Contents

Source: YouTube
Case Study: Ytterbium-doped 975-nm Fiber Lasers
Special Spectroscopic Situation
Ytterbium-doped lasers emitting at 975 nm have a unique spectroscopic situation. The emission cross-section of ytterbium is maximized at this wavelength, but there is also significant reabsorption, requiring the Yb excitation density to be over 50% for positive gain.
Difficulty of Achieving Lasing at 975 nm
Lasing at 975 nm, for both core and cladding pumping, can be challenging due to the strong three-level characteristics of Yb excitation. The fiber type plays a crucial role in the design, especially for double-clad fibers.
Core-pumped Laser
Core-pumped single-mode fibers, like Yb 103 from CorActive, can be used for 975-nm fiber lasers. By optimizing parameters such as fiber length and pump input, reasonable power efficiency can be achieved.
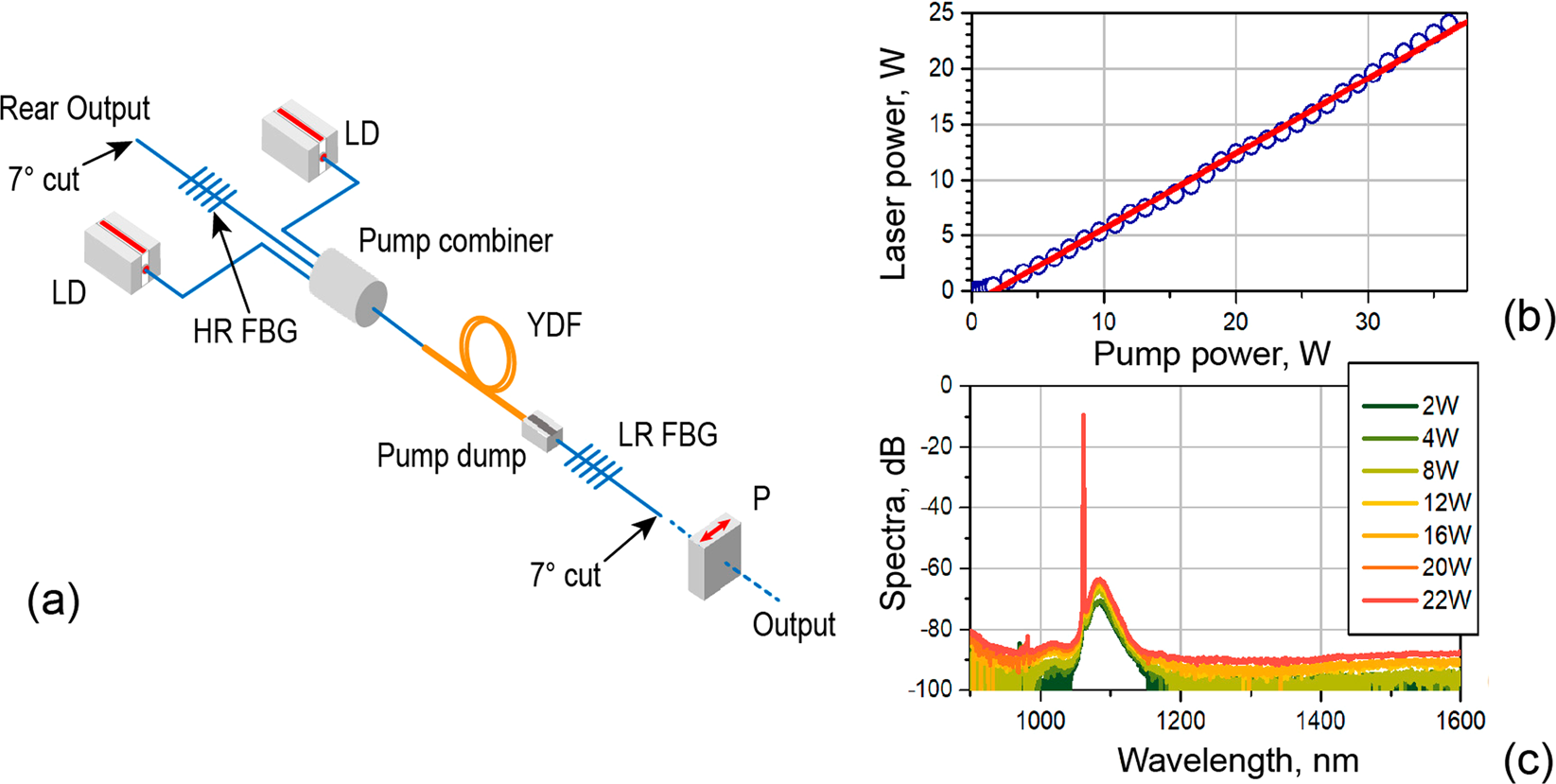
Cladding-pumped Laser
Double-clad fibers, such as DCF-YB-6/128 from CorActive, can be challenging for 975-nm lasers due to incomplete pump absorption and strong amplified spontaneous emission (ASE). The use of ring-doped fiber designs can help overcome these challenges.
Ring-doped Fiber Solution
In ring-doped fiber designs, Yb doping is placed in a ring around the fiber core, reducing overlap with the laser light and minimizing ASE. While not commercially available, custom fiber designs can be created to achieve better efficiency and reduced ASE.
Conclusions
Designing Yb-doped fiber lasers at 975 nm is feasible with core-pumped fibers, but challenges arise with cladding-pumped fibers. Simulation software like RP Fiber Power can aid in optimizing designs and understanding unexpected behaviors in fiber lasers.
Final Thoughts
Ytterbium-doped 975-nm fiber lasers offer unique challenges and opportunities in laser design. By exploring different pumping techniques and fiber designs, researchers can enhance the efficiency and performance of such lasers for various applications.
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.