Contents
Source: Goseeko
The Fascinating World of Fresnel Equations
Understanding the Basics
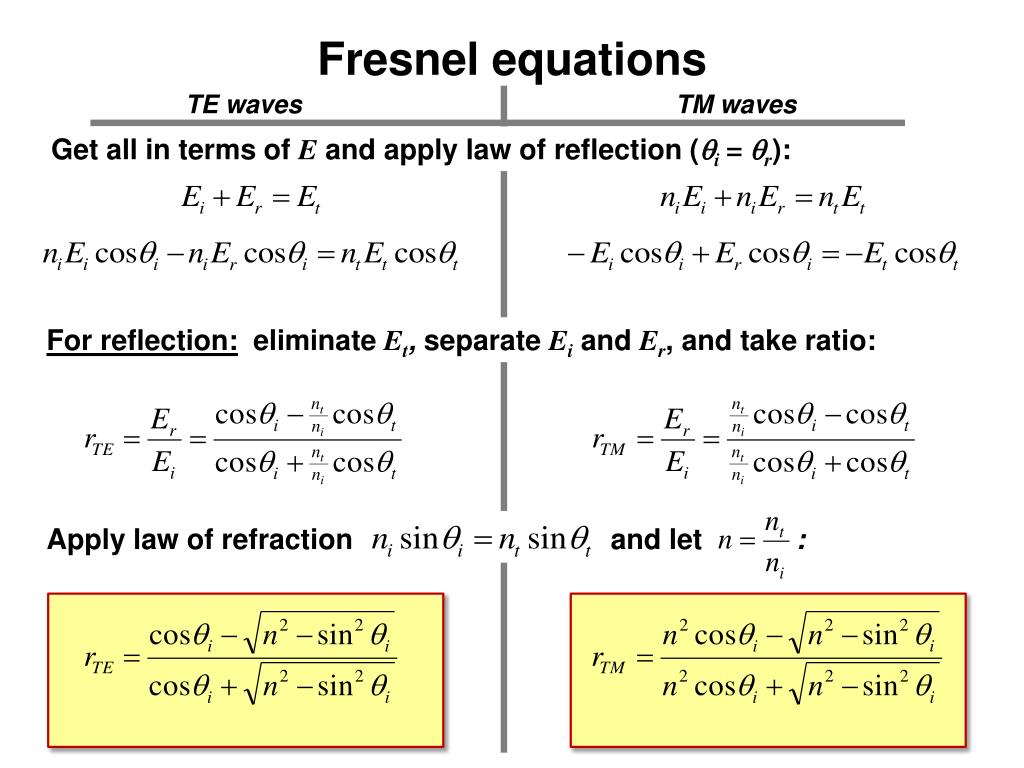
Fresnel equations play a vital role in determining the amplitude coefficients for transmission and reflection at the interface between two transparent media. These equations are defined for two different polarization directions: s polarization and p polarization. In s polarization, the electric field vector is perpendicular to the plane of incidence, while in p polarization, the electric field vector lies in the plane of incidence.
Key Equations
The amplitude transmission coefficients for s and p polarizations are determined by the refractive indices of the two media and the corresponding propagation angles. The power reflection coefficients can be obtained by squaring the amplitude coefficients. To calculate transmissivity, a correction factor is required to consider the different propagation angles.
Application to Absorbing Media
Fresnel equations can also be applied to absorbing media, such as metals, by using complex refractive indices. In this case, the reflection and transmission coefficients are no longer real numbers. Calculating power transmission for absorbing media with non-normal incidence poses challenges due to the varying optical intensity along wavefronts.
Surface Quality Considerations
In practical applications, surface irregularities can impact the accuracy of Fresnel equations in describing interface optical properties. Even minor surface imperfections can cause significant wavefront distortions. However, meticulous surface preparation techniques can ensure high optical quality, particularly with methods like optical contact bonding.
Exploring Further
While Fresnel equations provide valuable insights into light behavior at interfaces, there are still more nuances to discover in the realm of optics. Continuous exploration and experimentation can lead to a deeper understanding of optical phenomena and their practical applications.

Source: YouTube
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



