Contents

Source: Bystronic
Understanding Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers are a pivotal technology in the realm of photonics, offering robust solutions for a variety of applications. This post delves into the intricacies of fiber lasers, exploring their design, operation, and unique advantages over traditional bulk lasers.
What are Fiber Lasers?
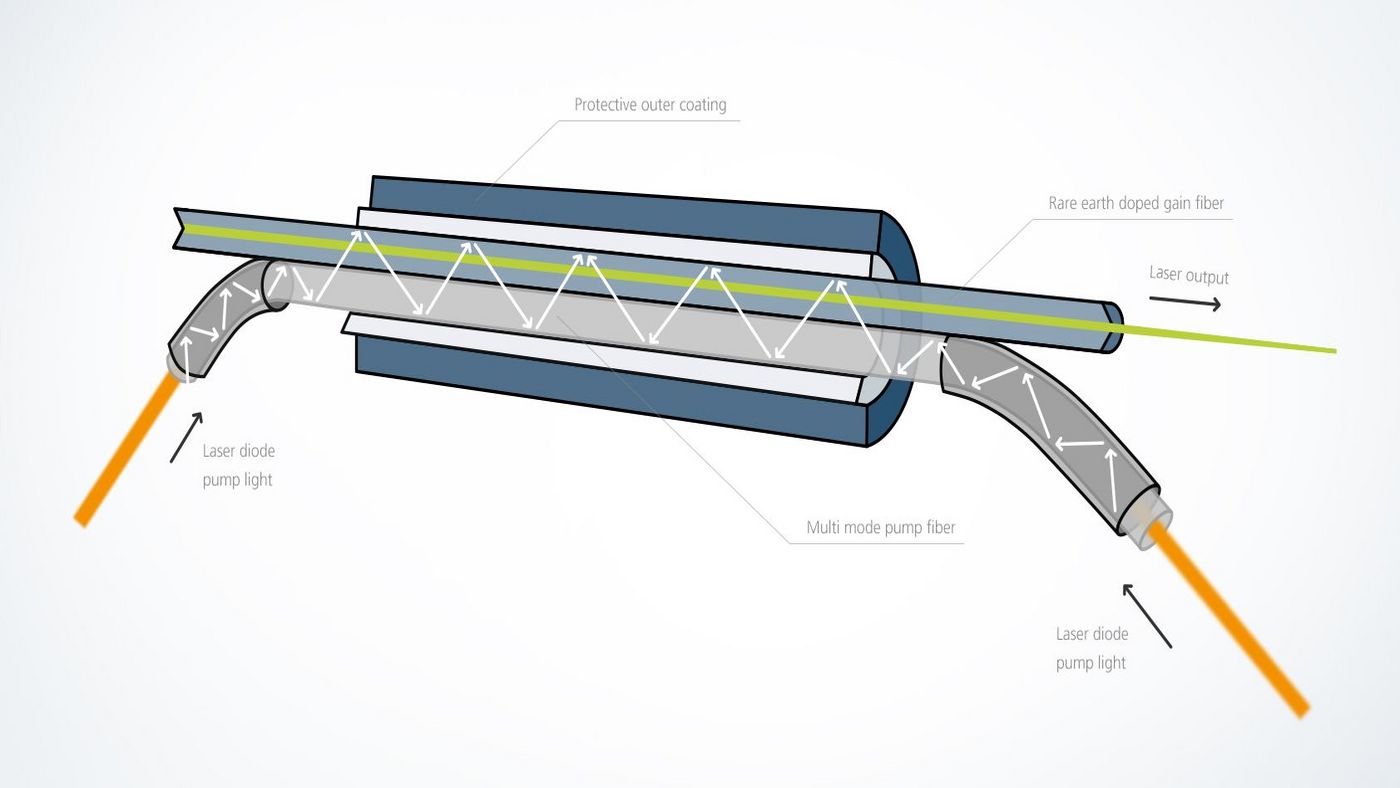
Fiber lasers are a type of solid-state laser where the active gain medium is an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements such as erbium, neodymium, or ytterbium. This design allows for high power output and excellent beam quality, making fiber lasers ideal for applications ranging from telecommunications to industrial machining.
Designing Fiber Laser Systems
The design of a fiber laser system requires a thorough understanding of its components and operational principles. A simulator is often used to model the behavior of fiber lasers, providing insights into their optimization. The resonator design can vary, including linear resonators with mirrors or fiber loop mirrors for more complex configurations.
Fiber Laser Resonators
Forming a laser resonator with fibers involves using reflectors such as fiber Bragg gratings or dielectric coatings on fiber ends. These components help in achieving the desired laser output by managing the light within the fiber effectively. For mass production, fiber Bragg gratings are preferred due to their durability and efficiency.
Types of Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers come in various forms, each tailored for specific applications:
High-Power Fiber Lasers
High-power fiber lasers are capable of delivering outputs from hundreds of watts to several kilowatts. These lasers are extensively used in industrial processes like laser cutting and welding due to their high efficiency and precision.
Upconversion Fiber Lasers
These lasers utilize the upconversion process to generate visible light from infrared sources. They are particularly useful in medical and scientific applications where specific wavelengths are required.
Narrow-Linewidth Fiber Lasers
Single-frequency fiber lasers achieve extremely narrow linewidths, making them suitable for applications requiring high spectral purity, such as precision spectroscopy and coherent optical communications.
Q-Switched and Mode-Locked Fiber Lasers
Q-switched lasers produce short, high-energy pulses, while mode-locked lasers generate ultrafast pulses in the picosecond or femtosecond range. These lasers are crucial for applications in scientific research and materials processing.
Raman Fiber Lasers
Raman fiber lasers exploit Raman scattering to achieve wavelength conversion. They are used in telecommunications for wavelength division multiplexing and other applications requiring specific wavelengths.
Advantages of Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers offer several advantages over traditional bulk lasers. Their waveguiding properties and small mode area result in higher gain and efficiency. Additionally, the fiber form factor facilitates heat dissipation, enhancing the laser’s power handling capabilities.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, fiber lasers can present challenges in design and operation. High optical intensities can lead to saturation effects, and the quasi-three-level nature of many fiber laser transitions can complicate their behavior. Advanced simulation tools are often employed to predict and mitigate these challenges.
Conclusion
Fiber lasers represent a versatile and powerful technology in the field of photonics. Their unique properties and capabilities make them indispensable in a wide range of applications, from industrial manufacturing to scientific research. As technology advances, the potential for fiber lasers continues to expand, promising even greater innovations in the future.
Source: TRUMPF
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



