
Source: Wikipedia
Understanding the Field of View in Optical Instruments
The field of view (FoV) is a crucial concept in the context of optical instruments such as telescopes and cameras. It refers to the extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment through the instrument. The field of view is typically expressed as the angular area visible through the instrument, and it can be influenced by several factors, including the design of the optical system and the size of the sensor or film used.
Defining the Field of View
The field of view can be quantified in multiple ways. It is generally described in terms of the full angle or half-angle of view in horizontal, vertical, and diagonal directions. The shape of the field can vary, being circular or rectangular, depending on the optical system’s configuration.
Another way to express the field of view is by specifying a solid angle, which provides a three-dimensional understanding of the observable area. The center of the entrance pupil often serves as the reference point for these angles.
Field of View vs. Angle of Acceptance
While the term “field of view” is commonly used, the “angle of acceptance” is also employed, particularly in non-imaging optical systems. This term defines the range of angles over which the system can effectively gather light.
Factors Affecting the Field of View
The field of view of an optical system is often intentionally limited to enhance image quality. This is achieved using a field stop, an optical aperture that defines the edges of the field of view sharply. However, when the field of view is restricted by an aperture not positioned in the image plane, vignetting effects may occur, leading to a gradual decrease in image brightness towards the edges.
Advanced optical designs, such as those incorporating aspheric lenses, can provide a wider field of view without significant degradation in image quality, though they may be more expensive or bulkier.
Field of View in Cameras
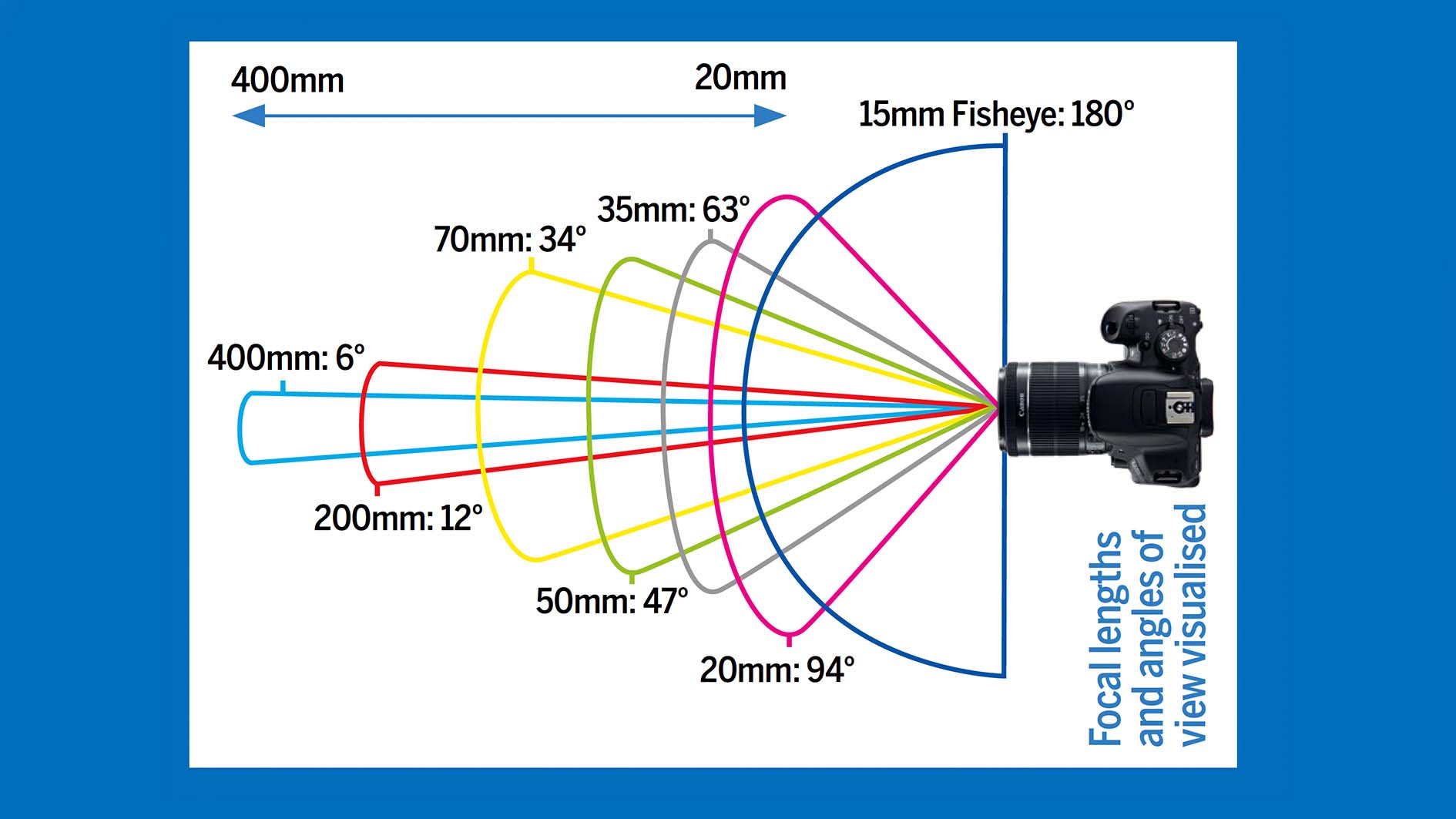
In cameras, the field of view is influenced by both the lens used and the size of the image sensor or film. The focal length of the lens plays a critical role, with shorter focal lengths providing a wider field of view. Wide-angle lenses, including fish-eye lenses, offer extensive fields of view but may introduce image distortions.
Standard camera lenses are designed to mimic the human eye’s field of view, typically around 50° horizontally. Zoom lenses allow for adjustable fields of view, changing with the zoom setting.
Field of View in Telescopes
Telescopes are designed to magnify distant objects, and their field of view is inversely related to magnification. Higher magnification often results in a smaller field of view. However, certain optical designs, like the addition of a field lens in a Keplerian telescope, can expand the field of view.
Human Eye and Peripheral Vision
The human eye’s field of view is not precisely defined. Maximum resolution is achieved in the central vision, while peripheral vision offers lower image quality. Rapid eye movements help cover a broader angular range, compensating for the lower quality in peripheral vision.
Impact of Viewing Aids
Devices like corrective glasses or magnifying lenses can restrict the field of view. In some cases, such as with laser safety glasses, peripheral vision may be entirely blocked, potentially increasing safety risks.
Conclusion
The field of view is a fundamental aspect of optical instrument design, influencing how much of the world can be observed at once. Understanding its implications and limitations is essential for optimizing the performance of telescopes, cameras, and other optical systems.
Source: Digital Camera World
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



