Contents
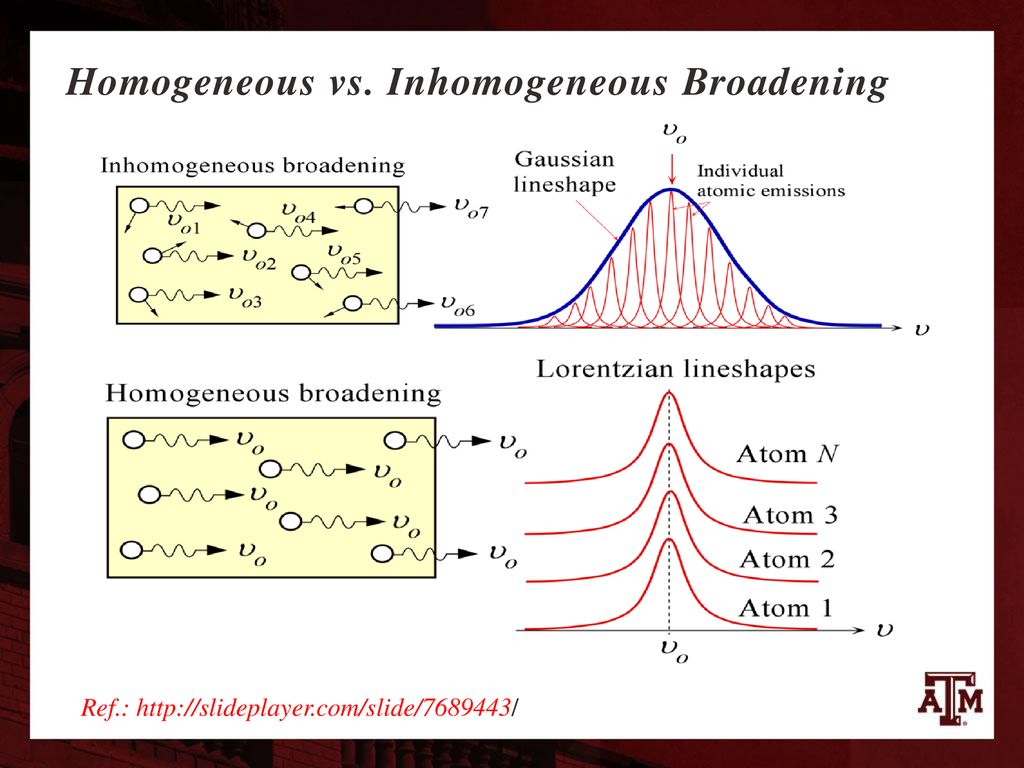
Source: SlidePlayer
Understanding Inhomogeneous Broadening in Photonics
In the realm of photonics, inhomogeneous broadening is a critical concept that explains the increase in the linewidth of atomic transitions. This phenomenon occurs due to various effects that cause different radiating or absorbing atoms (or ions) to interact with distinct wavelength components. Consequently, the spectral shapes of absorption and emission cross-sections vary for different atoms.
The Basics of Inhomogeneous Broadening
Inhomogeneous broadening results in fluorescence spectra that exhibit peaks broader than those of individual atoms. This occurs because the spectrum represents an average over numerous differently emitting atoms. Similarly, absorption spectra can also be broadened due to such inhomogeneous effects.
Causes of Inhomogeneous Broadening
Several factors can lead to inhomogeneous broadening:
- Doppler Broadening: In gas lasers, the varying velocities of gas atoms cause different Doppler shifts, leading to broadening.
- Lattice Variations: In solid media, such as glasses and certain crystalline materials, laser-active ions may occupy different lattice locations. These ions experience diverse local electric and magnetic fields, contributing to broadening.
Inhomogeneous Saturation in Laser Gain Media
Inhomogeneous broadening is closely related to inhomogeneous saturation, particularly in laser gain media. This relationship affects how efficiently a laser medium can be saturated, impacting the overall performance of the laser system.
Conclusion
Understanding inhomogeneous broadening is essential for optimizing the design and functionality of laser systems. By recognizing the various causes and effects of inhomogeneous broadening, researchers and engineers can develop more efficient photonic devices, enhancing their applications in numerous fields.

This document provides a structured and detailed explanation of inhomogeneous broadening in photonics, offering insights into its causes and implications. The use of an image from Wikipedia helps to visually illustrate the concept of the Doppler effect, which is one of the causes of inhomogeneous broadening.

Source: MDPI
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



