Contents
Source: YouTube
<>
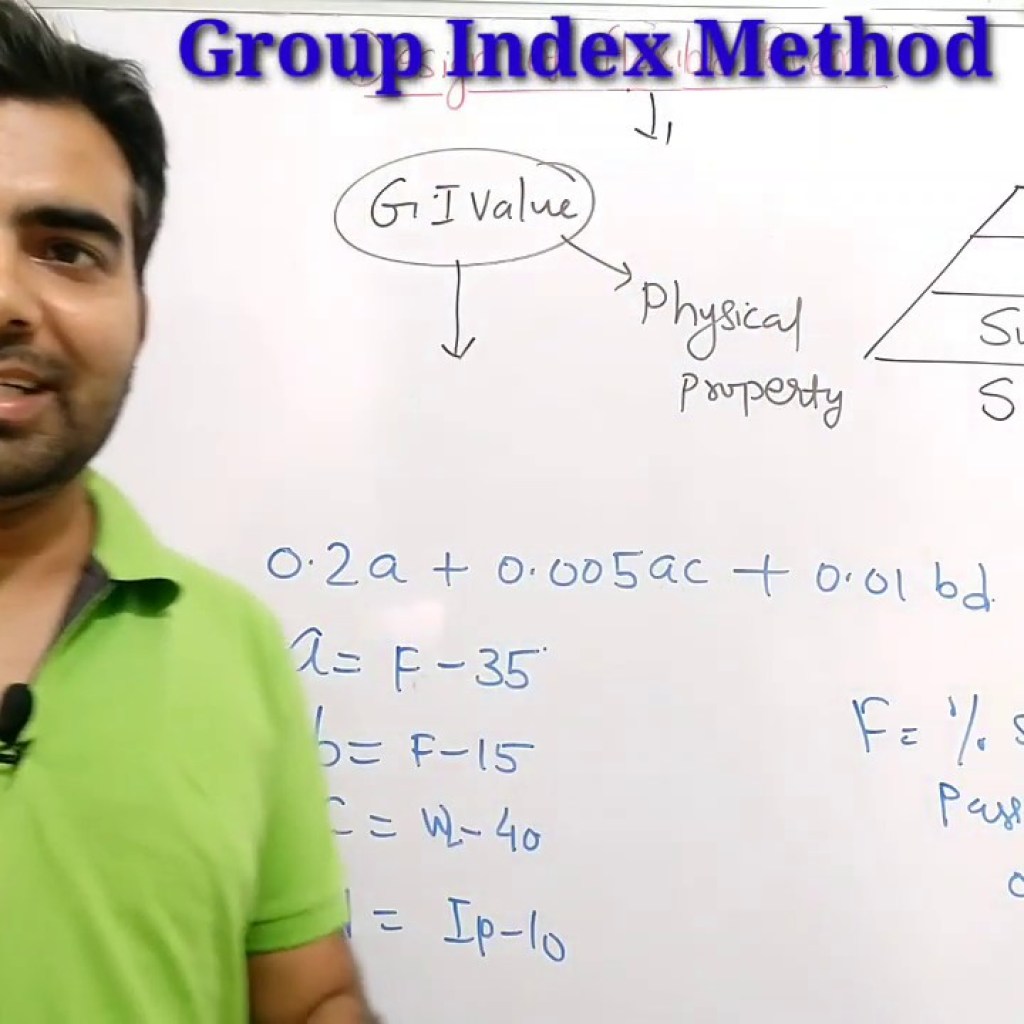
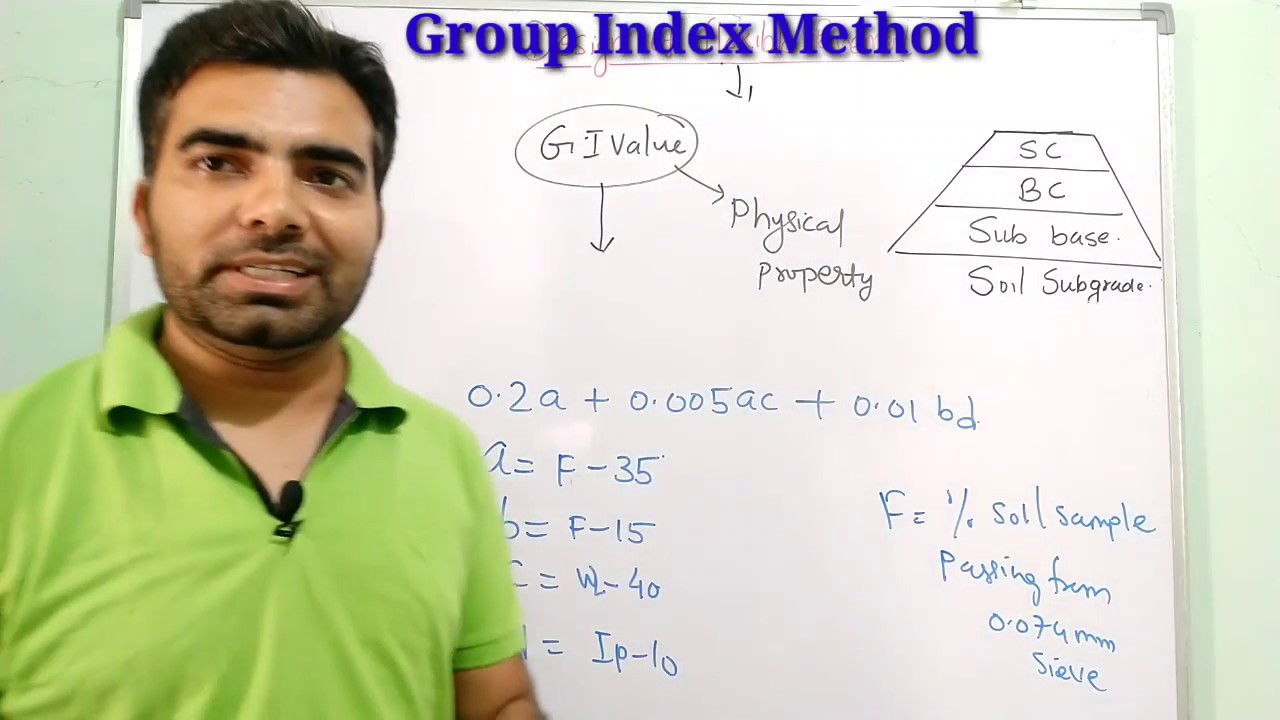
Group Index in Optics
Definition
The group index (or group refractive index) of a material is the ratio of the vacuum velocity of light to the group velocity in the medium. It depends on the refractive index at the wavelength of interest and its frequency dependence.
Applications
The group index is used in various applications such as calculating time delays for ultrashort pulses in a medium and determining the free spectral range of a resonator with a dispersive medium.
Characteristics
In optical crystals or glasses, the group index in the visible or near-infrared spectral range is typically higher than the ordinary refractive index, indicating that the group velocity is slightly slower than the phase velocity. In special cases, such as with artificial structures, significantly reduced group velocities can be achieved, leading to what is known as slow light.
Temperature Dependence
Similar to the refractive index, the group index of a material also varies with temperature. This can have implications for the behavior of light in the medium.
Waveguides and Fibers
For optical fibers and waveguides, the effective refractive index is used to calculate the group velocity, considering waveguide dispersion. This allows for the determination of the effective group index of a fiber.
Further Exploration
Understanding the group index is crucial in various optics applications, and further research can provide insights into its implications in different scenarios.

Source: Mathematics Stack Exchange
Feel free to comment your thoughts.