Contents
Source: Wikipedia
Microlenses: Small Optics with Big Applications
Operation Principles of Microlenses
Microlenses are optical lenses with diameters below 1 mm, often much smaller. They can work as refractive lenses, utilizing a radially varying thickness to achieve the desired optical phase change. Some microlenses employ diffractive optics, where diffraction is directly utilized as the operation principle. Gradient-index lenses (GRIN lenses) are another type of microlenses, consisting of layers with varying refractive indices.
Fabrication of Microlenses
Various techniques are used to fabricate microlenses, including injection molding, embossing, printing methods, photolithography, and lithography using lasers or diamond micro-drilling. These techniques allow for the production of high-quality microlenses, some even with aspheric shapes.
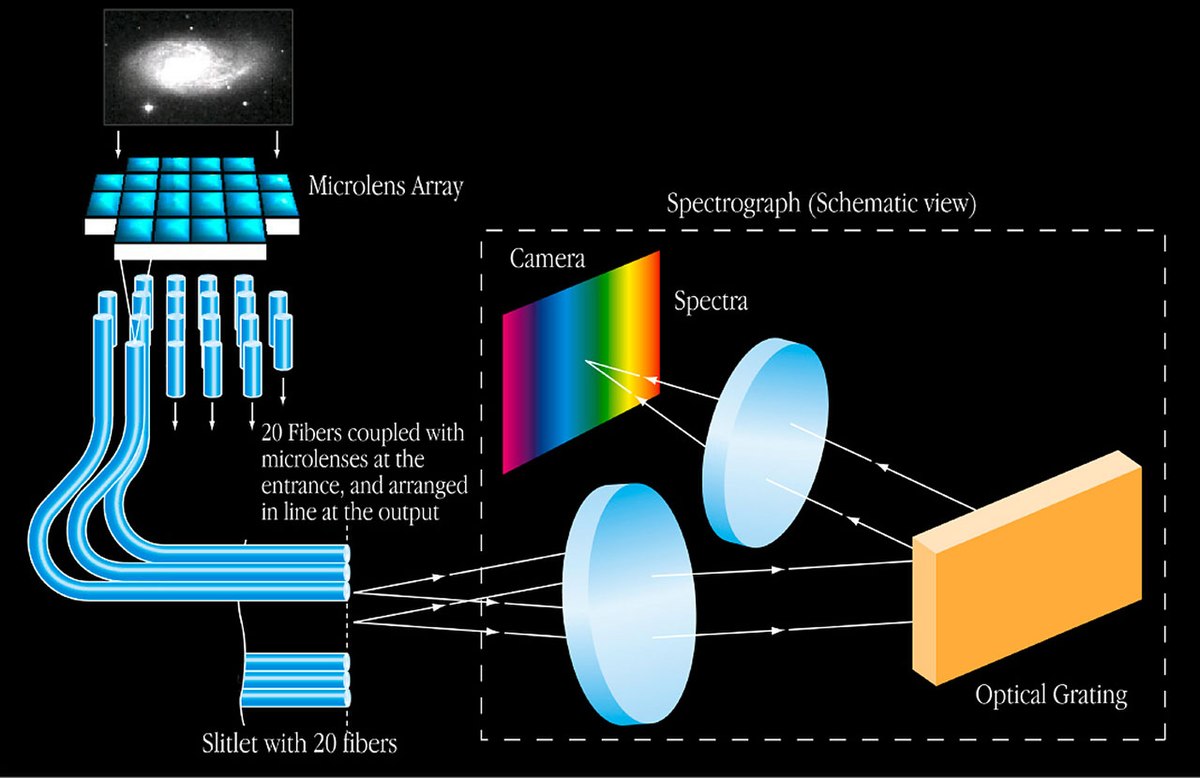
Microlens Arrays
Microlens arrays consist of multiple microlenses on a common substrate. They can be one- or two-dimensional, with applications in fiber collimation, laser diode collimation, integrated optics, imaging devices, and wavefront sensors, among others.
Applications of Microlenses
Microlenses find applications in various fields, including fiber optics, integrated optics, imaging devices, beam homogenizers, wavefront sensing, interferometry, and even in the compound eyes of insects and other animals.
Conclusion
Microlenses are versatile optical components with a wide range of applications, from telecommunications to biotechnology. Their small size and precise fabrication make them essential in modern optical systems, enabling advancements in various industries.

Source: 3D AG
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



