Contents
Source: FiberLabs Inc.
Understanding Single-Polarization Fibers
Single-polarization fibers are a specialized type of optical fiber that guides light predominantly in one linear polarization direction. This unique feature offers significant advantages in various applications, particularly where polarization control is critical.
Principles of Operation
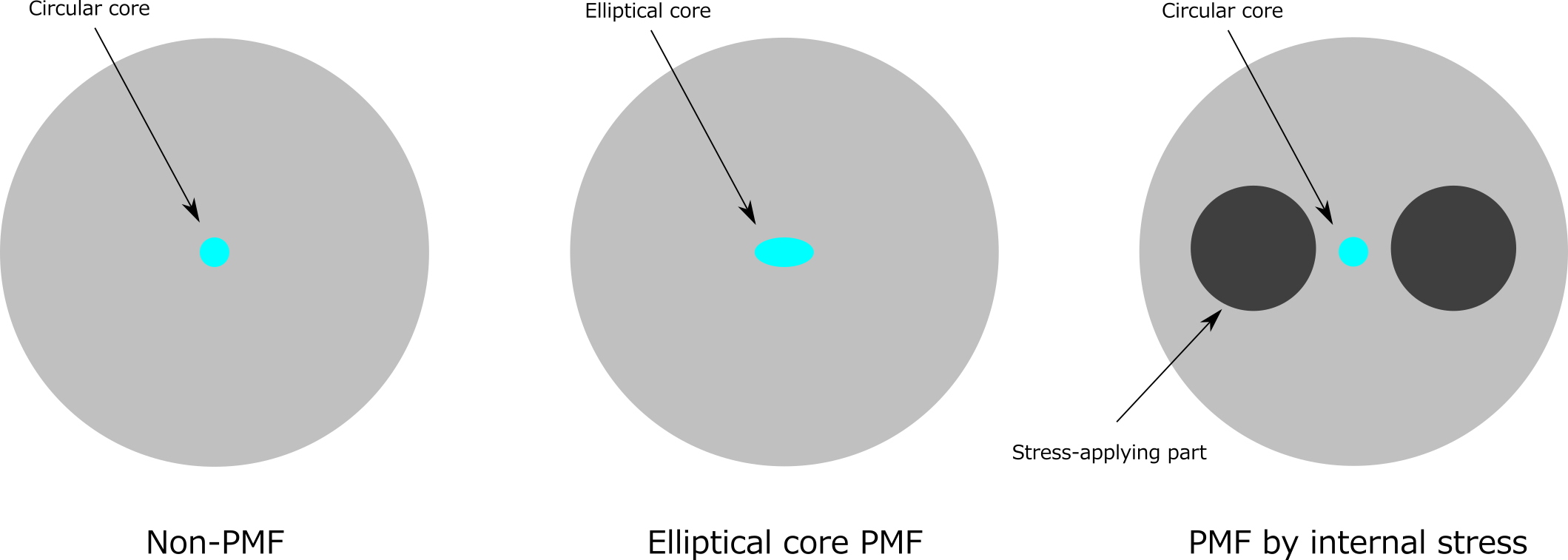
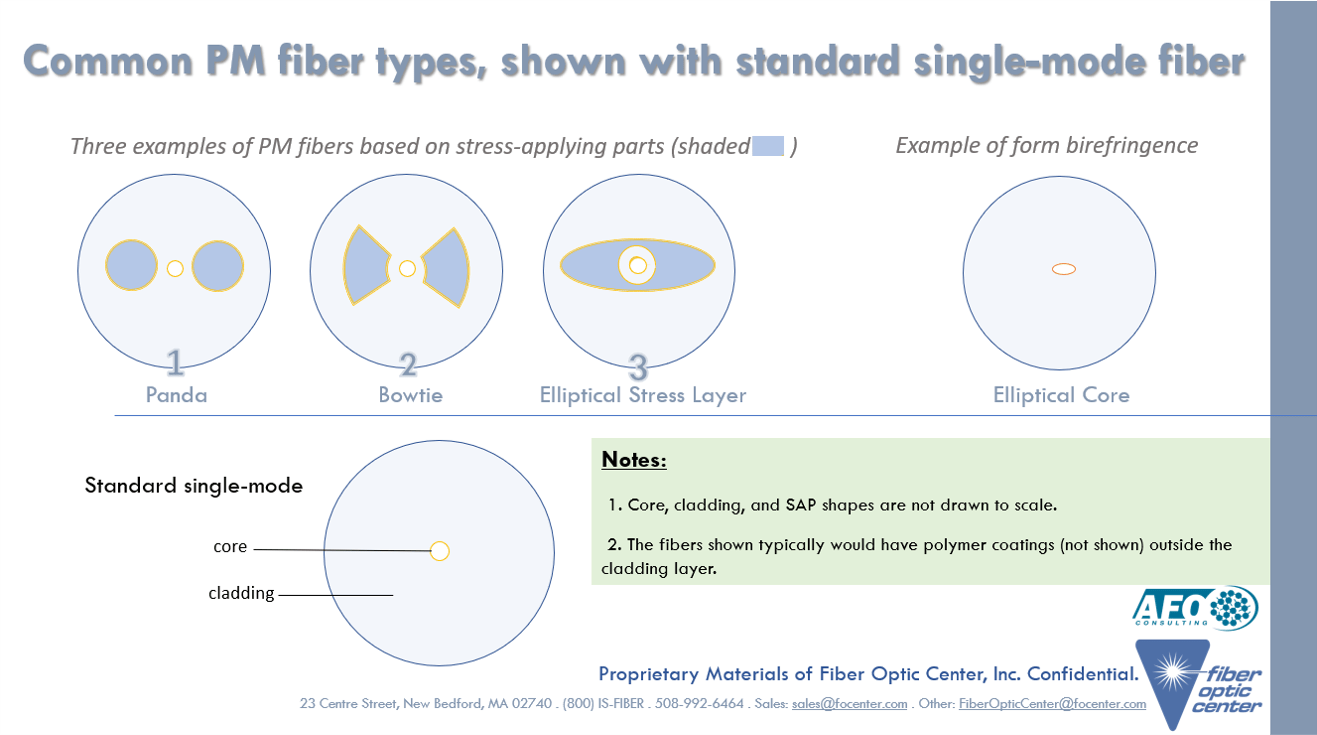
The operation of single-polarization fibers is based on several principles that ensure light is guided in only one polarization direction. One common technique involves the use of an elliptical core. This core design introduces significant birefringence, which is a difference in refractive indices depending on the polarization direction of light. As a result, only light polarized in a specific direction is effectively guided, while light in the orthogonal direction is attenuated.
Another approach involves breaking the rotational symmetry of the fiber by incorporating structures around the core, such as air holes. These are often referred to as side-hole fibers or hole-assisted fibers. The asymmetrical design further enhances polarization selectivity by acting as a leaky waveguide for the undesired polarization.
Additionally, mechanical stress can be applied to the fiber during manufacturing to induce birefringence, enhancing the polarization-dependent guiding properties. Photonic crystal fibers, which utilize a microstructured arrangement of air holes, also exhibit single-polarization characteristics by disrupting symmetry and guiding light based on polarization.
Applications
Single-polarization fibers are essential in a variety of applications. In fiber lasers, they ensure the emission of polarized light, which is crucial for applications requiring high precision and stability. These fibers are also used in fiber-optic sensors, where they help mitigate polarization-related issues that can affect measurement accuracy.
Furthermore, single-polarization fibers are employed in telecommunications to enhance signal quality by reducing polarization mode dispersion, a phenomenon that can degrade signal integrity over long distances.
Advantages and Challenges
The primary advantage of single-polarization fibers is their ability to maintain a stable and well-defined polarization state, which is critical in applications requiring high precision. However, designing and manufacturing these fibers involves challenges, such as achieving the desired birefringence and maintaining low optical losses across the operational wavelength range.
Moreover, the development of single-polarization fibers requires careful consideration of the fiber’s structural properties to ensure that the desired polarization characteristics are consistently achieved.
Conclusion
Single-polarization fibers play a pivotal role in modern optical technologies. Their ability to guide light in a single polarization direction is invaluable in applications ranging from laser systems to telecommunications. As research and development continue, these fibers will likely become even more integral to advanced photonic systems, providing enhanced performance and reliability.

Source: Fiber Optic Center
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



