Contents
Source: Ossila
Understanding Electroluminescence
Electroluminescence is a fascinating phenomenon that plays a crucial role in modern technology. It involves the emission of light as a result of electrical stimulation and is widely utilized in various applications, particularly in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and electroluminescent displays.
The Basics of Electroluminescence
Electroluminescence occurs when an electric current passes through a material, causing it to emit light. This process is distinct from other forms of luminescence, such as photoluminescence, where light is emitted due to the absorption of photons.
Electroluminescence in LEDs
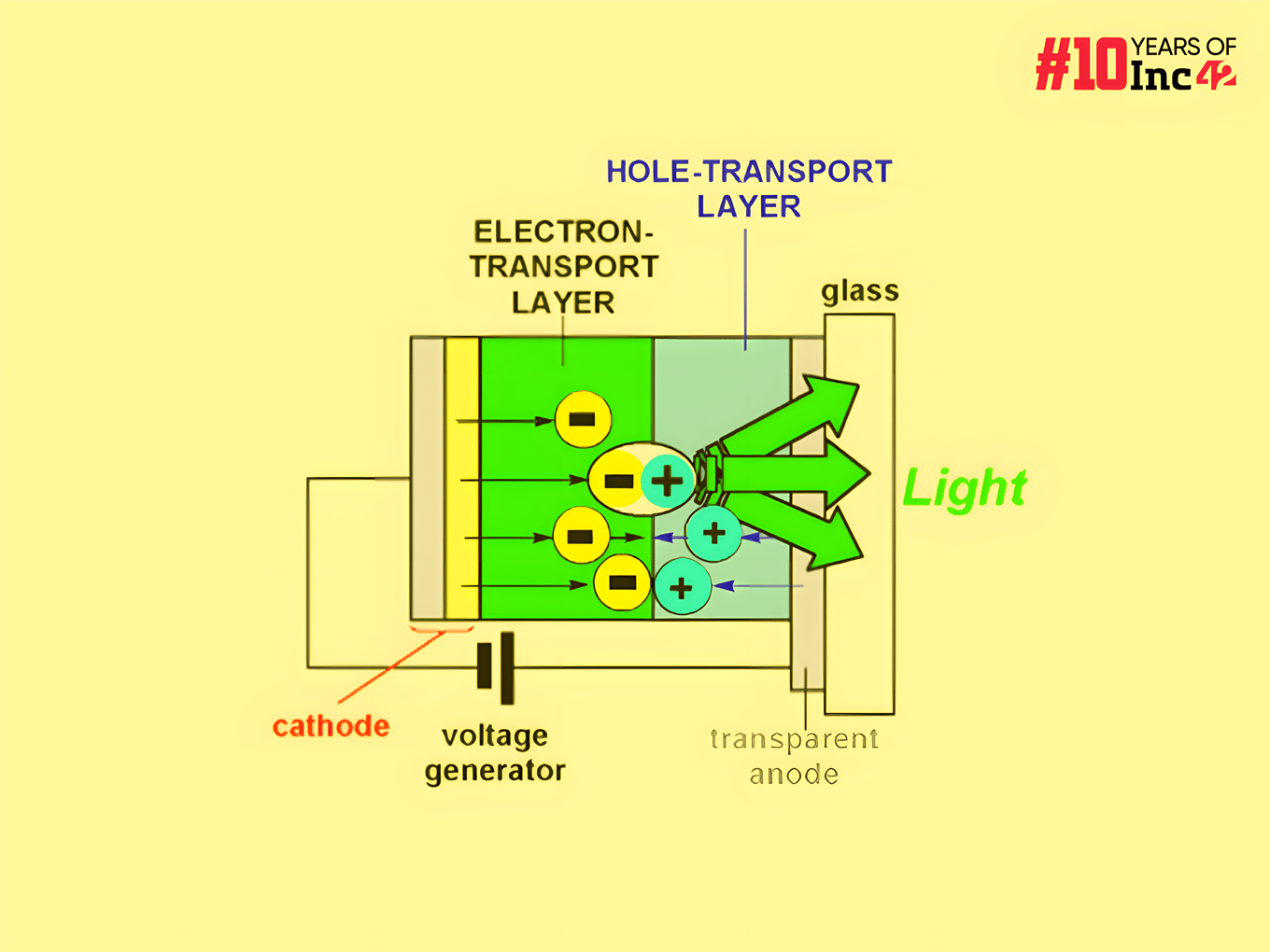
In the realm of LEDs, electroluminescence is achieved through semiconductor p–n junctions. When an electric current flows through these junctions, it generates electron-hole pairs. The recombination of these pairs results in the emission of light. The efficiency of this process is particularly high in direct band gap semiconductors with minimal crystal defects, often resulting in nearly one photon produced per electron-hole pair. The color of the emitted light is directly related to the bandgap energy of the semiconductor material.
Electroluminescent Displays
Electroluminescent displays work on a different principle compared to LEDs. These displays utilize a high voltage applied between two electrodes, with an electroluminescent material such as a phosphor placed between them. The electrons in this setup gain significantly more energy than in LED systems, enabling the emission of multiple photons from a single electron. For effective light extraction, one of the electrodes must be transparent or specially structured.
Other Forms of Electroluminescence
Cathodoluminescence
Another variant of electroluminescence is cathodoluminescence, which occurs when an electron beam strikes a luminescent material. This interaction promotes electrons from the valence band to the conduction band, creating electron-hole pairs. The subsequent recombination of these pairs results in photon emission, similar to the process in LEDs.
Applications and Implications
Electroluminescence has a wide array of applications in modern technology. LEDs, for instance, are ubiquitous in consumer electronics, lighting solutions, and display technologies. Electroluminescent displays are used in various devices, offering advantages such as thinness, flexibility, and low power consumption. The ongoing research and development in electroluminescent materials and technologies continue to drive innovations in these fields.
Conclusion
Electroluminescence is a vital phenomenon that underpins many of the technologies we use today. Its ability to convert electrical energy into light efficiently makes it invaluable in numerous applications. Understanding the principles of electroluminescence and its various forms can provide insights into the future advancements in lighting and display technologies.
Source: Inc42
Feel free to comment your thoughts.


