Contents
Source: ResearchGate
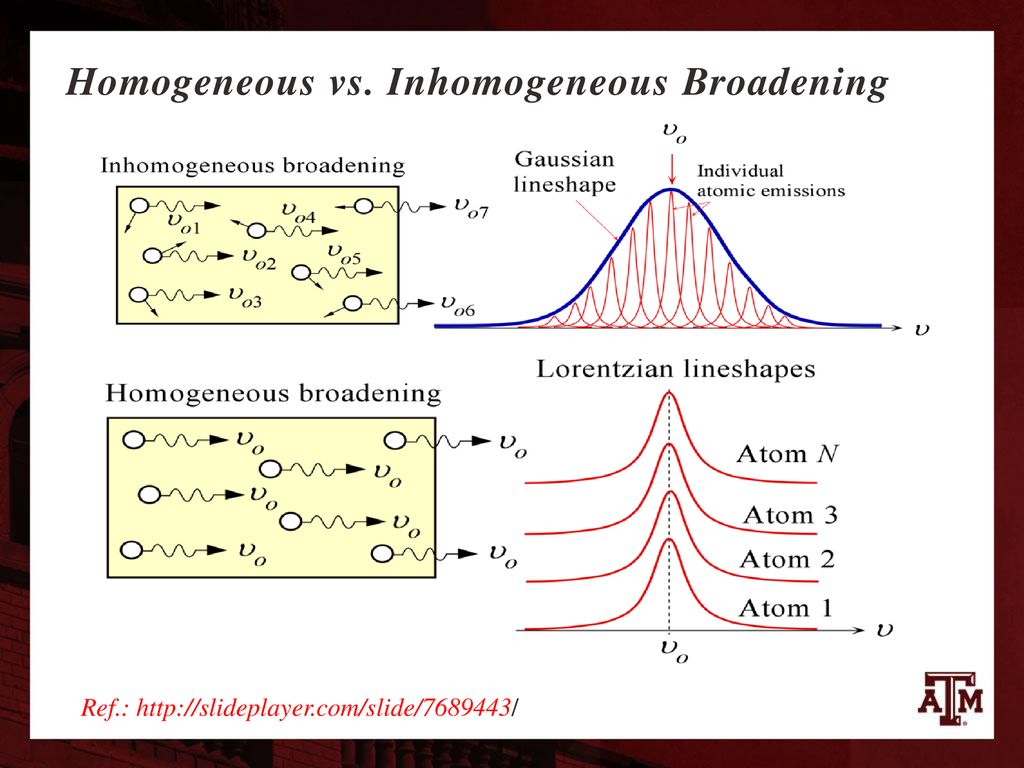
Understanding Homogeneous Broadening in Optical Transitions
In the realm of photonics, understanding the mechanisms that influence the behavior of light and its interaction with matter is crucial. One such mechanism is homogeneous broadening, which plays a significant role in determining the optical properties of materials.
What is Homogeneous Broadening?
Homogeneous broadening refers to the phenomenon where the optical linewidth of an electronic transition is increased uniformly across all radiating or absorbing atoms, ions, or molecules. This means that the spectral shapes of the transition cross-sections are identical for all participating atoms. As a result, each atom or ion exposed to a specific optical intensity will exhibit the same rates of optical transitions.
Mechanisms of Homogeneous Broadening
There are several mechanisms through which homogeneous broadening can occur:
- Natural Linewidth: Isolated non-moving atoms or ions display transitions with a natural linewidth. This arises from the finite lifetimes of the energy levels involved, leading to a broadening effect.
- Collisional Broadening: In gaseous environments, such as in a gas laser, all atoms or molecules of a particular species experience an average rate of collisions. These collisions contribute to collisional broadening, affecting the linewidth.
- Phonon Interactions in Crystals: In laser crystals, laser-active ions often occupy specific sites within the crystal lattice. For example, Nd3+ ions in Nd:YAG crystals replace yttrium ions. The interaction between these ions and the crystal lattice via phonons leads to homogeneous broadening. Rapid transitions between sublevels of Stark level manifolds can significantly reduce sublevel lifetimes, resulting in much larger linewidths than the natural linewidth.
Homogeneous Broadening and Laser Gain Media
Homogeneous broadening is closely related to homogeneous saturation in laser gain media. It facilitates achieving single-frequency operation, which is often desirable in laser applications. In contrast to inhomogeneous broadening, homogeneous broadening ensures that all atoms or ions respond uniformly to the optical field, simplifying the process of achieving a narrow linewidth.
Conclusion
Understanding homogeneous broadening is essential for the development and optimization of optical materials and laser systems. By recognizing the various mechanisms that contribute to this phenomenon, researchers and engineers can better design systems that leverage the uniform behavior of atoms and ions, leading to advancements in photonics technology.
Source: SlidePlayer
Feel free to comment your thoughts.


