Contents
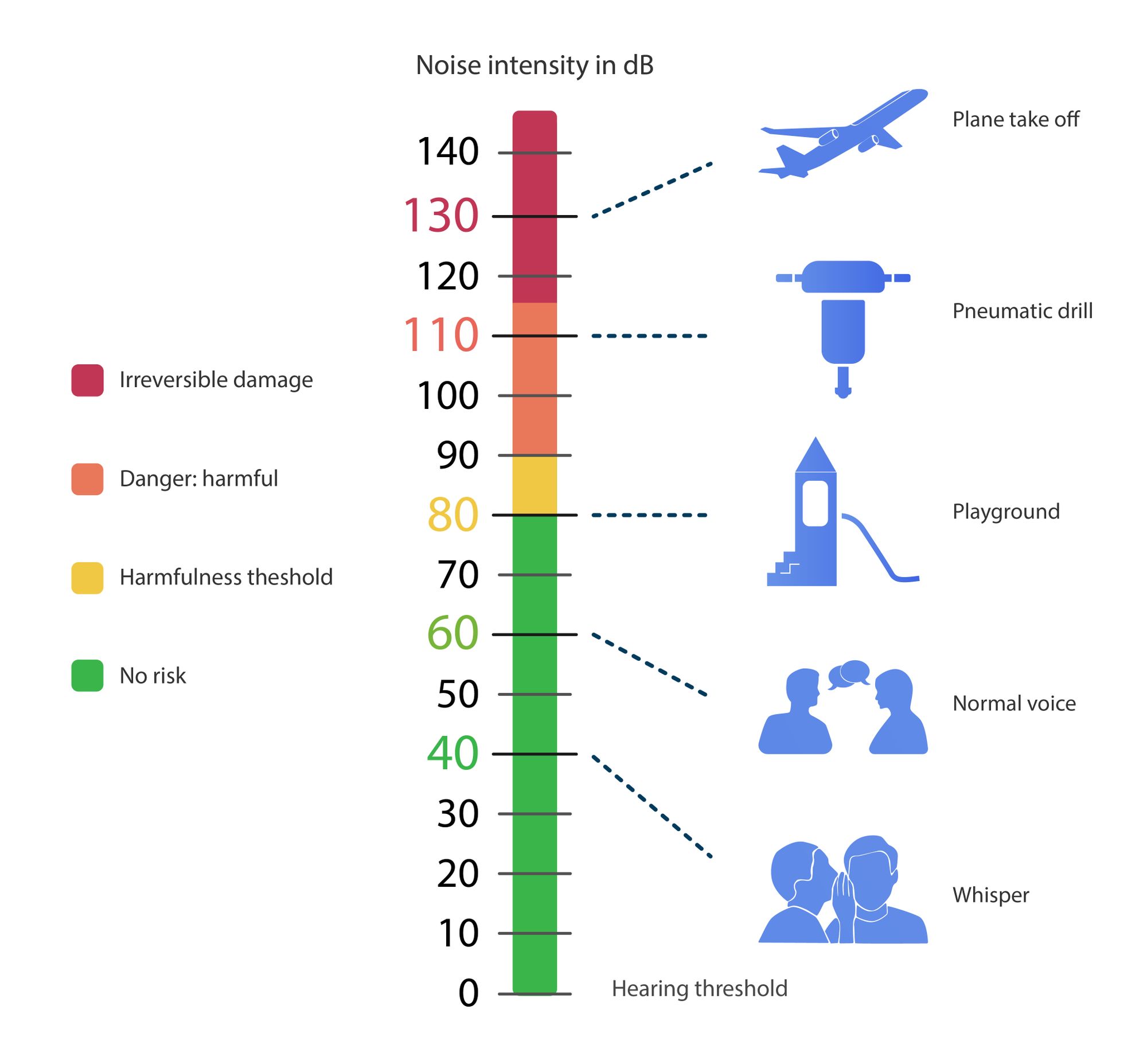
Source: Decibel Pro
<>
The Significance of Decibels in Photonics
Understanding Decibels
The decibel (dB) is a unit used to measure the gain of an amplifier or the loss of an optical component like a fiber or attenuator. It is a logarithmic unit where the number of decibels is 10 times the logarithm of the power amplification factor or loss factor.
Application in Optical Signals
Decibels are commonly used to quantify transmitted signals and noise in optical systems. They help in comparing power levels and signal strengths in various components like filters, lasers, and amplifiers.
Optical Power vs. Modulation Power
Optical power refers to the power of the signal itself, while modulation power is proportional to the square of the signal amplitude. Increasing optical input power can significantly impact signal power due to this relationship.
Frequently Used Specifications
Some common specifications related to decibels include dBc (dB relative to the carrier), dBc/Hz (used for noise in a 1-Hz bandwidth), and dBm (dB relative to a reference power of 1 mW). These specifications help in accurately measuring and comparing signal strengths and noise levels.
Enhancing Your Understanding
By grasping the concept of decibels and their applications in photonics, you can better analyze and optimize the performance of optical systems. Understanding decibels is crucial for professionals working in the field of photonics.
Questions and Further Exploration
If you have any questions or would like to delve deeper into the topic of decibels in photonics, feel free to explore additional resources and seek clarification from experts in the field.
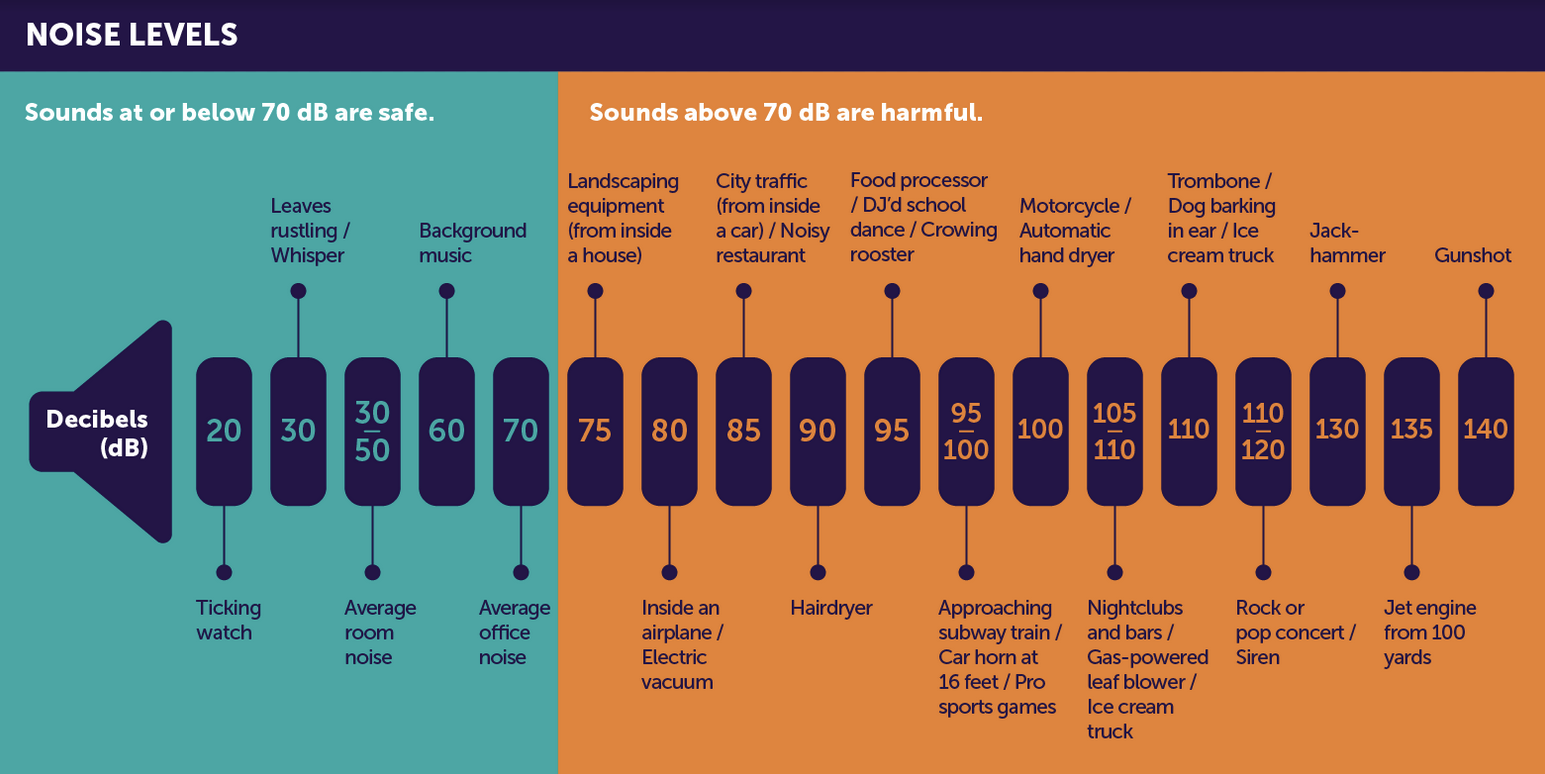
Source: Hearing Health Foundation
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



