
Source: Phys.org
Tapered Optical Fibers: Applications and Techniques
Optical fibers are critical components in modern telecommunications and various scientific applications. Tapered optical fibers, in particular, offer unique capabilities by altering the fiber geometry to achieve specific optical functions. This blog post delves into the production, applications, and significance of tapered optical fibers.
Introduction to Tapered Optical Fibers
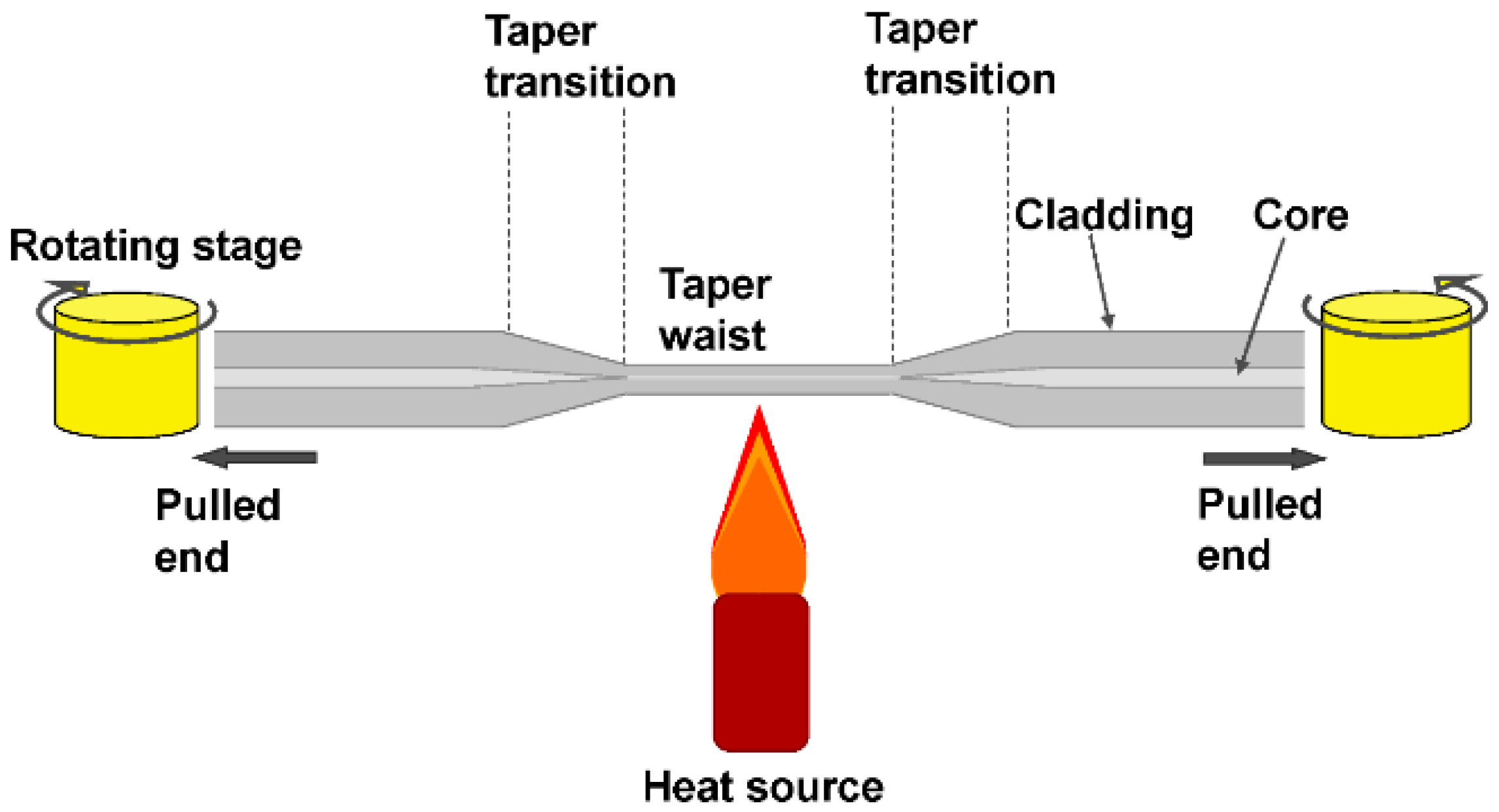
Tapered optical fibers are created by gently stretching a standard optical fiber while it is heated, typically over a flame. This process makes the fiber thinner over a length that can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. During tapering, both the fiber core and the cladding are reduced in diameter proportionally, affecting the fiber’s optical properties.
Applications of Tapered Fibers
Mode Matching
One common application of tapered fibers is mode matching. By reducing the mode area at one end of a single-mode fiber, it is possible to improve coupling efficiency with small-area waveguides. This is particularly useful in integrated photonic circuits where precise mode alignment is crucial.
Mode Filtering
Tapered fibers also serve as mode filters. In a moderately tapered region, higher-order modes become weakly guided or disappear entirely, leaving predominantly the fundamental mode. This characteristic is beneficial in applications requiring high beam quality, such as in laser systems.
High-Power Fiber Amplifiers
In high-power fiber amplifiers, tapered fibers are utilized to operate predominantly on the fundamental mode, even in few-mode fibers. This is achieved by designing the taper to support the fundamental mode while suppressing higher-order modes, thereby enhancing performance and efficiency.
Techniques for Tapering Fibers
Producing tapered fibers involves precise control over the heating and stretching process. Advanced techniques include indirect heating methods, such as using a sapphire taper or capillary, to achieve extreme tapering, resulting in nanofibers with diameters of a few hundred nanometers or less.
Fiber Couplers and Multi-core Fibers
When multiple fibers are heated together, they can form a common taper region, creating a fiber coupler. This setup allows light to couple from one fiber to another, functioning as a directional coupler. For multi-core fibers, tapering can induce lateral shifts and potential coupling between cores, necessitating careful design to minimize losses.
Applications in Imaging and Sensing
Tapered fibers are also used in imaging systems, such as fiber-optic endoscopes, where they provide magnification or demagnification. In sensing applications, tapered fibers enhance sensitivity and resolution, enabling precise measurements in various environments.
Conclusion
Tapered optical fibers offer versatile solutions in photonics, from improving mode coupling to enabling high-power applications. As technology advances, the techniques and applications of tapered fibers continue to expand, promising new innovations in telecommunications, sensing, and beyond.

Source: MDPI
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



