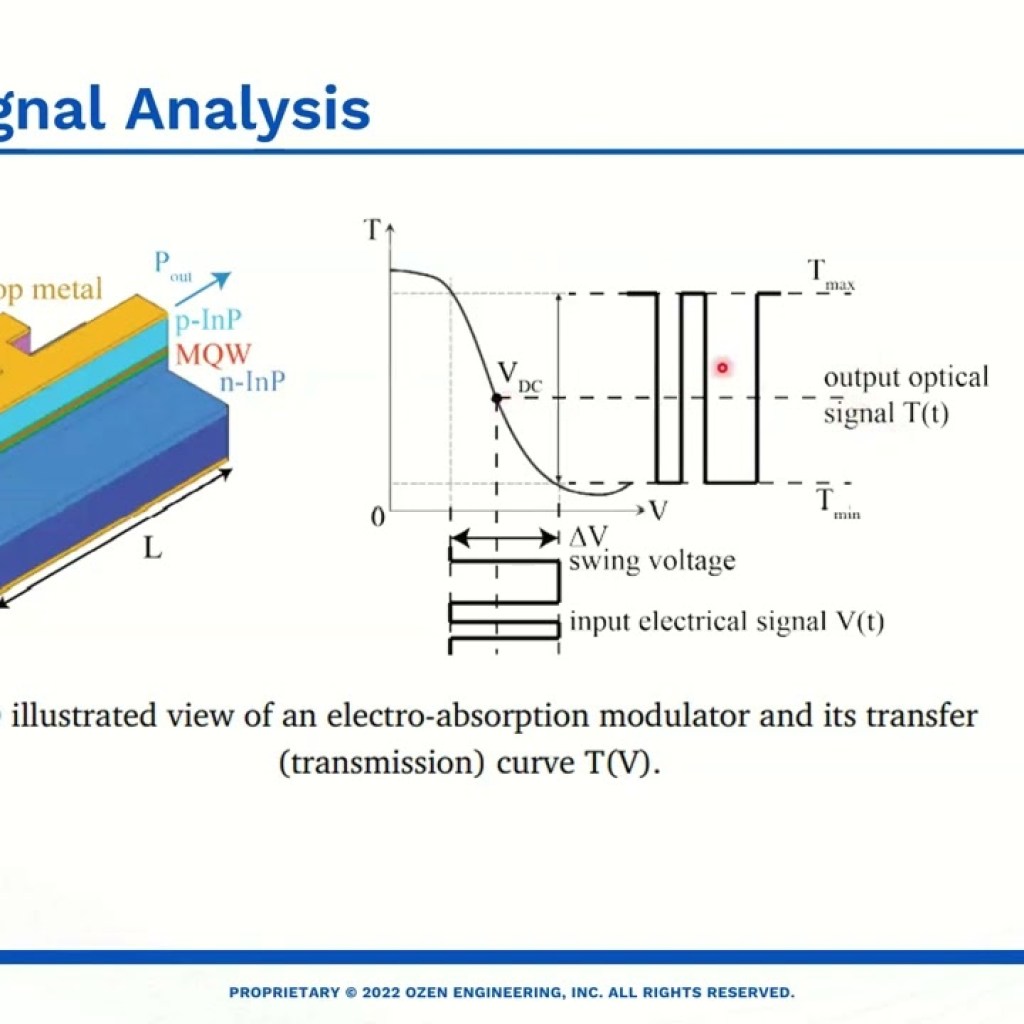
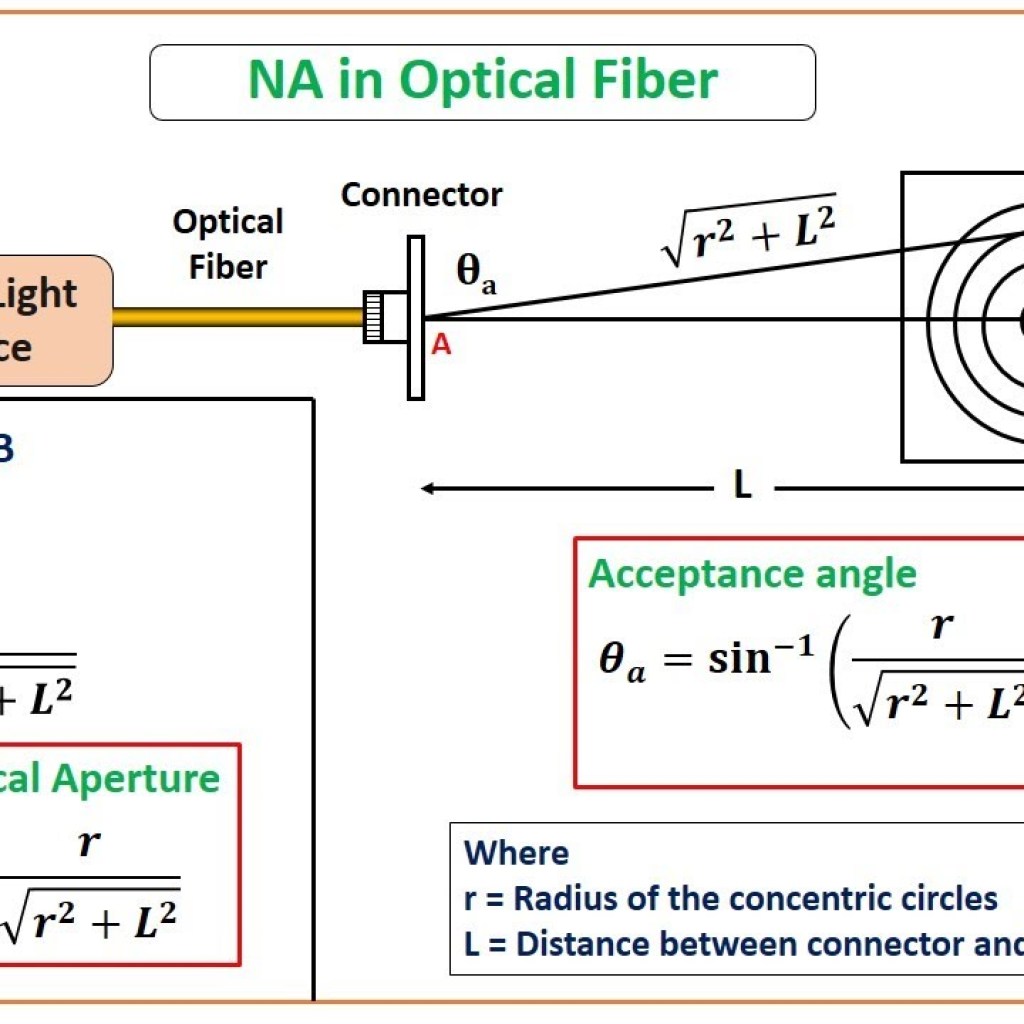
Dispersive Mirrors
Source: OPTOMAN Understanding Dispersive Mirrors in Laser Optics What are Dispersive Mirrors? Dispersive mirrors are specialized mirrors used in laser optics that introduce chromatic dispersion. They are essential for applications like dispersion compensation in laser resonators, pulse compression, and other femtosecond laser optics and signal processing tasks. Types of Dispersive Mirrors Dispersive mirrors are typically […]
Dispersive Mirrors Read More »