Contents
- 1 Unlocking the Future: Free-Space Optical Communication (FSO)
Unlocking the Future: Free-Space Optical Communication (FSO)
In the ever-evolving landscape of communication technologies, Free-Space Optical Communication (FSO) stands out as a promising and innovative solution. As our dependence on high-speed and reliable communication continues to grow, FSO emerges as a beacon of light, quite literally, in the realm of data transmission. This blog post delves into the intricacies of FSO, exploring its principles, applications, advantages, challenges, and its potential to shape the future of communication.
Understanding Free-Space Optical Communication (FSO)
The Basics
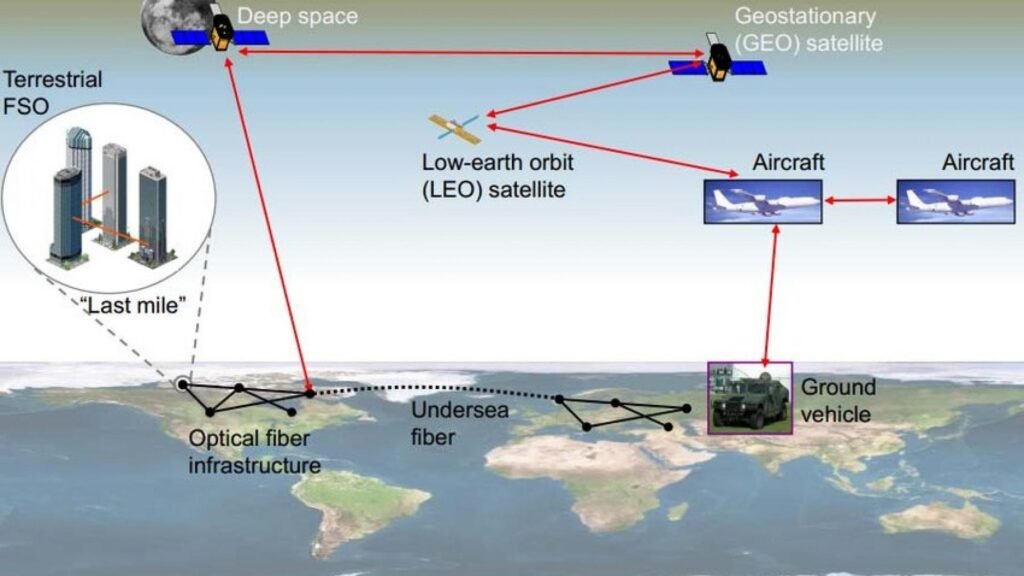
Free-Space Optical Communication is a communication technology that employs light to transmit data through free space, typically in the form of laser beams. Unlike traditional communication methods that rely on cables or fibers, FSO utilizes the atmosphere as the transmission medium. This approach offers several advantages, such as higher data rates and increased security.
How FSO Works
At its core, FSO operates by encoding data onto optical signals, typically in the infrared spectrum, and transmitting these signals through the air to a receiving station. The transmitted signal is modulated to represent digital information, and the receiving station decodes the signal to retrieve the original data.
One of the key components in FSO systems is the optical transceiver. This device includes a laser for transmitting data and a photodetector for receiving signals. The laser emits a beam of light, which carries the data in the form of modulated pulses. The receiving station detects these pulses using the photodetector, and the data is then extracted.
Applications of Free-Space Optical Communication
Telecommunications
One of the primary applications of FSO is in telecommunications. As the demand for high-speed internet and data transmission continues to soar, FSO provides a viable solution for bridging the connectivity gap. FSO can be employed to establish high-capacity links between communication nodes, enabling faster and more efficient data transfer.
Urban Connectivity
In urban environments where laying fiber optic cables can be challenging and expensive, FSO offers a cost-effective alternative. The ability to transmit data through the air allows for the deployment of communication links in densely populated areas without the need for extensive infrastructure development.
Military and Defense
The secure and high-speed nature of FSO makes it an ideal choice for military and defense applications. FSO systems can be used for secure communication between military bases, providing a reliable and interference-resistant means of transmitting sensitive information.
Disaster Recovery
In scenarios where traditional communication infrastructure may be compromised, such as during natural disasters, FSO can play a crucial role in establishing temporary communication links. Its flexibility and ease of deployment make it a valuable asset for disaster recovery efforts.
Advantages of Free-Space Optical Communication
High Data Rates
One of the standout features of FSO is its ability to achieve extremely high data rates. The use of optical signals allows for data transmission at rates that rival or even surpass traditional communication methods. This makes FSO a compelling choice for applications where speed is of the essence.
Low Latency
FSO systems exhibit low latency, making them suitable for applications that require real-time communication. This is particularly important in sectors such as finance, gaming, and healthcare, where delays can have significant consequences.
Secure Communication
The nature of FSO, transmitting data through free space, provides a level of security that is inherently difficult to breach. Unlike wired communication, which can be susceptible to physical tapping, FSO offers a more secure alternative, making it attractive for applications that prioritize data security.
Ease of Deployment
Deploying FSO systems is relatively straightforward compared to laying cables or fibers. This ease of deployment is especially advantageous in situations where establishing communication links quickly is essential, such as in temporary setups or disaster-stricken areas.
Challenges in Free-Space Optical Communication
Atmospheric Interference
One of the primary challenges faced by FSO systems is atmospheric interference. Factors such as fog, rain, and snow can attenuate the optical signals, leading to signal degradation or loss. Researchers and engineers are actively working on developing techniques to mitigate these effects, such as adaptive optics and advanced error correction algorithms.
Line-of-Sight Requirements
FSO systems require an unobstructed line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. This limitation can be a hurdle in urban environments with tall buildings or in areas with geographical features that obstruct the line of sight. To address this, FSO systems may need to be strategically placed or combined with other communication technologies for a reliable connection.
Security Concerns
While FSO inherently provides a high level of security, it is not immune to certain types of attacks. For example, eavesdropping using specialized equipment to intercept the optical signals is a potential threat. Encryption techniques and secure key exchange protocols are crucial to mitigating these security concerns.
Cost
While FSO can be a cost-effective solution in certain scenarios, the initial setup costs can be relatively high. The cost of high-quality transceivers, precise alignment equipment, and other necessary components can pose a barrier to widespread adoption. However, as technology advances and economies of scale come into play, the cost of FSO systems is expected to decrease over time.
The Future of Free-Space Optical Communication
As technology continues to advance, the future of Free-Space Optical Communication looks promising. Researchers are actively addressing the challenges associated with FSO, paving the way for its integration into mainstream communication networks. Here are some potential developments and trends to watch for:
Advanced Atmospheric Compensation Techniques
Ongoing research aims to enhance FSO systems’ resilience to atmospheric interference. Advanced techniques, such as adaptive optics and intelligent algorithms for real-time compensation, show promise in mitigating the impact of weather conditions on FSO links. These developments could significantly improve the reliability of FSO in diverse environments.
Hybrid Communication Networks
To overcome the line-of-sight limitations of FSO, future communication networks may adopt hybrid approaches. Combining FSO with other technologies, such as traditional fiber optics or wireless communication, can create robust and resilient networks capable of providing high-speed connectivity in a variety of conditions.
Integration with 5G and Beyond
As the world transitions to 5G and beyond, the demand for high-speed and low-latency communication will continue to rise. FSO can complement these next-generation networks by providing additional capacity and reducing latency in specific scenarios. Integration with 5G infrastructure could unlock new possibilities for FSO in urban environments and beyond.
Interplanetary Communication
Looking even further into the future, FSO holds potential applications in interplanetary communication. The vacuum of space provides an ideal medium for optical signals to travel vast distances without the limitations imposed by Earth’s atmosphere. FSO could play a role in establishing communication links between spacecraft, space stations, and even future colonies on other celestial bodies.
Conclusion
Free-Space Optical Communication represents a fascinating frontier in the world of communication technologies. Its unique ability to transmit data through the air, coupled with high data rates and low latency, positions FSO as a compelling solution for various applications. While challenges such as atmospheric interference and line-of-sight requirements exist, ongoing research and technological advancements are addressing these issues, paving the way for a future where FSO plays a prominent role in our interconnected world.