Contents

Source: Vision-Doctor.com
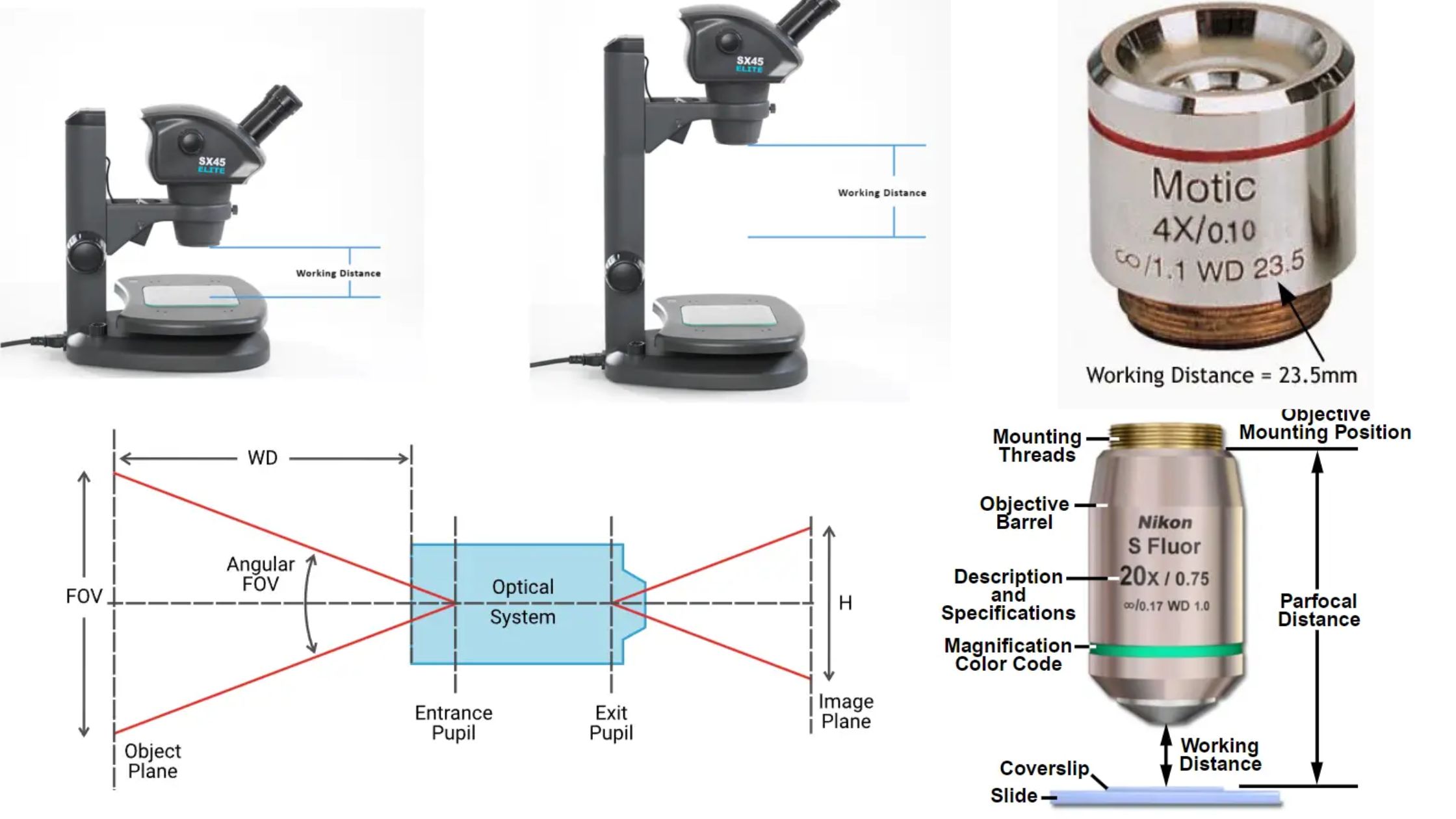
Working Distance in Optics
The working distance of an optical system, such as a camera lens or microscope objective, refers to the distance between the front of the lens and the object being observed or imaged. It plays a crucial role in various applications and can impact the performance and usability of the optical system.
Importance of Working Distance
In photography, particularly in macro photography of insects, having an adequate working distance is essential to avoid disturbing the subjects. Some macro lenses have limited working distances, which can make it challenging to capture detailed images without getting too close to the subject.
Microscope objectives, especially those with high magnification, often have very small working distances, sometimes less than 1 mm. While this is necessary for achieving high magnification, it can pose challenges when trying to illuminate the sample from different angles or when dealing with delicate specimens.
For laser material processing applications, a large working distance is beneficial for several reasons. It helps prevent debris from contaminating the optics and allows for easier manipulation of the laser beam focus over significant distances. Maintaining a high beam quality is crucial for achieving a large working distance in laser systems.
Measurement and Considerations
It is important to note that the working distance may not always be the same as the front focal distance of the lens. Mechanical components or protrusions in the optical path can affect how the working distance is defined and measured. Understanding the specific definition of working distance in a given optical system is essential for accurate measurements and calculations.
Moreover, even when the object is placed at the beam focus of the lens, the focus may not coincide with the focal plane if the incoming light is not collimated. This distinction is critical in optical systems where precise focusing is required.
Conclusion
Working distance is a fundamental parameter in optical systems that influences their performance and versatility across various applications. Whether in photography, microscopy, or laser processing, understanding and optimizing the working distance can lead to improved results and efficiency in optical instrumentation.
Source: Biology Notes Online
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



