Contents

Source: Wikipedia
The Fascinating World of Dye Lasers
Introduction to Dye Lasers
Dye lasers are a type of laser that utilize a dye as the gain medium. These dyes are typically organic molecules dissolved in liquid form. The range of laser dyes available is vast, covering a wide spectrum of wavelengths. Names like exalite, coumarin, rhodamine, and pyrromethene represent families of dyes with variations in chemical structures and emission wavelengths.
Characteristics of Laser Dyes
Laser dyes are known for their tunability across different wavelength regions. They are commonly used in conjunction with solvents such as ethanol, p-dioxane, and dimethylsulfoxide. It is important to note that many laser dyes and solvents can be hazardous to health and should be handled with caution.
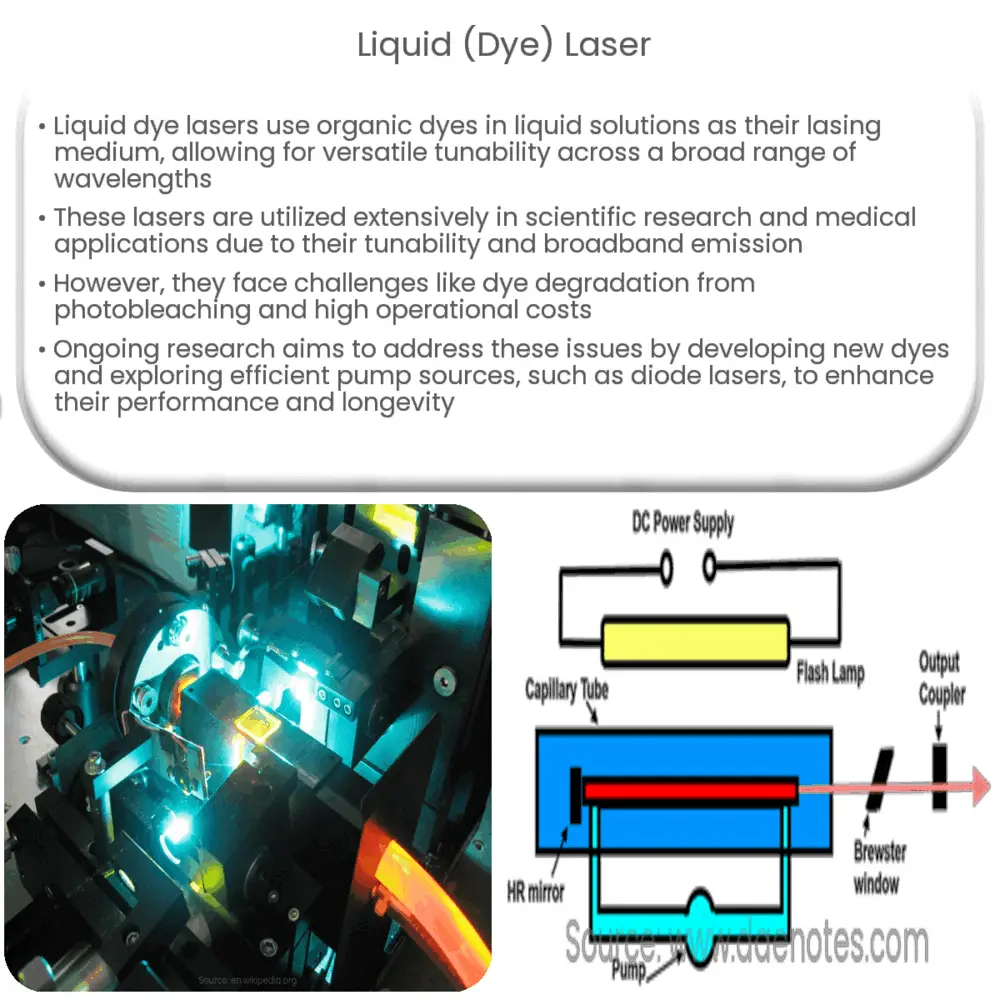
Pumping Options for Dye Lasers
Dye lasers are often pumped with green lasers for longer wavelengths and ultraviolet light for shorter wavelengths. Pumping can also be achieved using excimer lasers, nitrogen lasers, or flash lamps. The choice of pumping method depends on the desired output characteristics of the laser.
Dye Laser Resonators
The resonator of a dye laser typically contains a dye jet or cuvette as the gain medium. Various frequency-selective elements enable wavelength tuning within a certain range. Laser resonators for dye lasers are designed to achieve stable output characteristics and precise wavelength control.
Recovery and Degradation
Dye molecules in dye lasers can become trapped in triplet states, affecting their ability to participate in the lasing process. Techniques such as using thin dye jets or cuvettes help in the recovery of dye molecules. Due to chemical degradation during operation, dye solutions need to be exchanged periodically.
Applications and Future Developments
While dye lasers have been widely used in the past, they have certain limitations such as degradation during operation and the need for expensive pump sources. Solid-state lasers have largely replaced dye lasers in many applications, especially in ultrashort pulse generation. However, dye lasers still find applications in areas like laser spectroscopy and intracavity laser absorption spectroscopy.
Conclusion
Dye lasers have played a significant role in the development of laser technology, offering tunability across a wide range of wavelengths. While they may have been overshadowed by solid-state lasers in certain applications, dye lasers continue to be relevant in niche areas where their unique characteristics are advantageous. Further research and advancements in laser technology are likely to shape the future of dye lasers and their applications.
Source: Electricity – Magnetism
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



