Contents
Source: Nature
The Fabry–Pérot Interferometer: An Overview
Operation Principle
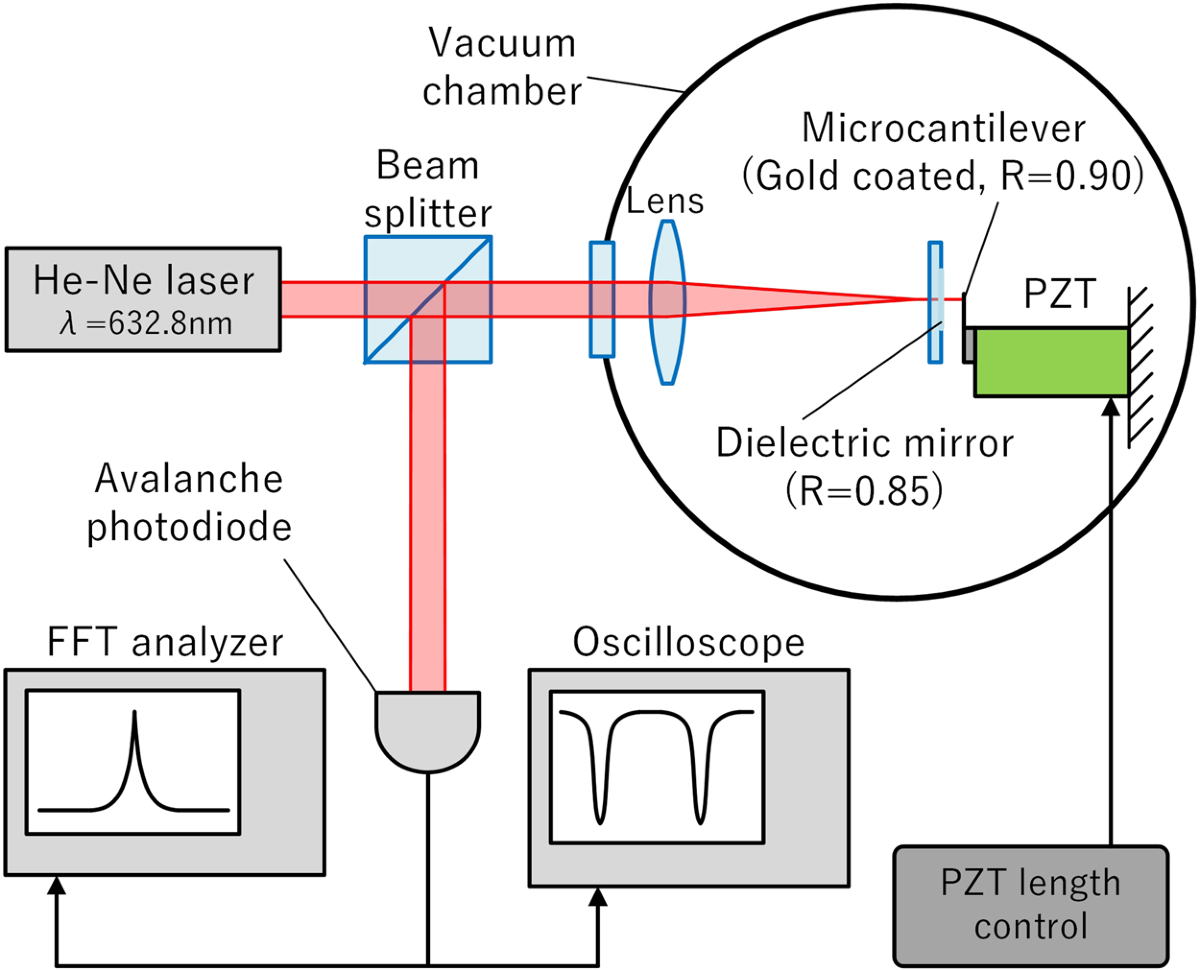
A Fabry–Pérot interferometer consists of two highly reflective mirrors with some transmissivity, forming a resonator with sharp resonances in transmission. In resonance, the input and circulating waves constructively interfere, leading to minimal reflection. In anti-resonance, most radiation is reflected.
Frequency-Dependent Transmittance
The resonance frequencies can be tuned by changing the cavity length. By monitoring the transmitted power as the cavity length is varied, the optical spectrum of the incident light can be obtained.
Variants and Applications
Fabry–Pérot interferometers can have planar or curved mirrors and are used in various applications. They are utilized to analyze laser modes, as reference cavities, and for spectral analysis. Shorter interferometers provide a larger free spectral range, enabling high-resolution spectral analysis.
Gires–Tournois Interferometer
A variant of the Fabry–Pérot interferometer, the Gires–Tournois interferometer, is used for generating chromatic dispersion.
Conclusion
The Fabry–Pérot interferometer is a versatile device used in optical spectrometry and laser characterization. Its ability to provide high-resolution spectral information makes it invaluable in various scientific and industrial applications.

Source: Stoppi – Homemade Physics Experiments
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



