Contents

Source: Wikimedia Commons
<>
Understanding Common-Path Interferometers
Sagnac Interferometer
A Sagnac interferometer is designed with the interfering beams traveling along a ring in opposite directions. This setup is commonly used for gyroscopes due to the path length difference generated by rotations around an axis perpendicular to the loop plane.
Point Diffraction Interferometers
Point diffraction interferometers are utilized for wavefront sensing. By focusing the investigated beam to a pinhole in a plate with small transparency, interference of light passing through the pinhole and other parts of the plate can be observed.
Interferometers Based on Different Polarizations
In common-path interferometers with different polarizations, the interfering beams travel in the same direction but with varying polarization states. This setup allows for interference to occur at a polarizer, with the path length difference created based on birefringence.
Applications
Common-path interferometers find applications in various fields such as gyroscopes, Fourier transform spectroscopy, wavefront sensing, femtosecond time-resolved interferometry, and pulse characterization.
Conclusion
Common-path interferometers offer advantages in terms of alignment stability and mechanical noise suppression compared to traditional interferometer setups. Their versatility makes them valuable tools in a wide range of scientific and industrial applications.
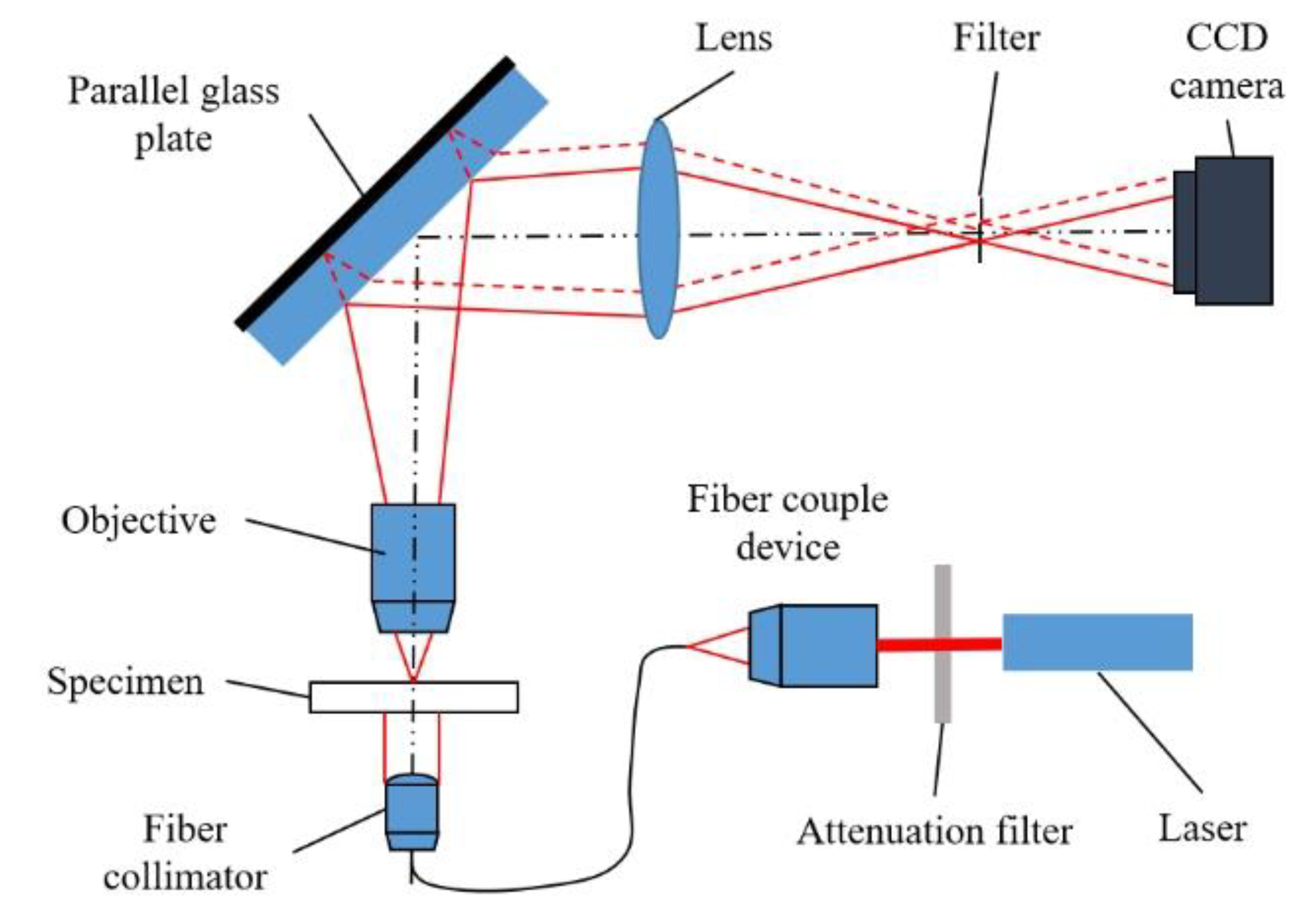
Source: MDPI
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



