Contents
Source: cpb.iphy.ac.cn
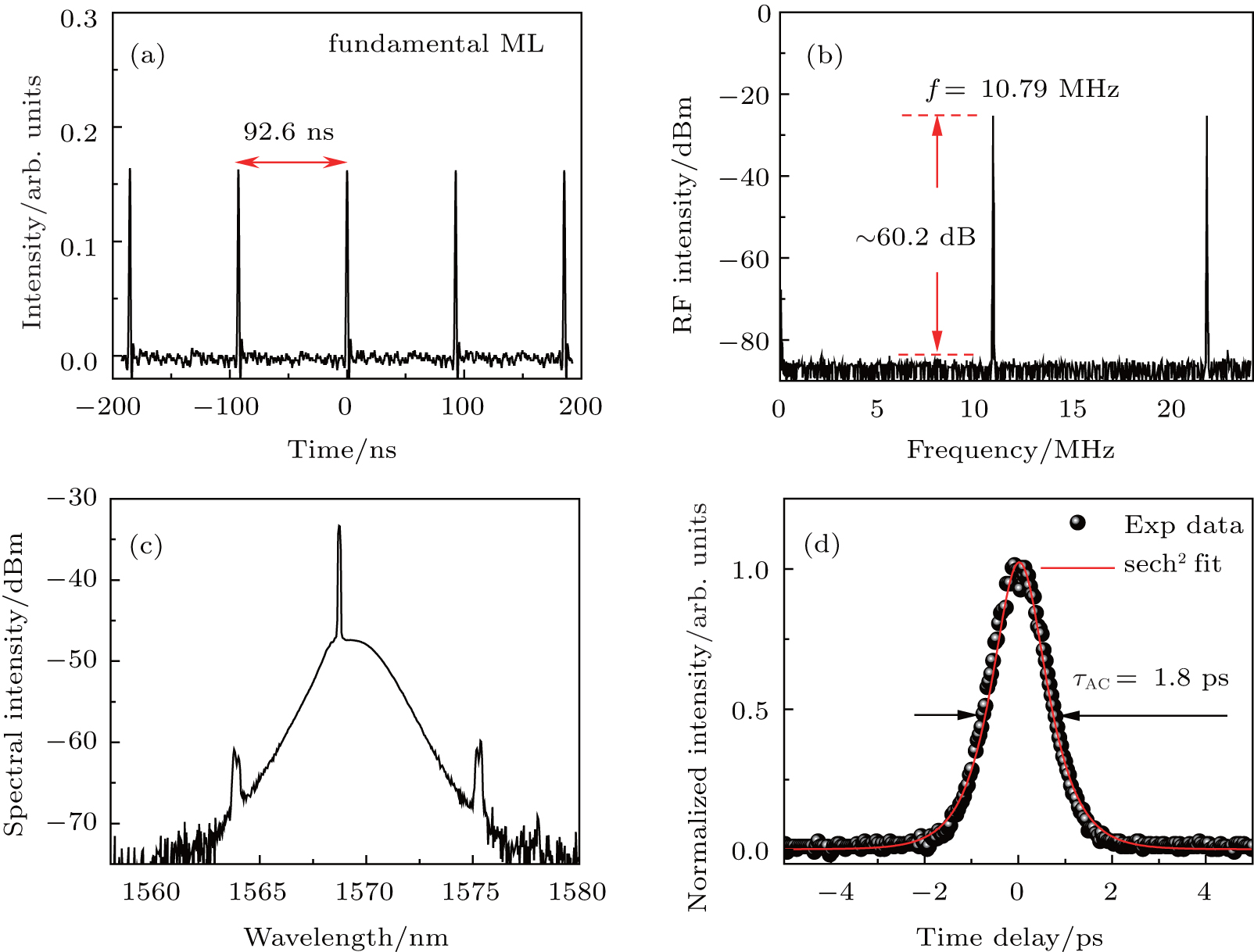
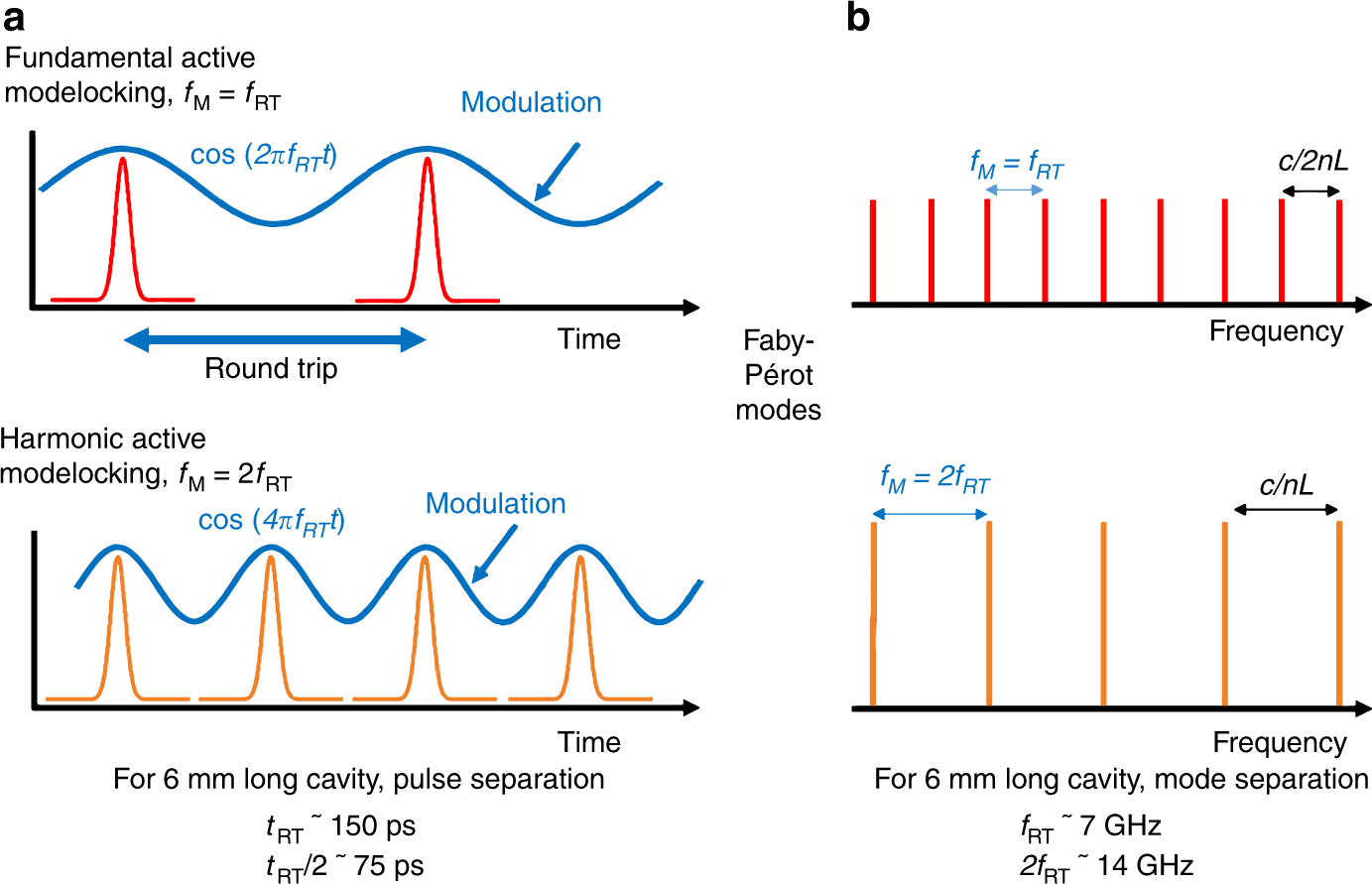
Understanding Harmonic Mode Locking in Fiber Lasers
Harmonic mode locking is a technique used in high pulse repetition rate fiber lasers to generate pulse trains with multiple ultrashort pulses circulating in the laser resonator with a constant temporal spacing. This method is employed in lasers with multi-gigahertz pulse repetition rates.
Challenges Associated with Harmonic Mode Locking
Harmonic mode locking comes with technical challenges that need to be addressed:
- Ensuring a constant pulse energy to prevent fluctuating pulse energies or pulse drop-outs.
- Managing the phase coherence of circulating pulses.
- Obtaining a stable pulse spacing, especially in passively mode-locked lasers to minimize timing jitter.
- Dealing with supermode noise, where the laser may hop to different sets of modes, leading to increased high-frequency laser noise.
Suppression of Supermode Noise
To suppress supermode noise, various methods can be employed:
- Using intracavity spectral filters.
- Implementing electronic feedback systems.
- Leveraging nonlinear and dispersive effects.
While suppressing supermode noise may require a more sophisticated setup, it can result in harmonically mode-locked lasers with significantly lower laser noise, such as timing jitter and phase noise, compared to fundamentally mode-locked lasers.
Rational Harmonic Mode Locking
A variation of harmonic mode locking is rational harmonic mode locking, where the modulation frequency is a multiple of the round-trip frequency. This approach can lead to higher pulse repetition rates, although sometimes with a non-constant pulse energy.
Overall, harmonic mode locking in fiber lasers offers a powerful method for generating high-repetition-rate pulse trains, with the potential for achieving low laser noise levels when supermode noise is effectively suppressed.
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



