Contents

Source: Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
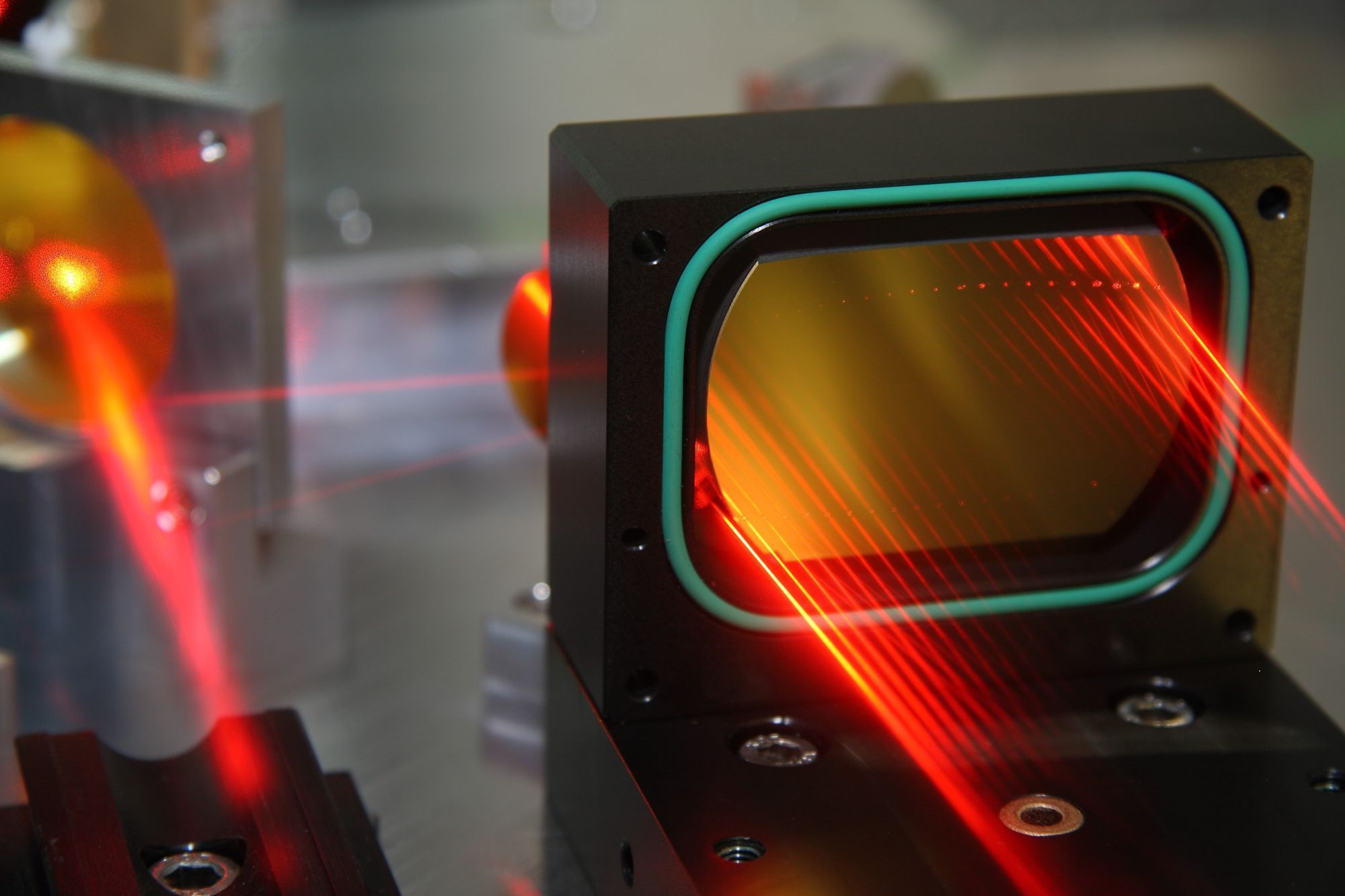
Laser Spectroscopy: Exploring the Interaction of Light with Matter
Understanding Spectroscopy and Laser Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy involves studying the interaction of light with matter. Laser spectroscopy specifically utilizes lasers as light sources for this purpose, allowing for precise measurements and analysis.
Properties of Lasers in Spectroscopy
Lasers offer significant advantages for spectroscopy due to their coherence, narrow linewidths, and high intensity. These properties enable various techniques and applications in laser spectroscopy.
Methods of Laser Spectroscopy
- Laser Absorption Spectroscopy: Involves measuring light absorption in a sample as a tunable laser is scanned across different wavelengths.
- Frequency Comb Spectroscopy: Utilizes frequency combs generated by mode-locked lasers for precise frequency measurements.
- Raman Spectroscopy: Exploits Raman scattering to analyze vibrational and rotational modes in a sample.
- Photoacoustic Spectroscopy: Detects sound waves generated by laser-induced absorption in a sample.
- Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy: Uses ultrafast laser pulses for time-resolved measurements and analysis.
- Laser-induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: Vaporizes materials using intense laser pulses for elemental analysis.
Laser Sources for Spectroscopy
Various types of lasers, including continuous-wave and mode-locked lasers, are employed in laser spectroscopy based on specific requirements of the applications. Laser noise and stability are crucial considerations for precision spectroscopy.
Applications of Laser Spectroscopy
- Detecting trace gases in the atmosphere
- Monitoring pollutants in water
- Medical substance concentration measurements
- Artwork analysis for authenticity
- Industrial process monitoring and quality control
- Temperature measurements based on level populations
Conclusion
Laser spectroscopy plays a vital role in various fields, offering precise and rapid methods for material analysis and characterization. Its applications range from environmental monitoring to industrial processes and beyond, showcasing the versatility and importance of laser-based spectroscopic techniques.
Source: Larissa
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



