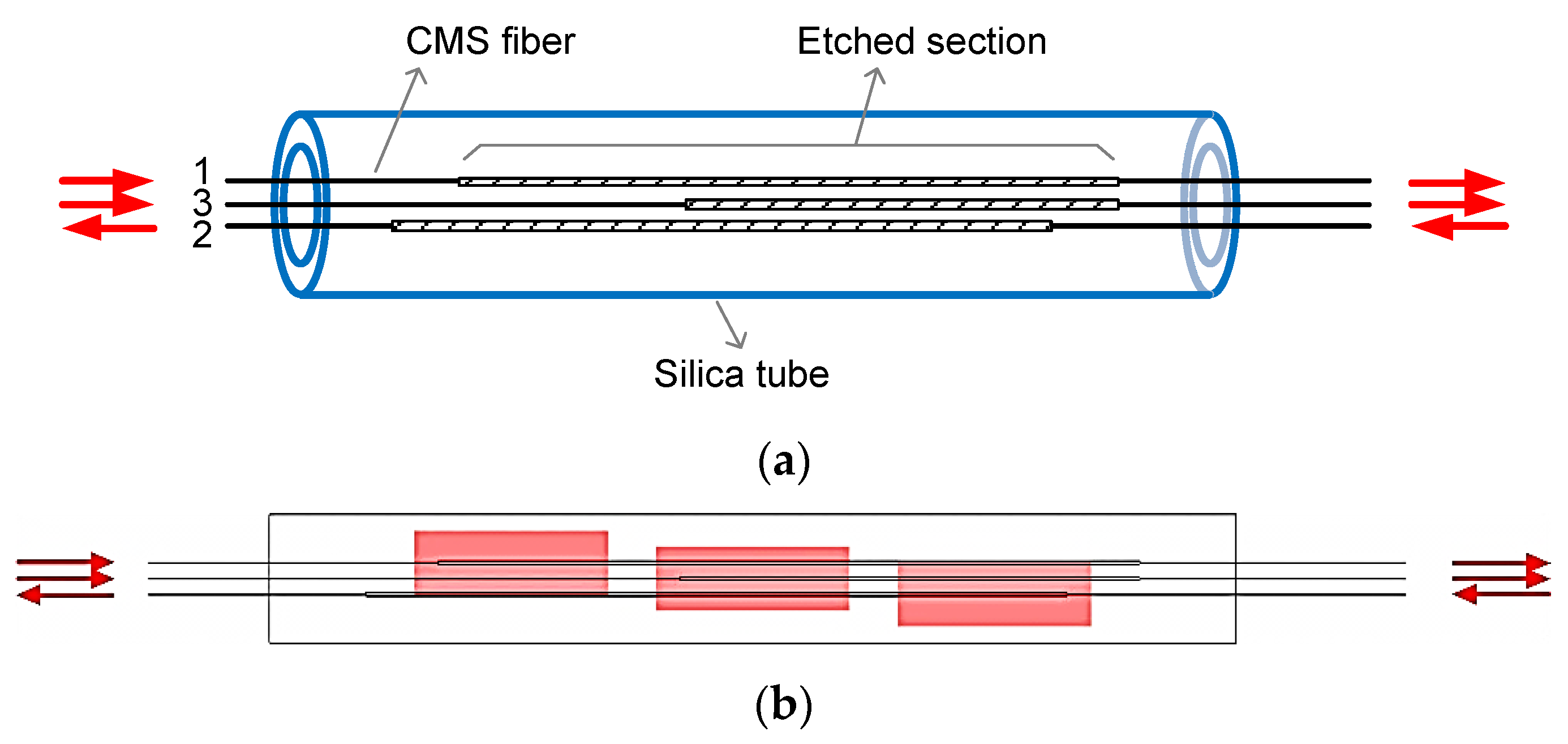
Modes of Multimode Fiber
Multimode fibers are optical fibers designed to carry multiple light rays or modes simultaneously. These fibers are characterized by their larger core diameter, allowing multiple pathways for light propagation. This makes them ideal for short-distance communication, such as within buildings or campuses, due to their ability to handle high data rates.
Modulating a Light Beam
Modulation involves varying a property of the light wave, such as its amplitude, frequency, or phase, to encode information. This process is fundamental in optical communication systems, enabling the transmission of data over long distances with minimal loss and interference.
Understanding Broadband Light Sources
Broadband light sources emit light over a wide range of wavelengths. Unlike monochromatic sources, which emit a single wavelength, broadband sources are essential for applications requiring a wide spectral range, such as spectroscopy and optical coherence tomography.
Nonlinear Scattering Phenomena
Nonlinear scattering occurs when the intensity of light affects its interaction with matter, leading to phenomena such as Raman scattering and Brillouin scattering. These effects are harnessed in various applications, including sensing, imaging, and telecommunications.
Frequency Combs in Precision Measurement
Frequency combs are a series of discrete, equally spaced frequency lines generated by mode-locked lasers. They have revolutionized precision measurements, enabling advancements in fields such as metrology, spectroscopy, and telecommunications.
Focusing a Laser Beam
Focusing a laser beam involves converging the light to a specific point, enhancing its intensity. This technique is vital in applications like laser cutting, material processing, and medical surgeries, where precision and control are paramount.
Amplifying Ultrashort Pulses
Ultrashort pulses, typically in the femtosecond range, require amplification for various applications, including high-resolution imaging and laser machining. Techniques such as chirped pulse amplification (CPA) are employed to enhance their energy without compromising pulse duration.
Rotating Polarization
Polarization rotation is the process of altering the orientation of the electric field vector of a light wave. This is crucial in applications like LCD displays, optical isolators, and polarization-sensitive measurements.
Compressing Femtosecond Pulses
Pulse compression is the technique of shortening the duration of optical pulses, enhancing their peak power. This is achieved using dispersive elements that compensate for pulse broadening, enabling applications in high-precision spectroscopy and ultrafast laser systems.
Adjusting Laser Wavelength
Adjusting the wavelength of a laser involves tuning its emission to a specific frequency. This capability is essential in applications such as spectroscopy, where different wavelengths interact uniquely with materials, providing valuable insights into their properties.
Conclusion
Advanced optical concepts play a pivotal role in the development of cutting-edge technologies. Understanding these principles not only enhances our ability to manipulate light but also drives innovation across various fields, from telecommunications to medical diagnostics.
Source: MDPI
Feel free to comment your thoughts.