Contents
Source: Edmund Optics
Understanding Hyperspectral Imaging: Techniques and Applications
Introduction to Hyperspectral Imaging
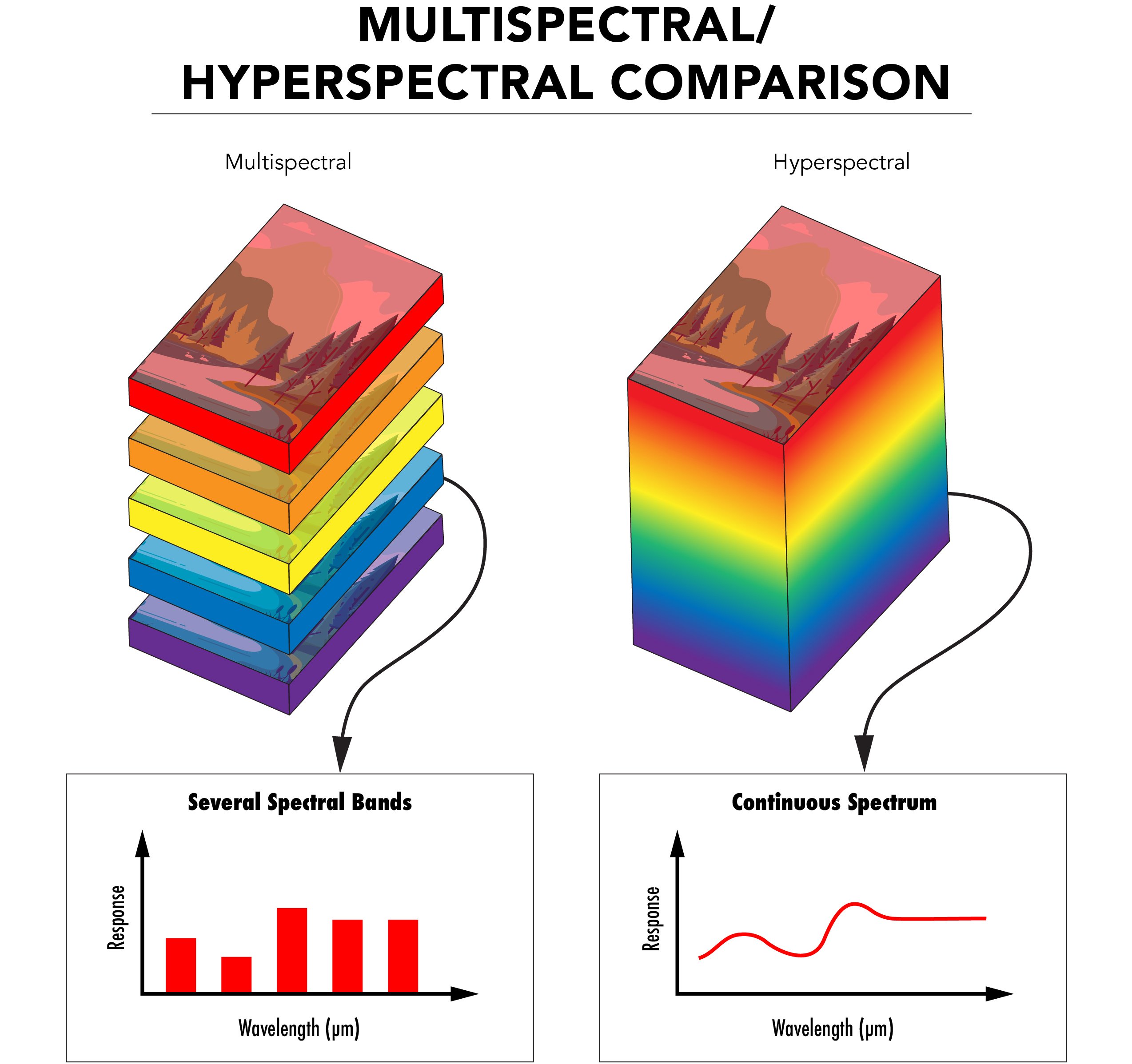
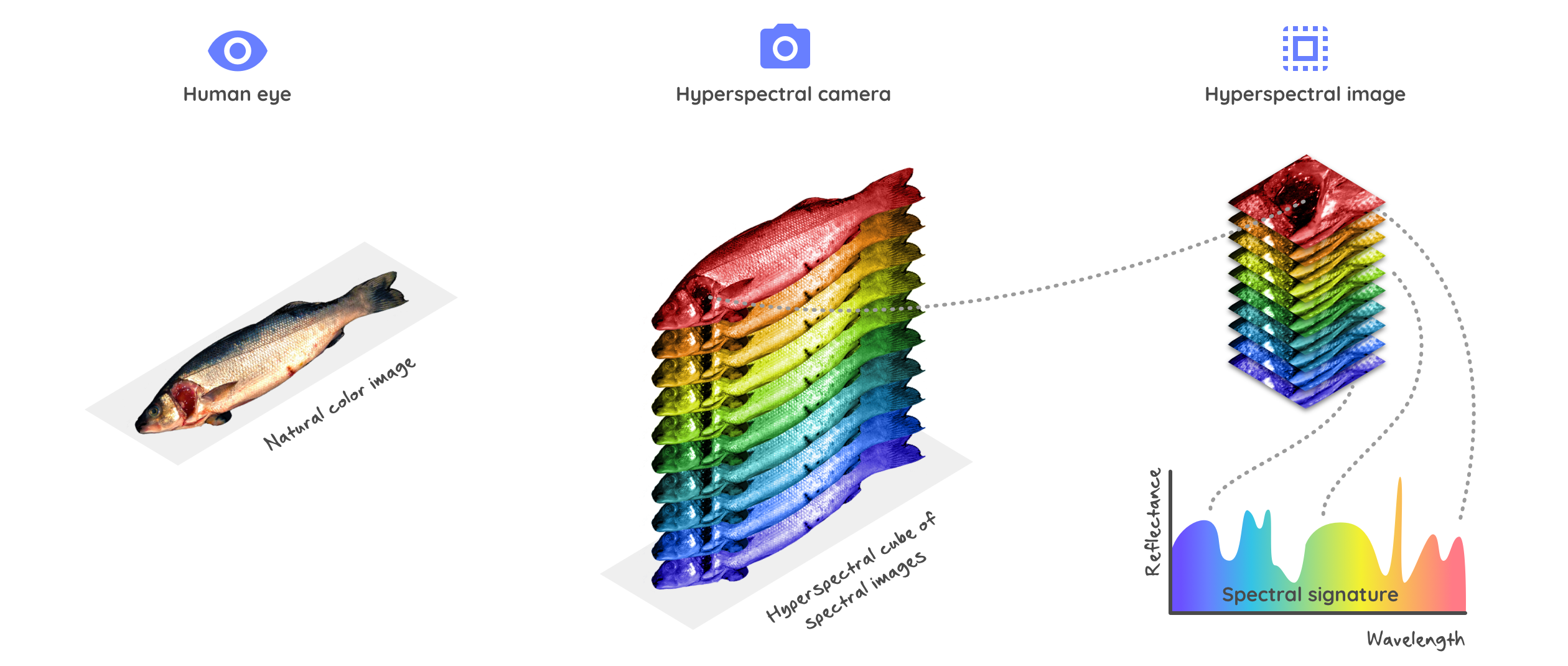
Hyperspectral imaging is an advanced imaging technique that captures a full optical spectrum for each pixel in an image. Unlike multispectral imaging, which uses a limited number of broad wavelength bands, hyperspectral imaging employs hundreds or thousands of narrow, contiguous wavelength channels. This results in a three-dimensional dataset known as a hyperspectral cube, which provides detailed spectral information across a wide range of wavelengths.
Principles of Hyperspectral Imaging
Point Scanning
Point scanning involves using a spectrometer with a two-dimensional scanning device. At any given time, the system captures light from a specific direction and records its optical spectrum. While this method can utilize conventional spectrometers, it is generally inefficient and prone to motion artifacts due to its slow acquisition time.
Line Scanning
Line scanning, or push broom scanning, is the most common technique for acquiring hyperspectral images. It captures data for one line at a time using an optical slit and a diffraction grating. This method is faster and reduces motion artifacts compared to point scanning. However, it only uses light from one line at a time, limiting its efficiency.
Spectral Scanning
Spectral scanning integrates a tunable optical bandpass filter into a camera, capturing images one wavelength slot at a time. While it allows for the use of conventional imaging equipment, its light efficiency is limited as only a small spectral slot is utilized at any given time.
Spatiospectral Scanning
This technique combines aspects of both spatial and spectral scanning, capturing a diagonal slice of the hyperspectral cube with each recording. It requires scanning in one dimension to complete the data acquisition.
Snapshot Imaging
Snapshot imaging is particularly useful in astronomy, where efficient light use is critical. It avoids spatial or spectral scanning by capturing the entire hyperspectral cube in a single snapshot. Although this method requires complex and costly setups, it provides comprehensive data efficiently.
Data Processing and Display
Hyperspectral imaging generates vast amounts of data, often requiring advanced processing techniques for analysis. Monochrome images for various wavelength channels can be displayed, or false color scales can be applied to highlight specific spectral information. Automatic processing is frequently employed to extract valuable insights from the data.
Applications of Hyperspectral Imaging
Earth Monitoring
Hyperspectral imaging from satellites is extensively used for environmental monitoring, geological surveys, and military surveillance. It can detect vegetation health, minerals, and man-made structures with high precision.
Agricultural Quality Control
In agriculture, hyperspectral imaging helps identify defective products or foreign materials, such as spoiled nuts or stones. Automated systems use this technology for efficient sorting and quality control.
Astronomy
In astronomy, hyperspectral imaging is known as 3D spectroscopy or integral field spectroscopy. It provides detailed spectral data essential for classifying celestial bodies and studying cosmic phenomena.
Art Conservation
Hyperspectral imaging aids in art conservation by revealing the materials used in ancient artworks. This information is crucial for restoration and preservation efforts.
Biological and Chemical Analysis
The high spectral resolution of hyperspectral imaging allows for detailed analysis of biological specimens and chemical compositions, making it a valuable tool in medical diagnostics and research.
Conclusion
Hyperspectral imaging is a powerful tool that provides detailed spectral information across a wide range of applications. Its ability to capture precise data makes it invaluable in fields such as environmental monitoring, agriculture, astronomy, and art conservation. As technology advances, hyperspectral imaging will continue to evolve, offering even more innovative solutions to complex challenges.
Source: Condi food
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



