Contents
Introduction
Different kinds of beam delivery systems have been developed to direct light beams from a source to specific applications, often involving lasers. This is crucial in various fields such as laser material processing, medical procedures, and industrial applications. This blog post will delve into the types of beam delivery systems, their functionalities, and the factors to consider when implementing them.
Importance of Beam Delivery Systems
In laser material processing or medical applications like surgery, directing laser output precisely to a workpiece or target area is essential. Beam delivery systems play a pivotal role in achieving this precision. They enable the utilization of lasers in conjunction with robotics, allowing flexibility in moving the beam path without moving the entire laser system. The key advantage lies in the ability to place the laser source in a protected area while delivering the beam to the application area.
Types of Beam Delivery Systems
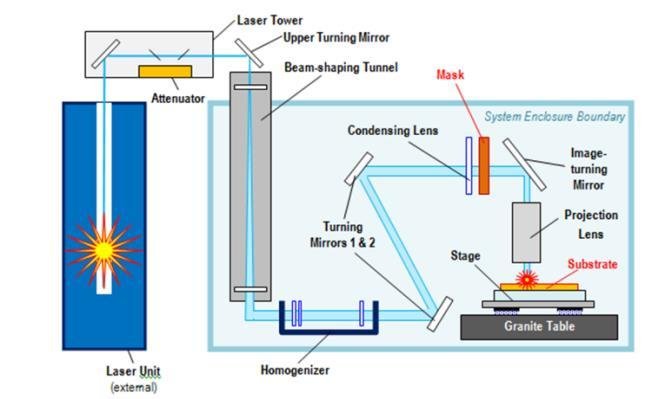
Free-space Beam Delivery Systems
Free-space systems use mirrors to direct laser output. Dielectric mirrors, with high reflectance, can handle high optical power levels, ensuring efficient power throughput. The beam path in fixed systems is encapsulated within an airtight tube system, leading to a laser processing head.
Articulated Mirror Arms
Articulated mirror arms provide a movable beam path. Components are designed for smooth movements, and precision is crucial for stability. Some systems involve rapidly rotating optics, such as rotating prisms, for specific applications like trepanning or helical drilling.
Challenges and Considerations
While free-space systems are versatile, there are challenges, including wavelength limitations of dielectric mirrors. The choice between fixed and movable beam paths depends on the application’s requirements.
Fiber-optic Beam Delivery Systems
Optical fibers offer flexibility in delivering laser beams, commonly integrated into fiber cables. Glass fibers, like silica fibers, transport light with low losses, especially in the near-infrared region. However, challenges arise in handling high power levels in extreme wavelength regions.
Fiber-to-fiber Couplers
Additional flexibility is achieved with fiber-to-fiber couplers, allowing for changes in the cable’s direction or use of purging gas.
Challenges with Fiber-optic Systems
Large core diameter and high numerical aperture in fibers can lead to complex beam evolution and losses in radiance, particularly in high-power applications.
Important Aspects of Beam Delivery Systems
Power Handling Capability
Considerations for power handling include average and peak power limits, avoiding overheating, and addressing nonlinear effects. Proper launch of the input beam is crucial to prevent damage.
Fixed or Movable Beam Path
The choice between a fixed or movable beam path depends on the application. Rapid operations may benefit from a movable beam path, achieving flexibility without moving heavy workpieces.
Pilot Beam
Some systems use a visible low-power pilot beam superimposed on the high-power beam for visibility. Proper alignment ensures reliable indication of the main beam’s position.
Pointing Stability and Beam Sharing
Beam pointing fluctuations, particularly with long articulated mirror arms, and the ability to share the laser beam between multiple locations are relevant considerations.
Beam Containment and Seal
Encapsulation of the beam path protects optics against scratching, dust, and laser hazards. Some systems may require a reliably sealed apparatus for specific environments.
Additional Features
Additional features may include robustness, integration of optical elements, maintenance of polarization direction, and adaptations for extreme wavelength regions.
Suppliers and Product Examples
Several suppliers offer diverse beam delivery systems with unique features. Examples include GLOphotonics, Optogama, few-cycle, Schäfter + Kirchhoff, and art photonics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, beam delivery systems are integral components in laser applications, providing the means to direct laser beams precisely for various purposes. Understanding the types, challenges, and crucial aspects helps in selecting the most suitable system for specific applications. As technology evolves, continuous innovation in beam delivery systems remains essential for advancing laser-related industries.