Contents
Source: YouTube
Understanding Intermodal Dispersion in Fiber Optics
Introduction to Intermodal Dispersion
Intermodal dispersion, also known as modal dispersion, is a critical phenomenon in the realm of fiber optics. It occurs when light travels through a multimode fiber or waveguide, and the group velocity is influenced not only by the optical frequency but also by the modes of propagation.
How Intermodal Dispersion Affects Fiber Optics
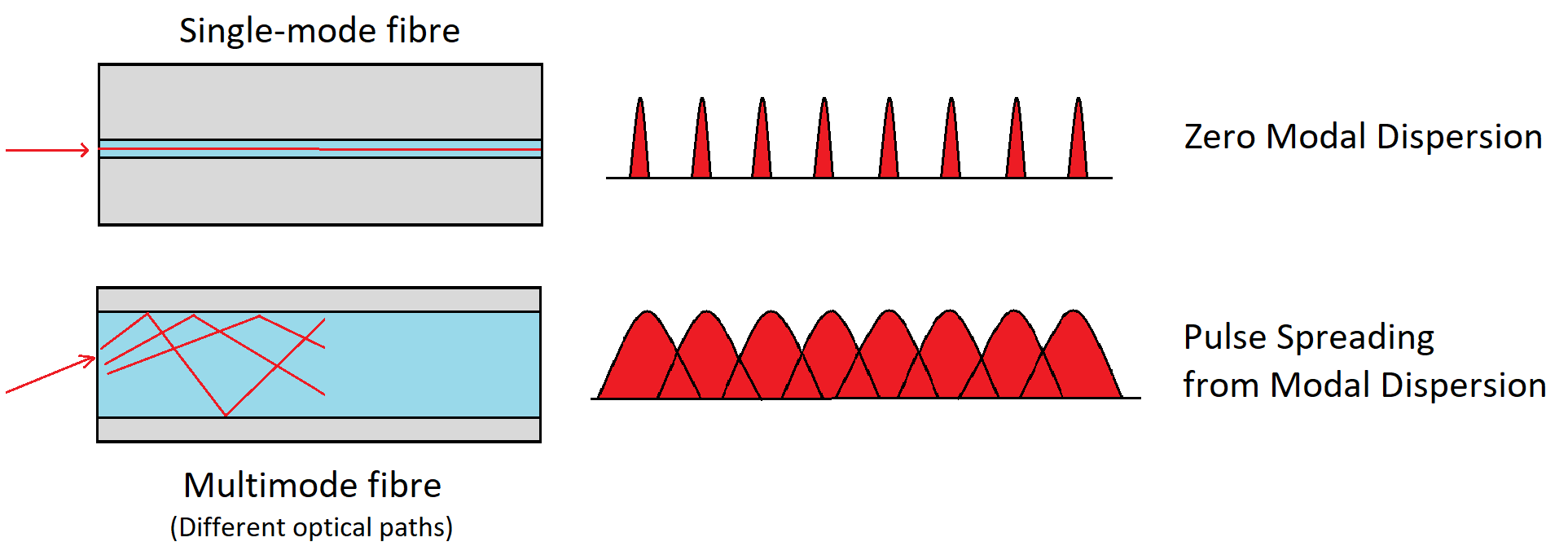
In a multimode fiber, multiple modes can propagate simultaneously. Each mode travels at a different speed due to varying group velocities. This results in different arrival times for each mode at the output, leading to pulse broadening. The fundamental mode, being the fastest, reaches the output first.

Quantifying Intermodal Dispersion: Differential Mode Delay
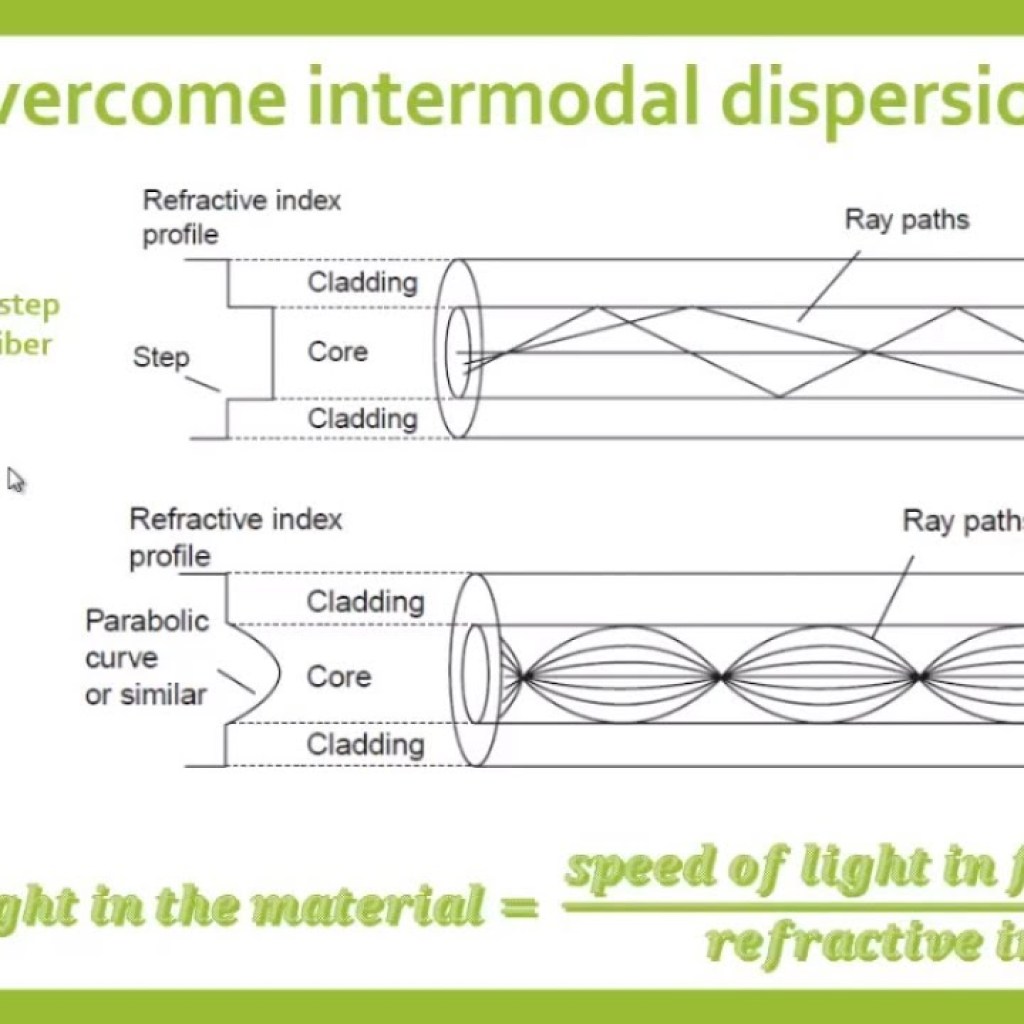
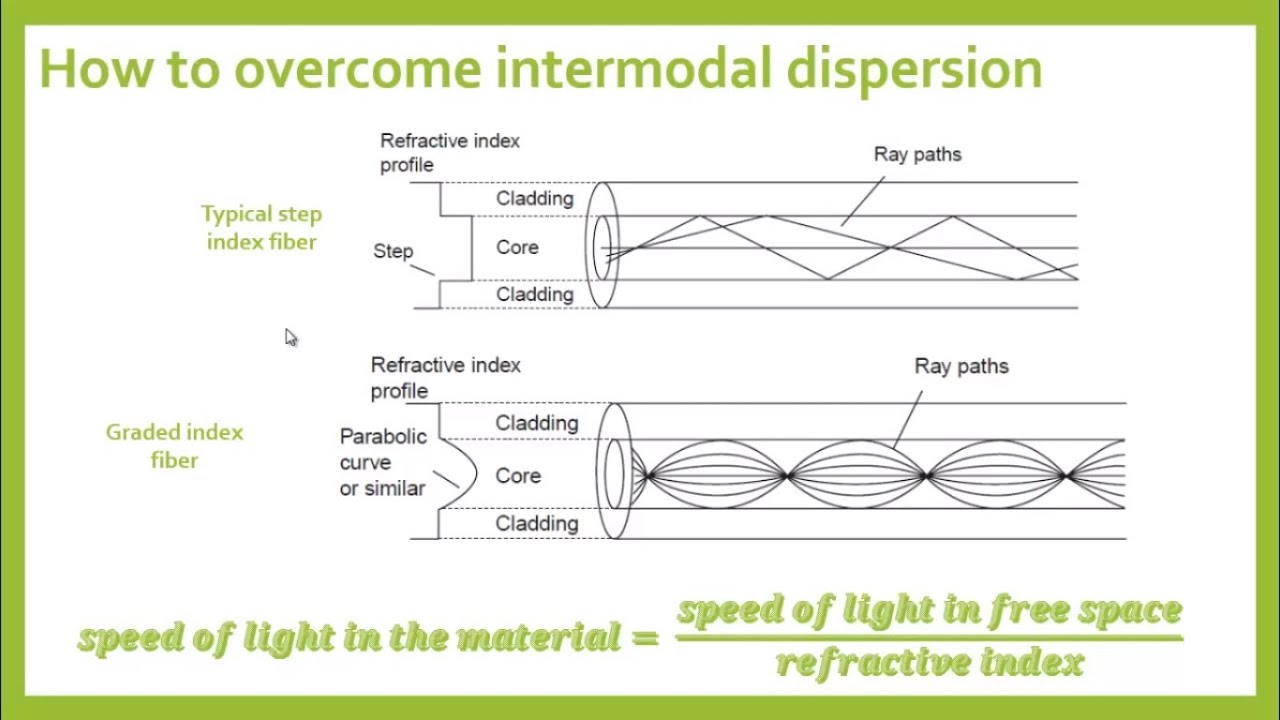
The strength of intermodal dispersion is measured by the differential mode delay (DMD). This delay is highly dependent on the refractive index profile of the fiber core. For instance, in a step-index fiber, higher-order modes exhibit lower group velocities, leading to significant differential group delays. This can be as much as 10 picoseconds per meter, or 10 nanoseconds per kilometer, which severely limits the data transmission rate in optical fiber communication systems.
Impact on Data Transmission
In optical fiber communication systems utilizing multimode fibers, intermodal dispersion can significantly constrain the data transmission rate. To prevent signal distortion, it is crucial to maintain pulse lengths that allow for adequate temporal overlap of different mode components. This requirement inevitably restricts the achievable data rate.
Solutions to Intermodal Dispersion
The most straightforward solution to eliminate intermodal dispersion is to employ single-mode fibers. With only one propagation mode, there are no differences in propagation times. Alternatively, using multimode fibers with a parabolic refractive index profile can also minimize intermodal dispersion.
Conclusion
Intermodal dispersion is a significant factor to consider in the design and implementation of fiber optic systems. Understanding its principles and effects is crucial for optimizing data transmission rates and ensuring efficient communication. By selecting the appropriate fiber type and configuration, the challenges posed by intermodal dispersion can be effectively managed.
Source: Modular Photonics
Feel free to comment your thoughts.