Source: YouTube
<>
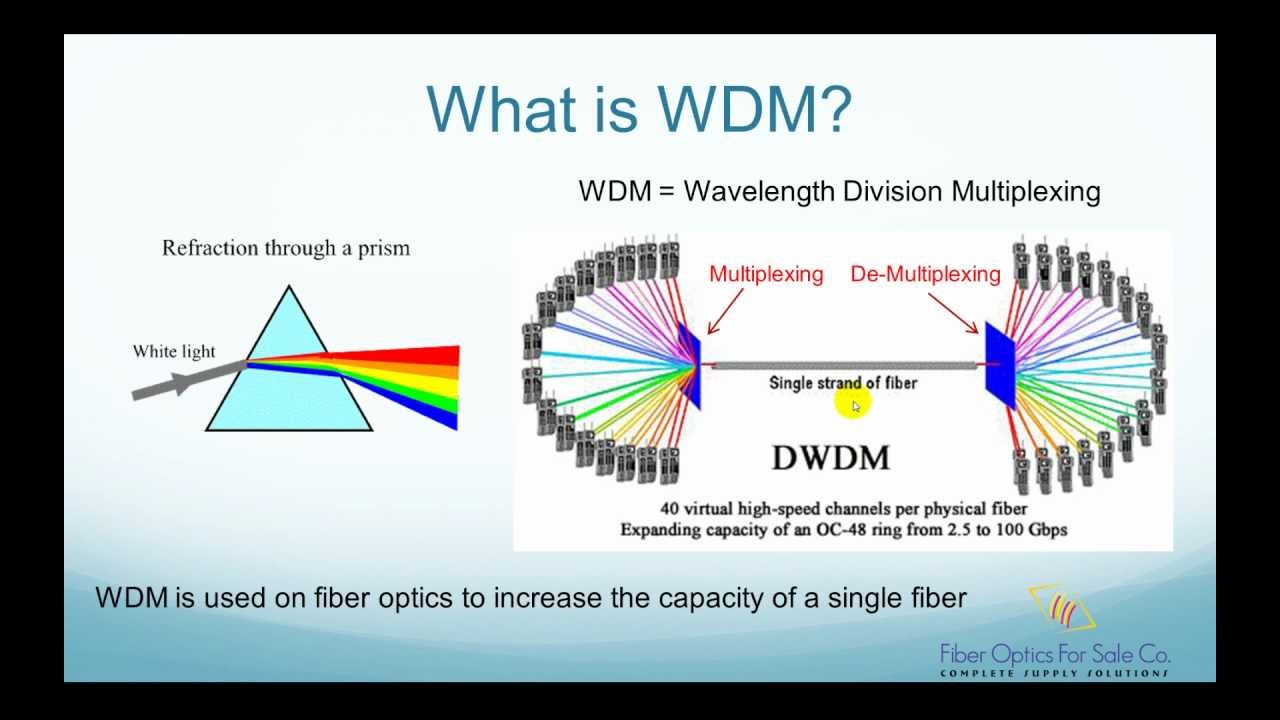
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Introduction
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is a technique used in optical fiber communications to transmit data in multiple channels with different wavelengths. By combining and separating optical signals with varying wavelengths, WDM significantly increases the transmission capacity of fiber-optic links.
WDM in Telecom Systems
In telecommunications, WDM allows for the efficient utilization of the vast bandwidth available in optical fibers. It involves dividing the optical spectrum into channels, each carrying data at moderate rates. This approach overcomes limitations associated with high data rates on a single channel, such as signal degradation over long distances due to dispersion.
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM)
CWDM uses a smaller number of channels with wider spacing, suitable for applications within metropolitan areas. It is cost-effective and supports data rates typically between 1 and 3.125 Gbit/s per channel.
Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)
DWDM, on the other hand, accommodates a larger number of channels with narrower spacing, ideal for high-capacity networks like the Internet backbone. It offers data rates ranging from 1 to 100 Gbit/s per channel and beyond.
Benefits of Wavelength Division Multiplexing
WDM not only enhances transmission capacity but also adds flexibility to communication systems. By utilizing add-drop multiplexers, different data channels can be injected or extracted at various points in the network, allowing for dynamic reconfiguration.
Combining WDM with Time Division Multiplexing
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) can complement WDM by distinguishing channels based on arrival time rather than wavelength. The combination of both techniques can achieve exceptionally high data rates exceeding 1 Tbit/s.
Case Study
A case study on optimizing an erbium-doped fiber amplifier for multiple signals illustrates the trade-offs between power efficiency and noise performance in WDM systems.
Conclusion
Wavelength Division Multiplexing is a critical technology in modern optical communications, enabling the efficient use of fiber-optic networks to meet the increasing demand for data transmission. Its versatility and scalability make it a cornerstone in high-capacity communication systems.
Source: Foss Fibre Optics.
Feel free to comment your thoughts.




