Contents

Source: Wikipedia
<>
Understanding Optical Phase in Photonics
Overview
Optical phase is a crucial concept in the field of photonics, where electromagnetic waves are characterized by their amplitude and phase. The phase of an optical wave determines the position of the electric field within an oscillation cycle. It evolves rapidly, with significant phase changes occurring within femtoseconds.
Key Concepts
Phasors and Complex Amplitudes
Optical waves can be described using phasors, which are complex amplitudes. The optical phase is associated with the complex phase of a phasor, representing the direction of propagation.
Coherence and Phase Evolution
Temporal coherence refers to the systematic evolution of optical phase over time, while spatial coherence relates to phase correlation at different points in space. Well-defined phase fronts are crucial for light with perfect spatial coherence.
Phase Changes in Optical Elements
Various optical elements induce spatially dependent phase changes on light beams. For instance, lenses apply phase changes proportional to the distance from the lens axis, while diffraction gratings generate phase shifts based on spatial coordinates.
Nonlinear Effects and Phase Modulations
Nonlinearities in optical media can lead to cross-phase modulation and self-phase modulation, where optical phases are influenced by overlapping waves. Phase modulators are used to control time-dependent phase changes in laser beams.
Applications of Optical Phase
Optical phases play a crucial role in phenomena such as interference effects, resonance in optical resonators, and efficient coupling of light. Phase matching is essential for some nonlinear processes, and phase stability affects laser linewidth and pulse characteristics.
Sign Conventions and Phase Measurement
Optical phases are described using different sign conventions, with physicists and engineers using varying approaches. Phase differences are important in measuring interference effects and optical metrology, where beat notes help determine tiny phase variations.
Phase Noise and Spectral Phase
Phase noise affects the stability of optical phases, with factors like spontaneous emission contributing to fluctuations. Spectral phase represents the optical phase in the frequency domain, influencing the optical spectrum of pulses and laser beams.
Conclusion
Understanding optical phase is essential for various applications in photonics, from interference phenomena to laser stability and phase-sensitive measurements. By grasping the intricacies of optical phase, researchers and engineers can advance technologies in optics and photonics.
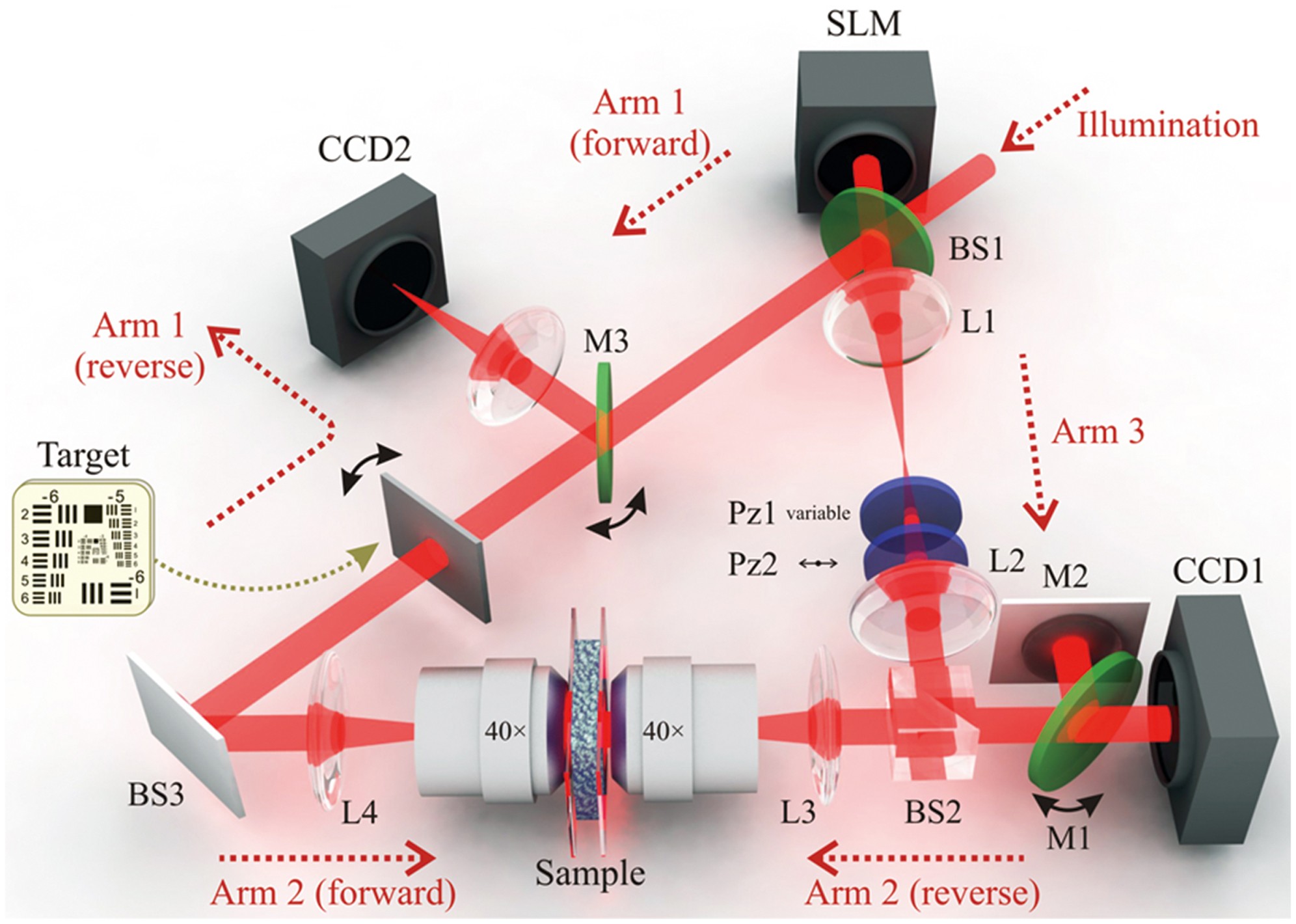
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



