Source: Edmund Optics
**Understanding Diffraction Gratings**
**Introduction to Diffraction Gratings**
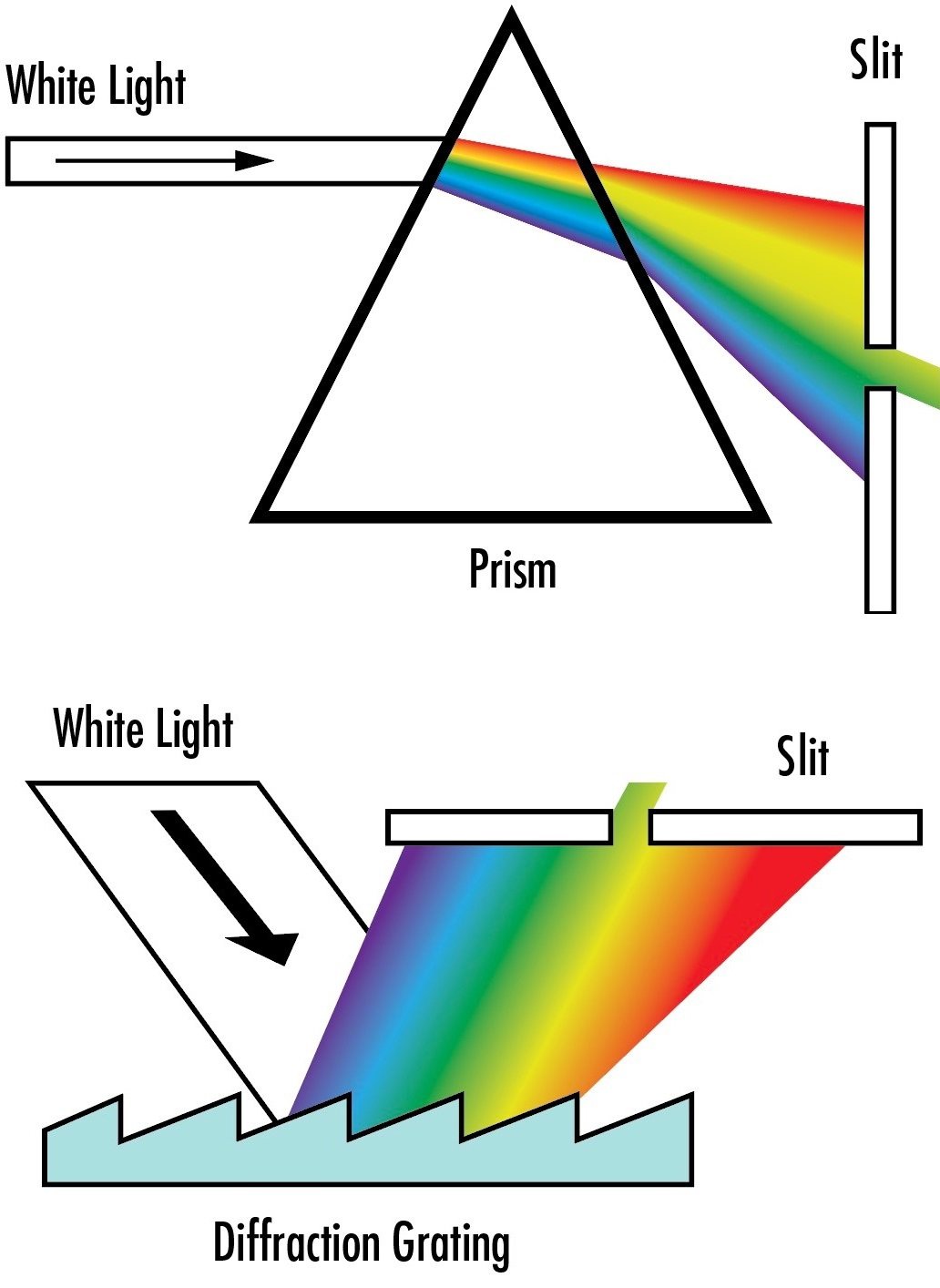
Diffraction gratings are optical devices that utilize the phenomenon of diffraction. They consist of a periodic structure that causes spatially varying optical amplitude and/or phase changes. There are different types of diffraction gratings, with reflection gratings being the most common, where a reflecting surface has a periodic surface relief leading to position-dependent phase changes.
**Details of Diffraction at a Grating**
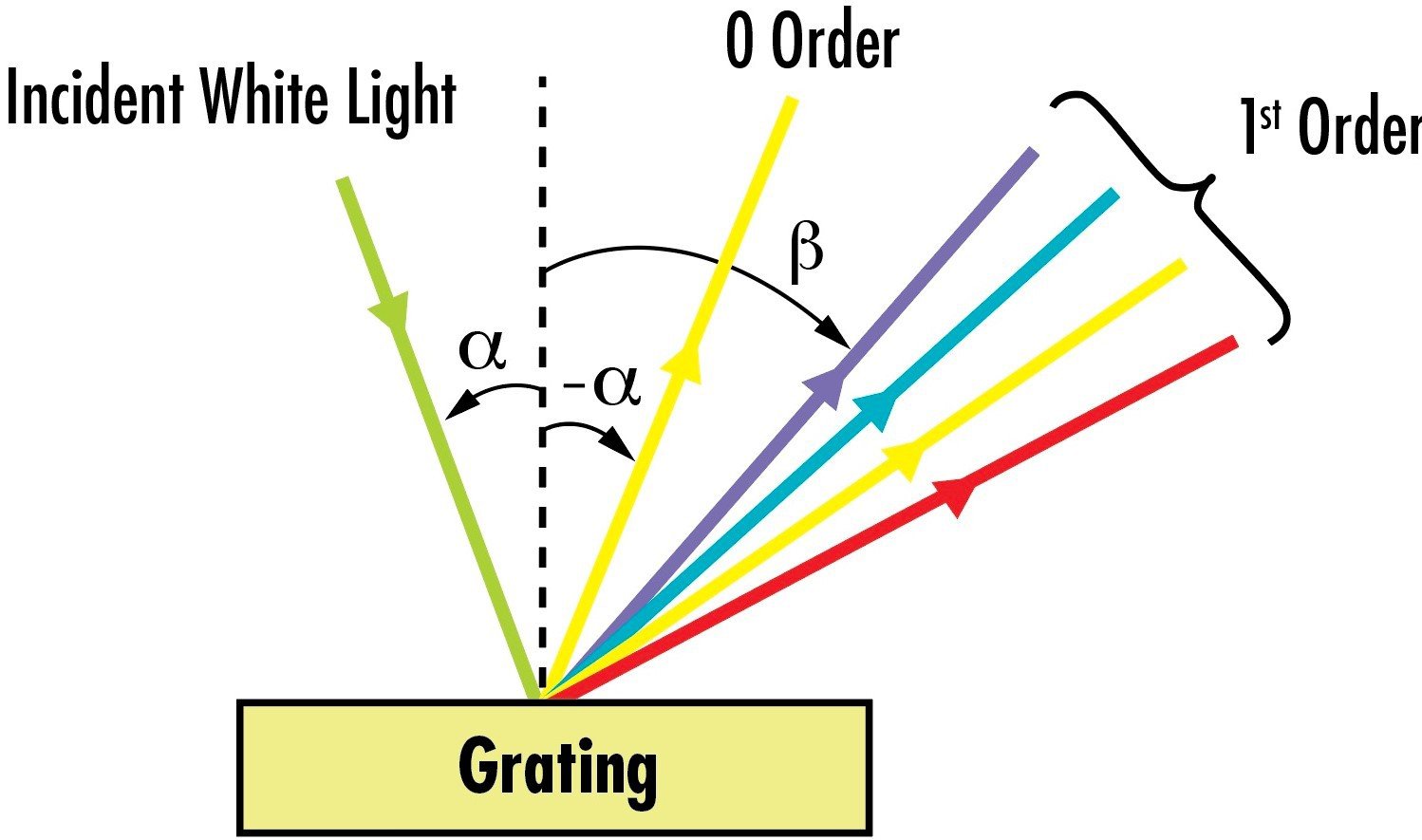
When light interacts with a diffraction grating, it produces multiple output beams according to different diffraction orders. The distribution of output power among these diffraction orders, known as diffraction efficiency, depends on the grating’s properties. High diffraction efficiency is crucial for applications such as pulse compression and spectrometry.
**Blazed Gratings**
Blazed gratings are optimized to direct most of the power into a specific diffraction order, resulting in high diffraction efficiency for that order. These gratings have a sawtooth-like surface profile that enhances their performance within a limited wavelength range.
**Echelle Gratings**
Echelle gratings are a special type of blazed gratings with a large blaze angle. They are commonly used in spectrometers for their high angular dispersion and are often combined with other gratings to avoid confusion from multiple diffraction orders.
**Littrow Configuration**
In the Littrow configuration, a diffracted beam, usually the first-order beam, travels back along the incident beam. This setup is utilized in applications like wavelength-tunable lasers to achieve specific resonant conditions.
**Fabrication Methods for Gratings**
Gratings can be fabricated using various techniques, including ruling engines for mechanically imprinting surface relief, laser micromachining, and holographic methods for finer structures. Replication processes can also be used for mass production of gratings.
**Different Types of Gratings**
Gratings can be classified based on their operation principles, materials used, and specific applications. Special types include transmission gratings, volume gratings, and grisms (gratings on prisms).
**Important Properties of Diffracting Gratings**
Properties such as line density, size, diffraction efficiency, polarization dependence, damage threshold, thermal sensitivity, and alignment sensitivity play crucial roles in the performance and application of diffraction gratings.
**Applications of Diffraction Gratings**
Diffraction gratings find applications in monochromators, spectrometers, pulse compression setups, wavelength tuning in lasers, spectral beam combining, and more. They are essential components in various optical systems for manipulating light and analyzing spectral content.
**Conclusion**
Diffraction gratings are versatile optical devices with a wide range of applications in modern optics and photonics. Understanding their properties and fabrication methods is essential for optimizing their performance in different optical systems.
Source: Edmund Optics
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



