Contents
Source: Technische Universität München
Understanding Optical Breakdown and Its Applications
Optical breakdown is a fascinating phenomenon that occurs when a material becomes electrically conductive due to the influence of intense electromagnetic fields. This process is particularly relevant in fields such as laser machining and spectroscopy.
What is Optical Breakdown?
Optical breakdown refers to the process where an insulating medium, such as air or glass, becomes conductive when subjected to a high-intensity electromagnetic field. This can occur when free electrons in the medium gain sufficient energy from the field to cause ionization, leading to a cascade of further ionizations in a process known as avalanche ionization. The result is the formation of a plasma, which has significant electrical conductivity.
Mechanism of Optical Breakdown
The mechanism behind optical breakdown is rooted in the acceleration of free electrons by the electromagnetic field. When these electrons collide with atoms or molecules, they can release additional electrons, creating a chain reaction. The process is highly dependent on the intensity and duration of the light pulses involved. For instance, femtosecond laser pulses can efficiently generate free carriers through multiphoton ionization, followed by strong absorption and further ionization.
Applications in Laser Machining
Optical breakdown can be both a challenge and a tool in laser machining. On one hand, it can degrade the quality of machining by defocusing the laser beam and causing energy loss before reaching the target. On the other hand, it can be harnessed to modify material properties in a controlled manner.
Laser Machining Techniques
In laser machining, particularly with transparent materials like glass or polymers, optical breakdown can be used to create small structures by altering the refractive index or transparency. Ultrafast laser pulses can be focused to induce breakdown only at the desired location, allowing for precise modifications. This technique is valuable in the fabrication of photonic integrated circuits and other microstructures.
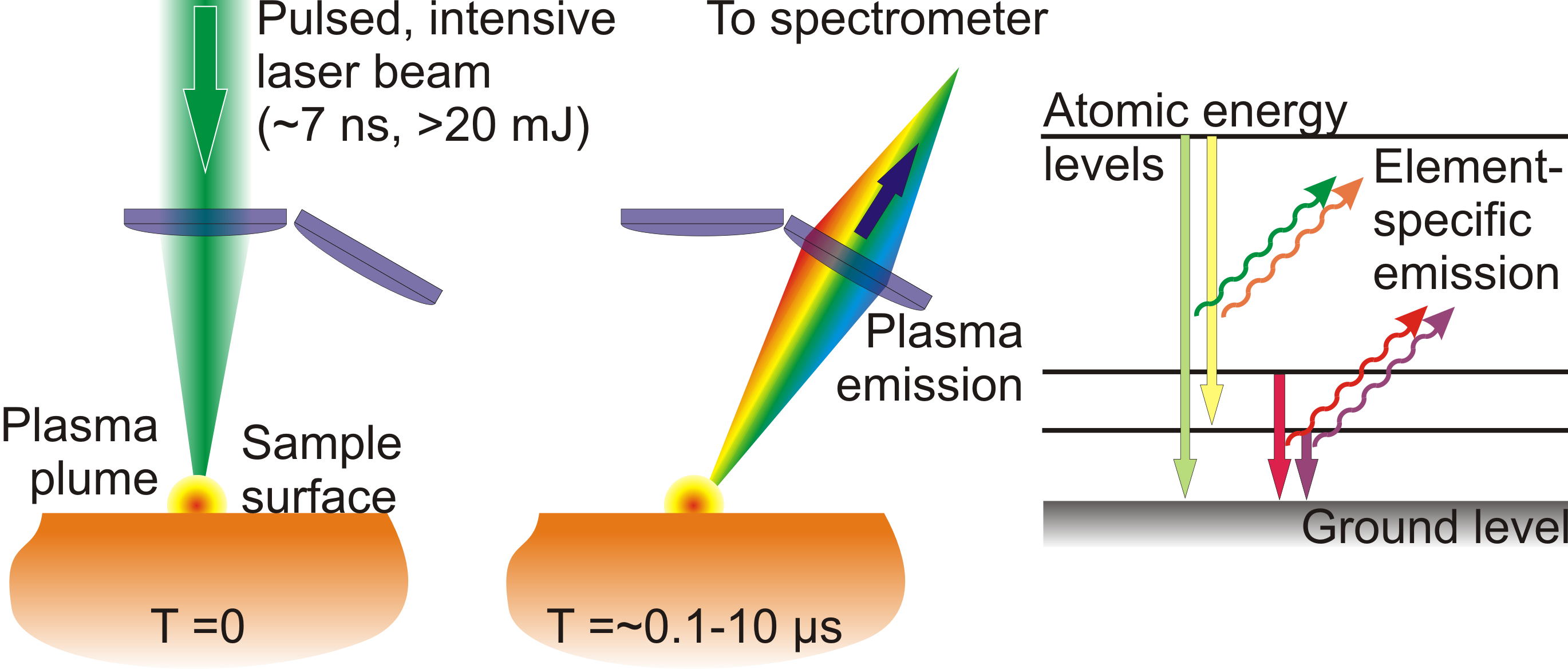
Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is a powerful analytical technique that utilizes the plasma generated by a laser pulse to determine the elemental composition of a sample. By analyzing the light emitted from the plasma, researchers can identify the chemical elements present. This method is particularly useful in remote sensing applications, such as the exploration of planetary surfaces.
Applications of LIBS
LIBS is being developed for various applications, including geological studies on Mars. The technique allows for rapid, in-situ analysis of rock compositions from a distance, making it ideal for use on robotic exploration vehicles.
Conclusion
Optical breakdown is a crucial concept in modern photonics, with significant applications in both industrial and scientific fields. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and potential applications of this phenomenon can lead to advancements in material processing, spectroscopy, and beyond.

Source: LTB Lasertechnik Berlin
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



