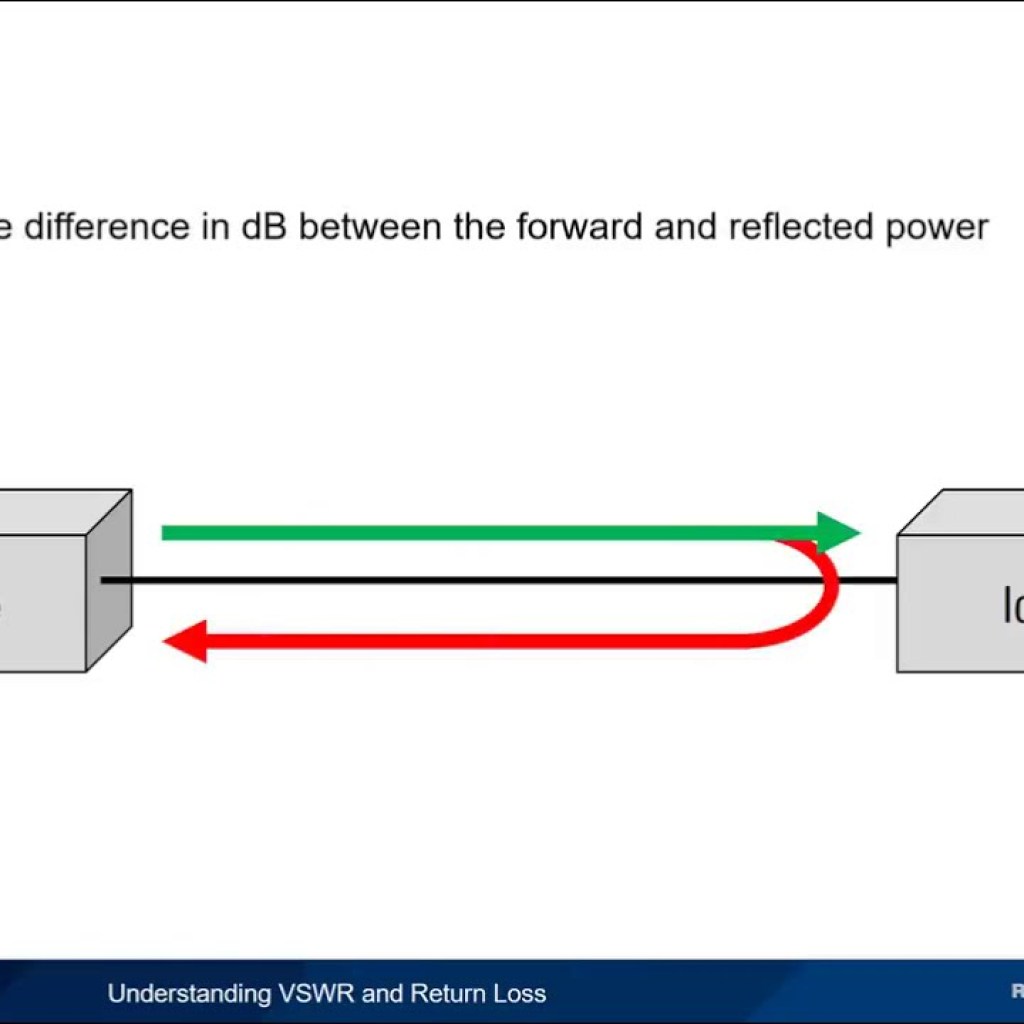
Return Loss
Source: YouTube The Significance of Return Loss in Optics Understanding Return Loss in Optics What is Return Loss? Return loss, also known as reflection loss, measures the reduction in optical power of reflected light compared to the incident light. It is typically expressed in decibels (dB), where a higher value indicates lower reflected power. Return […]