Contents
Source: Ultrafast Laser Physics – ETH Zürich
Understanding Thin-Disk Lasers
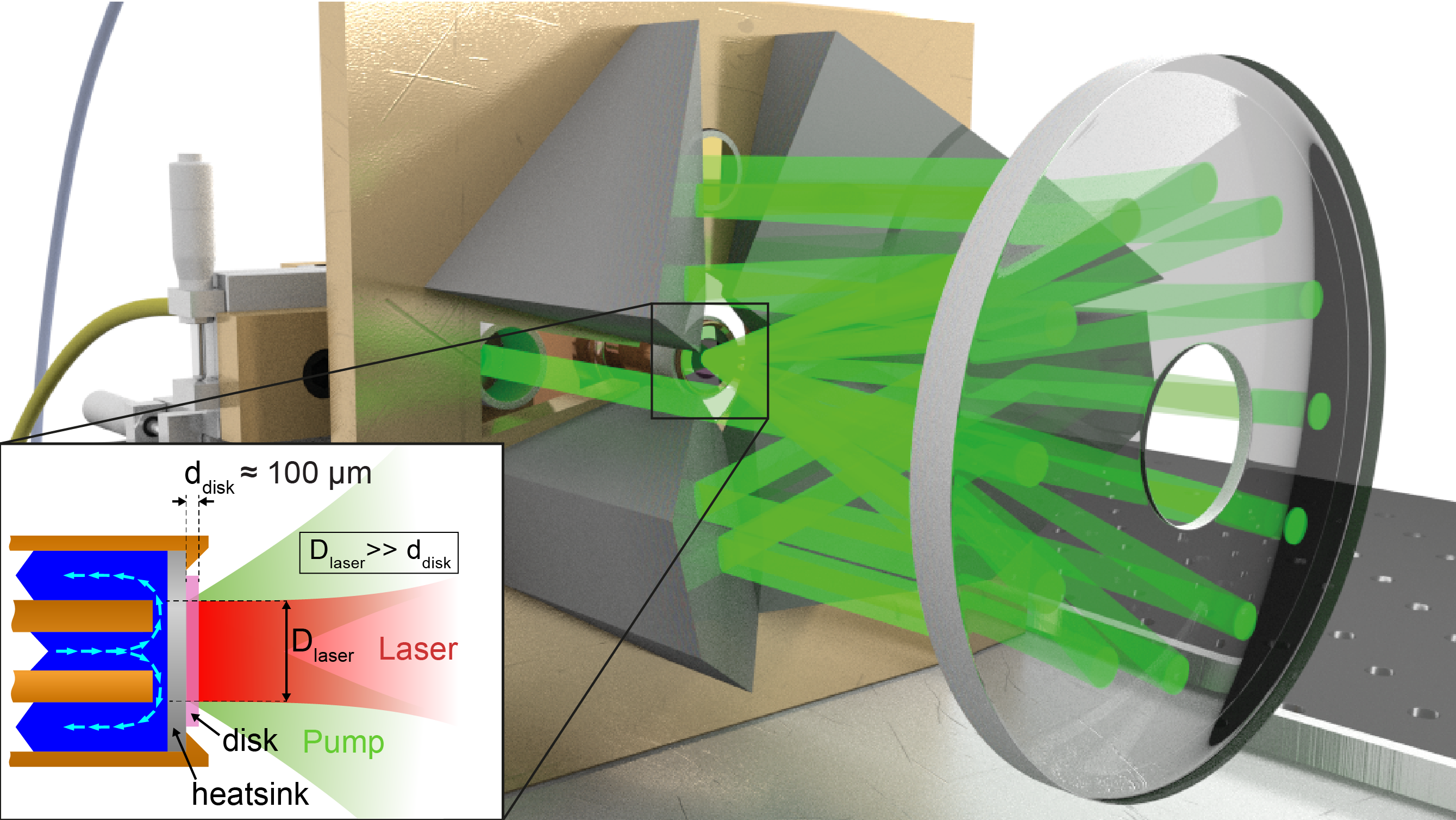
Thin-disk lasers are a type of high-power solid-state laser that utilizes a thin disk-shaped gain medium, as opposed to conventional rod or slab lasers. This design offers several advantages, including efficient heat extraction and minimized thermal effects.
Construction and Operation
The thin-disk laser consists of a thin disk of laser gain material, such as Yb:YAG, with a thickness much smaller than the laser beam diameter. The heat generated is extracted through one end face, reducing thermal lensing effects. The disk acts as an active mirror within the laser resonator, allowing for high-power operation with stable beam quality.
Multipass Pumping
To improve pump absorption efficiency, thin-disk lasers often use a multipass pump arrangement, allowing multiple passes of the pump radiation through the disk. This setup enables high-power operation without stringent requirements on pump beam quality.
Reduced Thermal Issues and Power Scalability
The thin-disk geometry results in minimal temperature rise and weak thermal effects, even at high output powers. This allows for power scalability by simply adjusting the pump power and area on the disk, without compromising beam quality or causing thermal issues.
Gain Media and Applications
Yb:YAG is a commonly used gain medium for thin-disk lasers, offering a shorter emission wavelength and larger gain bandwidth. These lasers are suitable for various applications, including pulse generation, high-power amplifiers, and nonlinear frequency conversion.
Competition and Future Developments
Thin-disk lasers face competition from fiber lasers, especially in terms of power and efficiency. However, ongoing research focuses on further developing thin-disk lasers for higher powers, improved performance, and new applications.
Overall, thin-disk lasers represent a promising technology for high-power laser systems, offering a combination of power scalability, beam quality, and efficiency that make them valuable tools in various industrial and scientific fields.

Source: Max-Born-Institut
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



