Contents

Source: MDPI
Understanding Glass Lasers
Glass lasers are a type of solid-state laser where the gain medium is a laser glass, which is doped with trivalent rare earth ions like Nd3+, Yb3+, Er3+, Tm3+, Pr3+ or Ho3+. These rare earth ions are essential for the lasing process in glass lasers.
Large Glass Lasers and Amplifiers
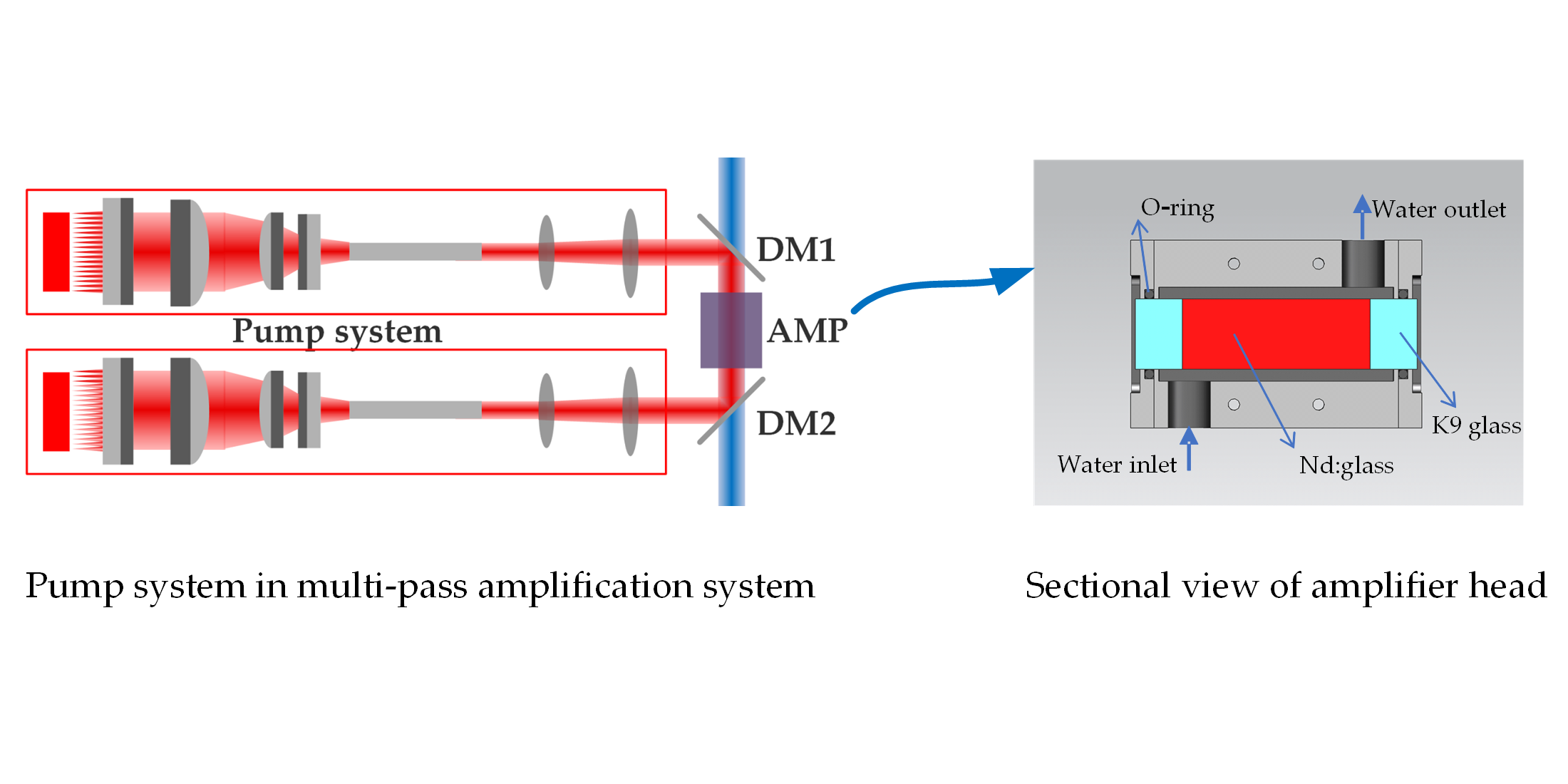
Large Pieces
One advantage of laser glasses is their ability to be fabricated in large sizes at a reasonable cost. This allows for the storage of large amounts of excitation energy, which can be crucial for applications like Q-switching in lasers or amplification in optical amplifiers.
Large Gain Bandwidth
Glass lasers have a large gain bandwidth, which is important for applications requiring ultrafast amplifiers to prevent gain narrowing of optical pulses and for wavelength tuning.
Reduced Emission Cross-sections
The emission cross-section and gain of a laser glass are lower compared to a laser crystal with similar doping concentration. This can be advantageous for Q-switched lasers and optical amplifiers by allowing for higher pulse energy and avoiding premature lasing.
Thermal Properties
Glass lasers have relatively low thermal conductivity, limiting their operation at high pulse repetition rates and average powers due to overheating risks. However, some laser glasses exhibit a weak temperature dependence of the refractive index, which can help manage thermal lensing.
Broad Pumping Transitions
Glass lasers have broad pumping transitions, enabling the use of more broadband pump radiation sources like laser diodes or lamps. This can be a cost-effective solution for certain applications despite lower efficiency.
Application Example: Laser-induced Nuclear Fusion
Large glass laser amplifiers are crucial for applications like inertial confinement fusion, where extremely high pulse energies and short pulse durations are required. Glass amplifiers are essential for generating the necessary pulse energies.
Small Glass Lasers
Small glass lasers are based on compact pieces of laser glass and are usually diode-pumped. The broader gain bandwidth of glass allows for relatively short pulses in the picosecond or femtosecond domain, as well as wavelength tuning.
Conclusion
Glass lasers offer unique advantages such as large gain bandwidth, reduced emission cross-sections, and broad pumping transitions, making them suitable for various applications ranging from inertial confinement fusion to compact diode-pumped lasers. Despite limitations in thermal properties, glass lasers play a significant role in the field of photonics.
Source: MDPI
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



