Contents

Source: Chemistry Student
Understanding Colorimetry
Introduction to Colorimetry
Colorimetry is a field that deals with the measurement of optical properties related to color impressions as perceived by human eyes. Unlike spectrophotometers that focus on physical properties of light, colorimetry is centered around human color perception. The human eye has three color receptors, limiting its spectral information capabilities compared to technical instruments.
Applications of Colorimetry
Colorimetry is used to measure properties of light sources, objects interacting with light, computer screens, printed materials, and more. It plays a crucial role in areas such as lighting, digital imaging, printing, fashion, and arts.
Color Spaces
Color values are represented in color spaces, where colors are expressed as coordinates. The development of colorimetry has led to various color spaces, with CIE color spaces being prominent. These spaces, like CIE 1931 XYZ and CIE RGB, are essential for quantifying color values.
Metamerism
Metamerism is a phenomenon where different light sources with varying spectral compositions can appear as the same color. This can lead to color discrepancies in applications like lighting and fashion, emphasizing the importance of considering metamerism in colorimetric measurements.
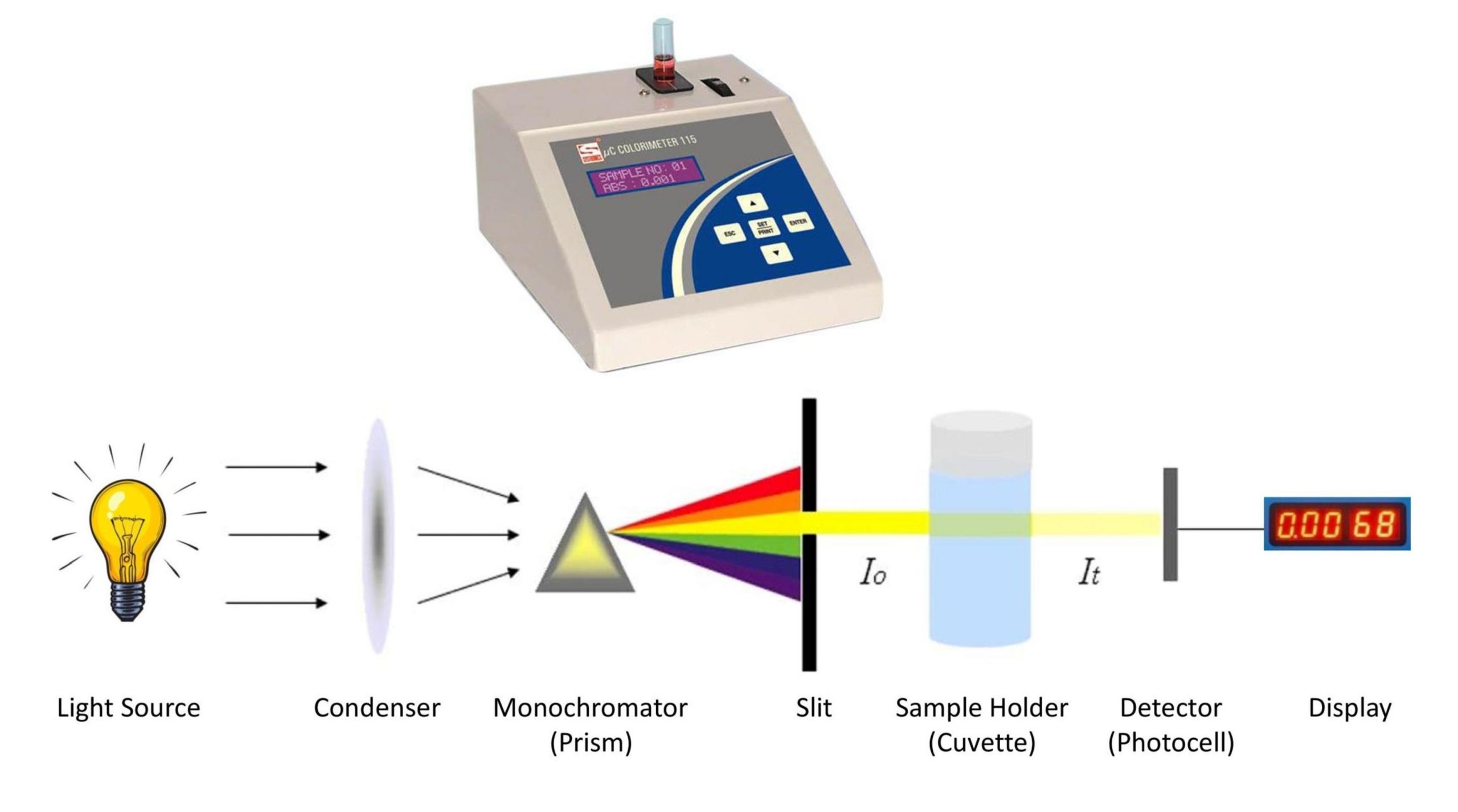
Instruments for Colorimetric Measurements
Colorimeters are specialized instruments used in colorimetry to measure color properties of light sources and objects. Optical spectrometers and spectrophotometers are also utilized to obtain wavelength-dependent measurements for calculating photometric quantities.
Limitations of Colorimetry
While colorimetry provides objective color information, human color perception is influenced by factors like individual variations in color vision, age-related changes in eye sensitivity, and environmental influences. These factors can impact the accuracy of colorimetric measurements in predicting actual color perception.
Conclusion
Colorimetry is a vital field for understanding and quantifying color properties for various applications. By considering the complexities of human color perception and the phenomenon of metamerism, colorimetry continues to play a significant role in industries relying on accurate color representation.
Source: LaboratoryTests.org
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



