Contents

Source: YouTube
Understanding Fiber-Optic Attenuators
Fiber-optic attenuators are essential components in the realm of fiber optics, primarily used to manage the power levels of optical signals within telecommunications systems. By ensuring that signal levels are suitable for receivers, they play a critical role in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of optical networks.
Types of Fiber-Optic Attenuators
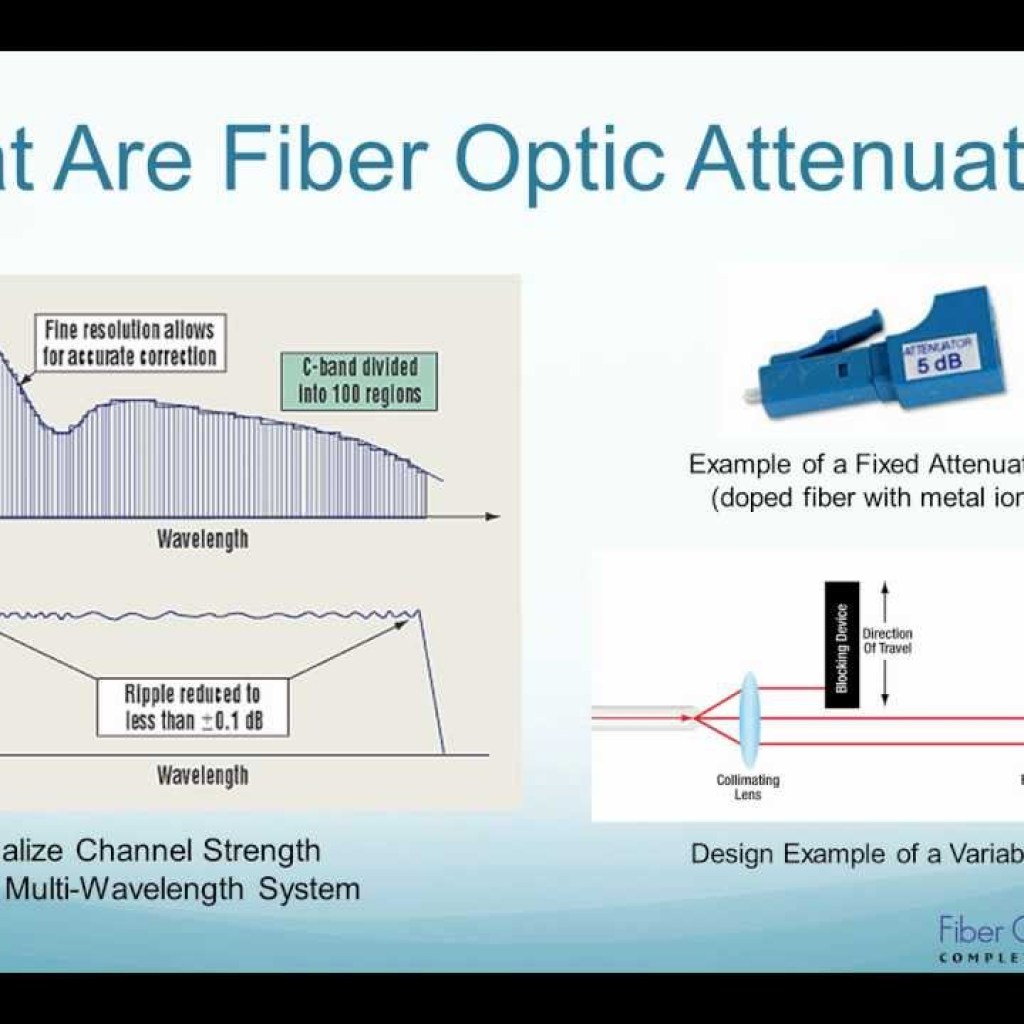
Fixed Attenuators
Fixed attenuators provide a constant level of attenuation, quantified by insertion loss in decibels. They are often used in situations where a specific amount of signal reduction is consistently required. Common fixed attenuator values include 1 dB, 5 dB, and 10 dB, with the ability to combine them for a variety of attenuation levels.
Variable Attenuators
Variable optical attenuators allow for adjustable insertion loss, typically ranging from 2 dB to 50 dB. The adjustment can be made through mechanisms such as wheels, screws, or electronic interfaces. These devices offer flexibility and precision, making them ideal for applications requiring dynamic signal management.
Working Principles
Fiber-optic attenuators operate based on various physical principles. One common method involves creating an air gap between two fiber ends, allowing only a portion of the light to pass through. Another approach uses misaligned fiber splices, where the degree of misalignment dictates the level of attenuation.
Some attenuators use lenses to collimate the beam from one fiber to another, with a blocking device like a movable blade to control light transmission. Alternatively, attenuation can be achieved through neutral density filters or bending losses, where tight turns in the fiber introduce controlled attenuation.
Key Considerations
Wavelength and Polarization Dependence
The effectiveness of an attenuator can vary based on the optical wavelength and polarization state of the light. Devices with minimal wavelength and polarization dependence are preferred for broadband applications.
Single-mode vs. Multimode Attenuators
Single-mode attenuators are commonly used in telecommunications, while multimode attenuators are suitable for broader applications. Multimode devices must minimize mode dependence to ensure consistent attenuation across different modes.
Precision and Return Loss
Precision in insertion loss is crucial for applications requiring exact signal levels. Additionally, high return loss is desirable to prevent light from reflecting back into the system, which could disrupt signal quality.
Applications of Fiber-Optic Attenuators
Fiber-optic attenuators are widely used in optical fiber communications to prevent signal overload, manage nonlinear effects, balance channel powers in WDM systems, and test system performance under varying power levels. They are indispensable for both temporary testing and permanent integration into telecom systems.
Conclusion
Fiber-optic attenuators are vital components in the management of optical networks, offering solutions to control and optimize signal power levels. Understanding their types, working principles, and applications is essential for anyone involved in the field of fiber optics.

Source: Precision Optical Technologies
Feel free to comment your thoughts.