Contents
Source: Wikipedia
<>
Understanding Dioptric Power in Optics
What is Dioptric Power?
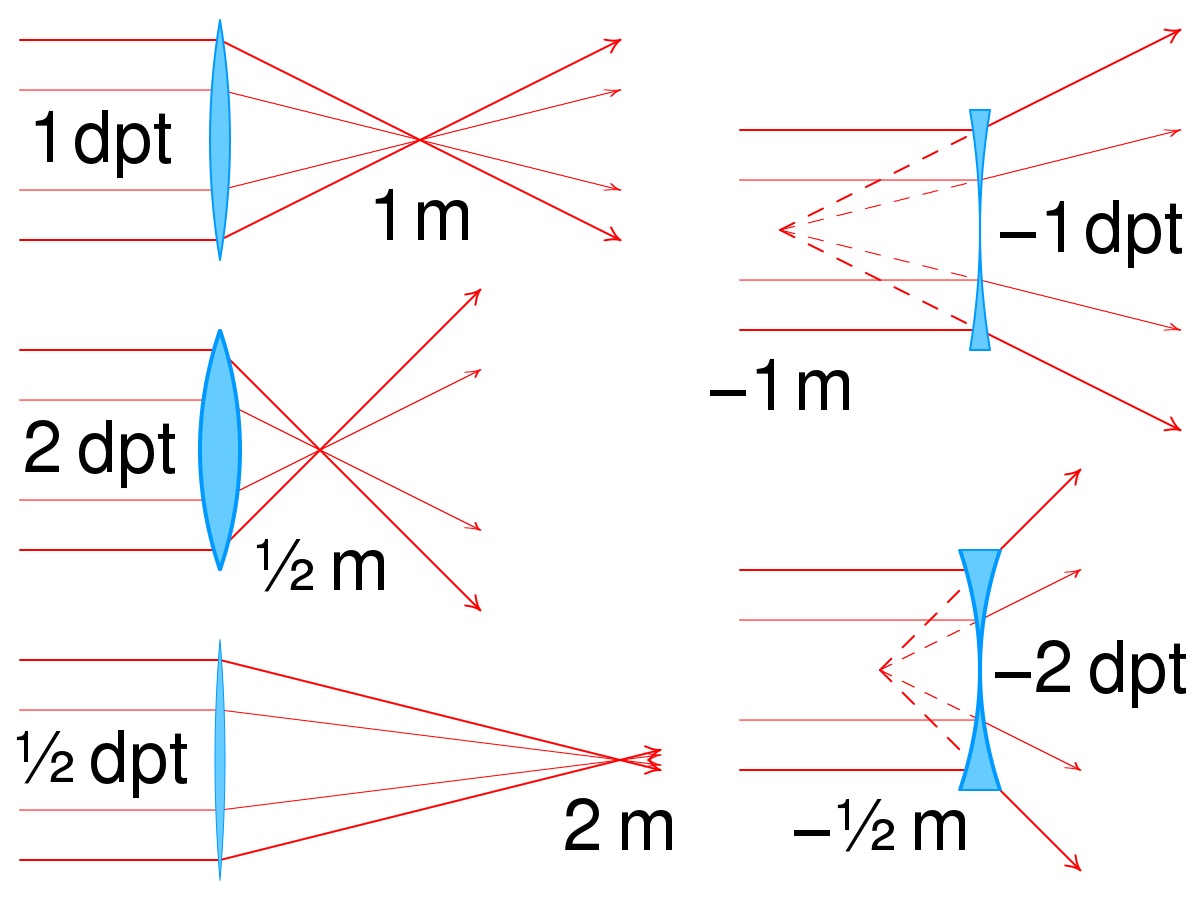
Dioptric power is the inverse of the effective focal length of an optical element. It is measured in diopters (dpt) or m-1. This specification is commonly used for prescription glasses, while focal length is more typical for standard lenses and objectives.
Dioptric Power vs. Focal Length
Dioptric power is often a more convenient measure than focal length. Stronger focusing action corresponds to higher dioptric power and shorter focal length. For example, in a laser crystal, the dioptric power of the thermal lens is proportional to dissipated power.
Optical Media Variation
When different optical media are present on both sides of the optics, additional considerations apply. The dioptric power calculation involves the effective focal lengths and refractive indices of the media involved.
Combination of Lenses
The dioptric power of two thin lenses in close proximity is the sum of their individual powers. When the distance between them is not negligible, the total dioptric power is calculated differently.
Example: Dioptric Power of Prescription Glasses
For prescription glasses, dioptric power calculations depend on the required correction for viewing distances. As age affects accommodation ability, different dioptric powers may be needed for various tasks like reading or viewing distant objects.
Complexities in Practice
Factors like astigmatism, different corrections for each eye, and proper adjustment of lens centers for both eyes can complicate the prescription of glasses, especially for high dioptric powers.
Further Considerations
Understanding dioptric power in optics is essential for designing optical systems and prescribing corrective lenses. It plays a crucial role in determining the focusing capabilities of optical elements and ensuring optimal vision for individuals with refractive errors.
Source: ResearchGate
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



