Contents
Source: MDPI
<>
Understanding Nonlinear Absorption in Photonics
Overview
Nonlinear absorption refers to a phenomenon where the absorption of light by a material is dependent on the intensity of the light. This can occur instantaneously or based on past intensities. In some cases, there is only nonlinear absorption, while in others, there may be a combination of linear and nonlinear absorption.
Saturable Absorption
Saturable absorption is a type of nonlinear absorption where the absorption coefficient decreases or saturates at higher intensities. This property is often utilized in laser technologies for pulse generation through passive mode locking or Q switching.
Two-Photon Absorption (TPA)
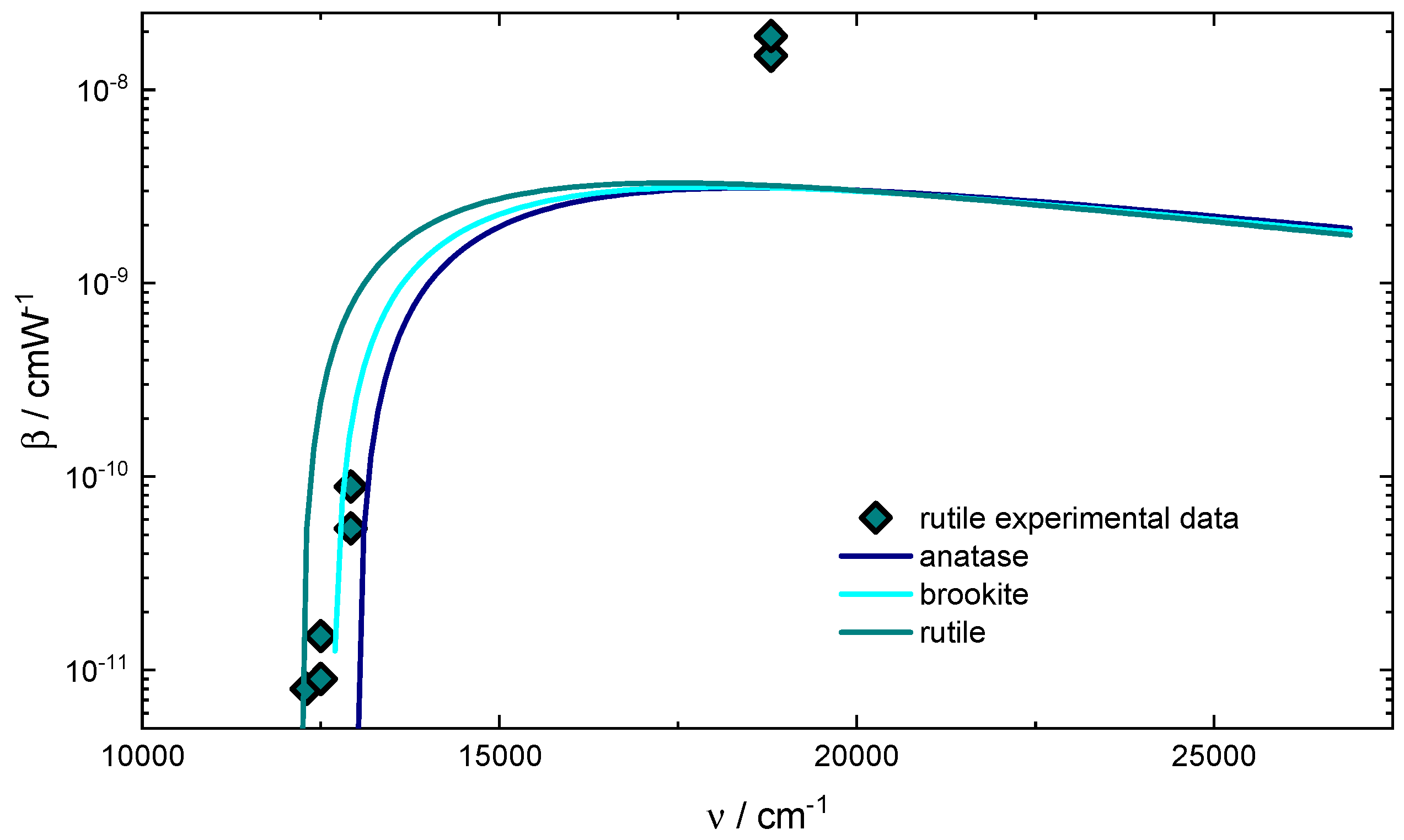
Two-photon absorption involves the simultaneous absorption of two photons to excite an electron to a higher energy state. This process enables absorption at intensities where single-photon absorption would be insufficient, such as in semiconductors. The absorption coefficient in TPA is proportional to the optical intensity.
Multiphoton Absorption
Multiphoton absorption involves the absorption of more than two photons in a single process. This phenomenon is significant in laser material processing, particularly in transparent media like glasses. High peak powers, achievable through short light pulses, are required for efficient energy deposition.
Applications
Nonlinear absorption processes find applications in various fields, including laser technology, material processing, and optical communication. Understanding and controlling nonlinear absorption mechanisms are crucial for optimizing the performance of photonic devices.
Conclusion
Nonlinear absorption plays a vital role in photonics, offering unique opportunities for manipulating light-matter interactions. By exploring and harnessing nonlinear absorption processes, researchers and engineers continue to advance the capabilities of optical technologies.

Source: ResearchGate
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



