Contents
Source: Fraunhofer Heinrich-Hertz-Institut – Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
The Advancements in Free-Space Optical Communications
Introduction
In the realm of optical communications, the utilization of free space for transmitting data is gaining traction. While fiber optics are commonly used for Earth-based data transmission, free-space optical communication offers an alternative method without the need for waveguide structures. This technology has historical roots dating back to the 1870s and is now being increasingly employed both on Earth and in space applications.
Transmission Challenges
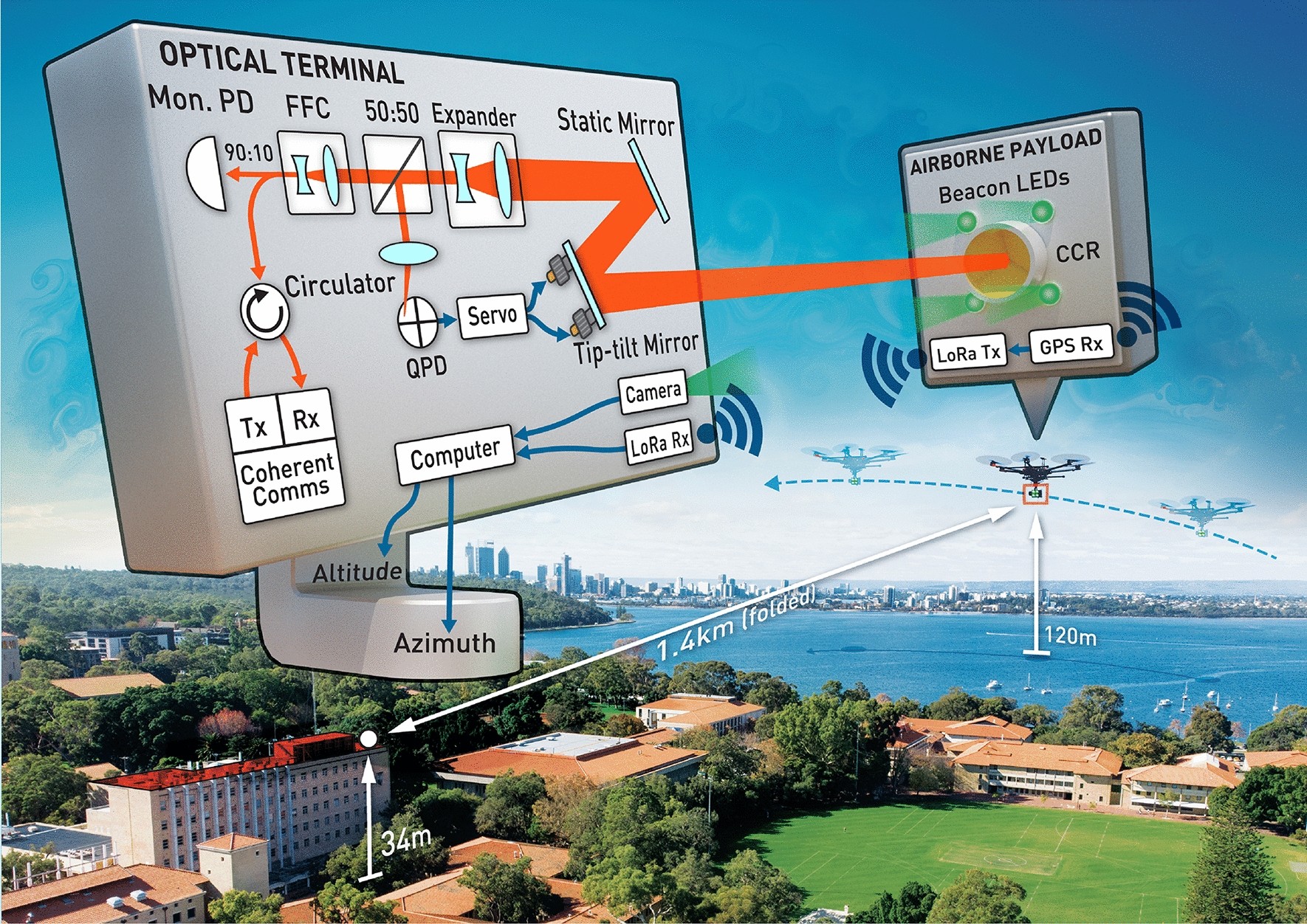
Free-space optical communication relies on unobstructed line of sight between sender and receiver, often necessitating specialized optics like telescopes. Laser sources are predominantly used due to their high directionality, crucial for efficient communication. Collimating the laser beam with minimal divergence is essential for long-distance transmission to limit power loss.
Optimizing Reception
On the receiver end, high sensitivity and directionality are key for maximizing power reception and minimizing interference. Large telescopes are commonly used to achieve these requirements, although precise alignment between transmitter and receiver is crucial. Atmospheric disturbances can pose challenges, but advanced signal processing techniques and adaptive optics can mitigate their effects.
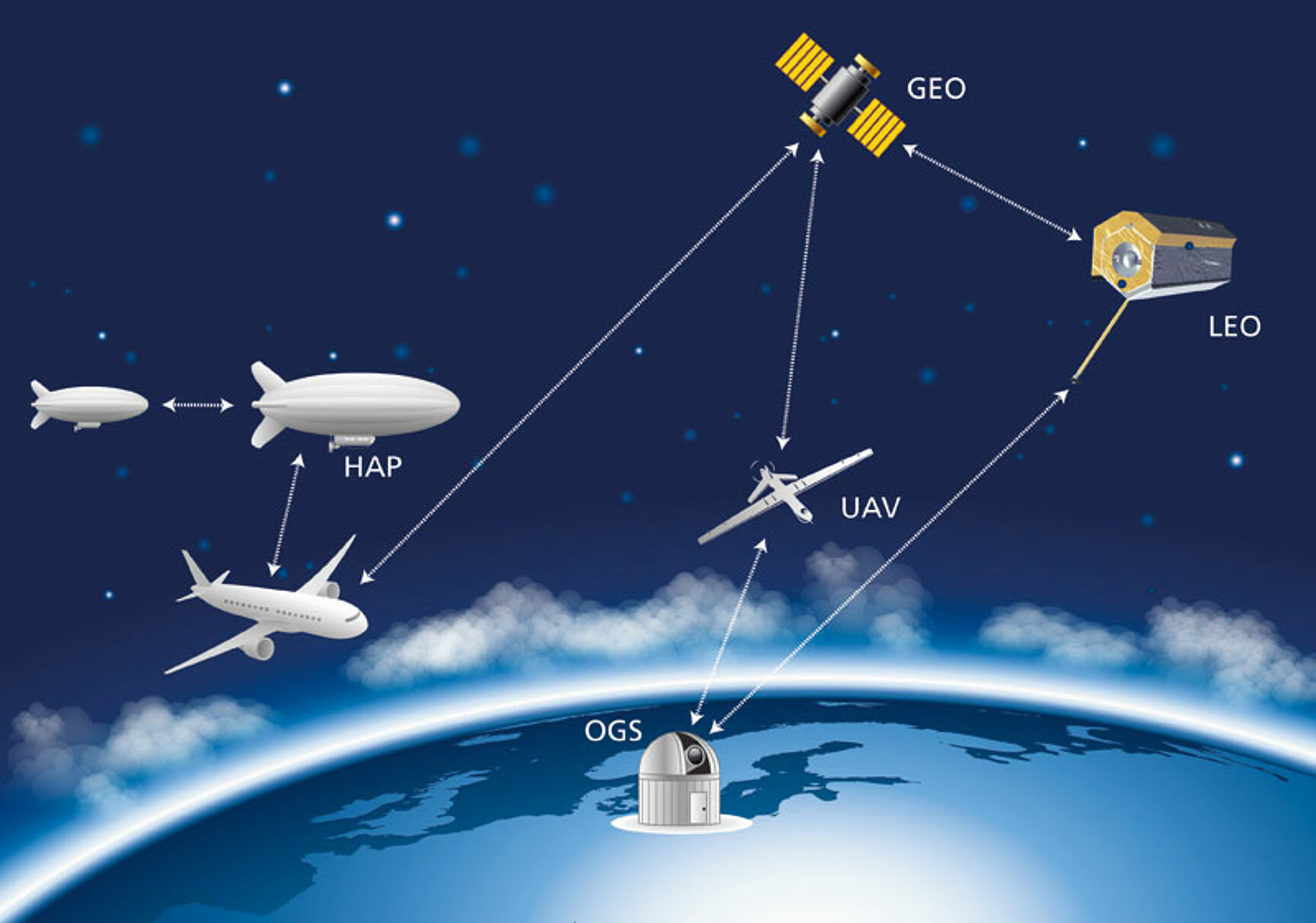
Space Applications
In space scenarios, optical communication plays a vital role in transmitting large data volumes between satellites or from distant spacecraft to Earth stations. Optical links offer higher data rates and lower power requirements compared to traditional radio links, making them ideal for interplanetary communication. However, they are more sensitive to weather conditions.
Urban Applications
Free-space optical links are also valuable for establishing data connections between buildings in urban areas. These links offer a cost-effective and easy-to-install alternative to cables, especially over short to moderate distances. While weather and obstructions can impact signal quality, optical links provide high data security and transmission capacity.
Advantages Over Radio Frequency
Laser data links offer high data rates, low power consumption, compact size, and reduced signal interception risks compared to radio frequency links. They do not require government frequency allocation and are less prone to mutual interference. Additionally, they provide enhanced data security and reliability, making them a promising choice for various communication needs.
Conclusion
Free-space optical communications present a compelling solution for diverse applications, ranging from inter-satellite transmissions to urban data links. With ongoing advancements in technology and signal processing, the future of optical communication in free space looks promising for achieving high-speed, secure, and reliable data transmission.
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



