Contents

Source: YouTube
Understanding Fiber Optic Splicing Techniques
Fiber optic technology has become integral to modern telecommunications, providing a medium for high-speed data transmission over long distances. A crucial aspect of fiber optic technology is the ability to efficiently connect optical fibers, ensuring minimal loss of optical power. This process is known as splicing, and there are various techniques employed to achieve this.
Introduction to Fiber Optic Splicing
Splicing optical fibers involves joining the ends of two fibers to facilitate the transmission of light from one to the other. The objective is to ensure that the light passes through with minimal loss and reflection. This is essential in maintaining the integrity and efficiency of fiber optic communications.
Mechanical Splicing
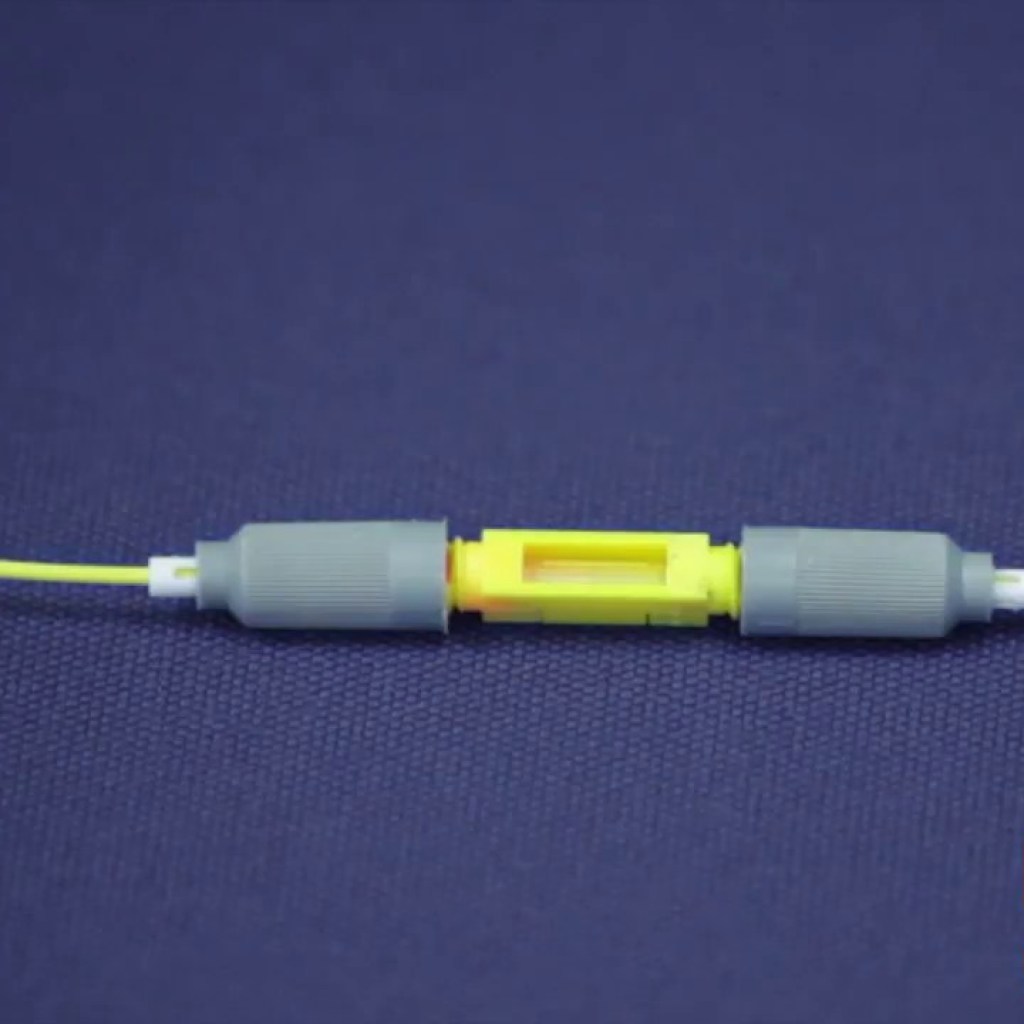
Mechanical splicing is a popular method for joining optical fibers. It involves the use of an alignment device that holds the fiber ends in place, ensuring that the cores are perfectly aligned. This method is advantageous due to its simplicity and the fact that it does not require expensive equipment.
The Splicing Process
The mechanical splicing process requires precision and attention to detail. Initially, the fiber cables must be prepared by stripping the protective jacket and any additional materials to expose the fiber. The fiber ends must then be cleaved to create smooth, perpendicular surfaces.
Once prepared, the fibers are inserted into the splicing device. A transparent window in the device allows for careful alignment of the fiber ends before securing them in place. In some cases, an index matching gel or epoxy is applied between the fibers to minimize reflection losses and maintain a stable connection.
Testing the Quality of Splices
After completing the splice, it is crucial to test its quality. A visual fault locator, which uses a visible laser, can help identify poor splices by highlighting stray light emissions. For more accurate measurements, an optical time-domain reflectometer can be used to assess insertion and return losses.
Comparing Mechanical and Fusion Splicing
Fusion splicing is another technique used for joining optical fibers. It involves melting the fiber ends together, typically resulting in higher quality connections with lower insertion and return losses. However, fusion splicing requires more expensive equipment and is less convenient for fieldwork compared to mechanical splicing.
Mechanical splicing, while potentially resulting in higher loss, is often preferred for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, especially in situations where connections may need to be adjusted or removed.
Conclusion
Both mechanical and fusion splicing have their place in fiber optic technology, each offering unique advantages. Understanding the differences and applications of these techniques is essential for professionals in the field of optical communications.

By mastering the art of splicing, one can ensure efficient and reliable fiber optic networks, capable of supporting the ever-growing demand for high-speed data transmission.

Source: TechLogix Networx
Feel free to comment your thoughts.