Contents
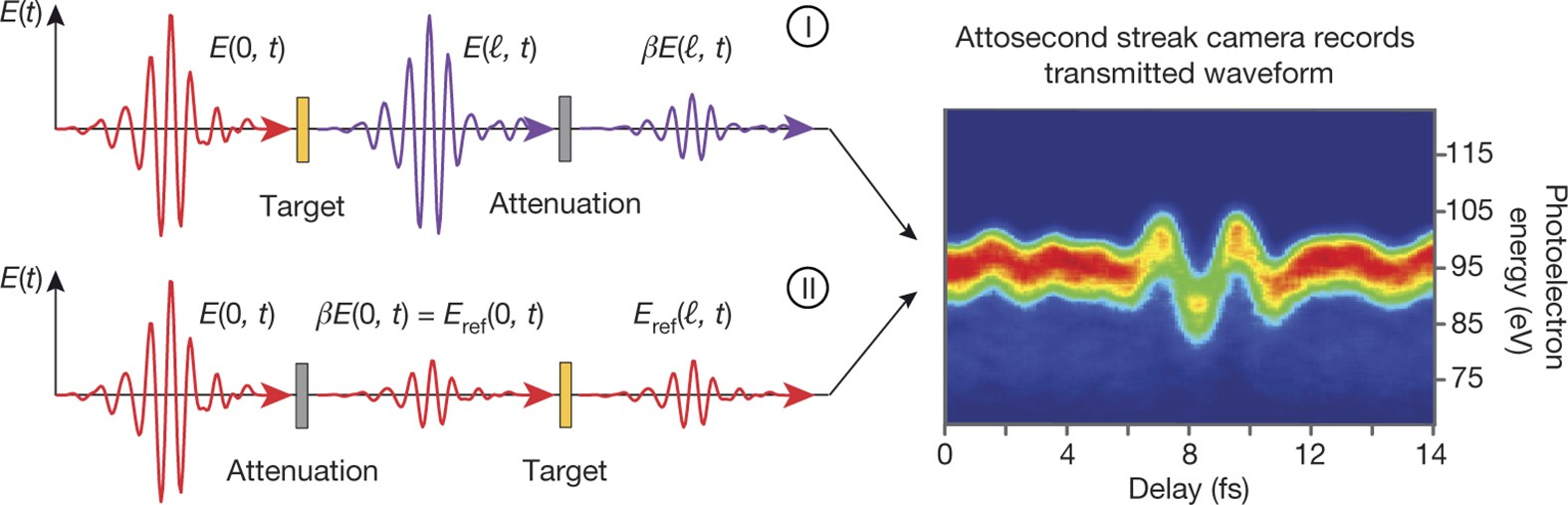
Source: Nature
Understanding Nonlinear Polarization in Optics
When light travels through a transparent medium, its electric field induces electric polarization in the medium, leading to the formation of a polarization wave. This polarization wave propagates alongside the electromagnetic field with the same phase velocity as the driving field.
Second-order Nonlinear Polarization
Nonlinear polarization can occur in crystal materials with a non-centrosymmetric structure. The second order of nonlinear polarization arises from a nonlinearity that depends quadratically on the electric field of the incident light wave. This nonlinear polarization wave can lead to processes like nonlinear frequency conversion.
Mathematical Representation
The nonlinear polarization can be mathematically represented by a tensor equation that considers the nonlinear susceptibility and the optical electric field. The direction of the nonlinear polarization may differ from the input light’s polarization direction.
Third-order Nonlinear Polarization
Higher-order nonlinear polarization can arise in various media and give rise to phenomena such as phase matching. Phase matching is crucial for efficient accumulation of nonlinear mixing products over a greater length of crystal, ensuring strong nonlinear effects.
Phase Matching in Nonlinear Optics
Phase matching is essential for maximizing the efficiency of nonlinear processes in optics. It ensures that the field amplitudes generated at different locations in the crystal do not cancel each other out, leading to significant nonlinear effects.
Understanding nonlinear polarization in optics is crucial for various applications, including frequency conversion, amplification, and oscillation processes in laser systems.
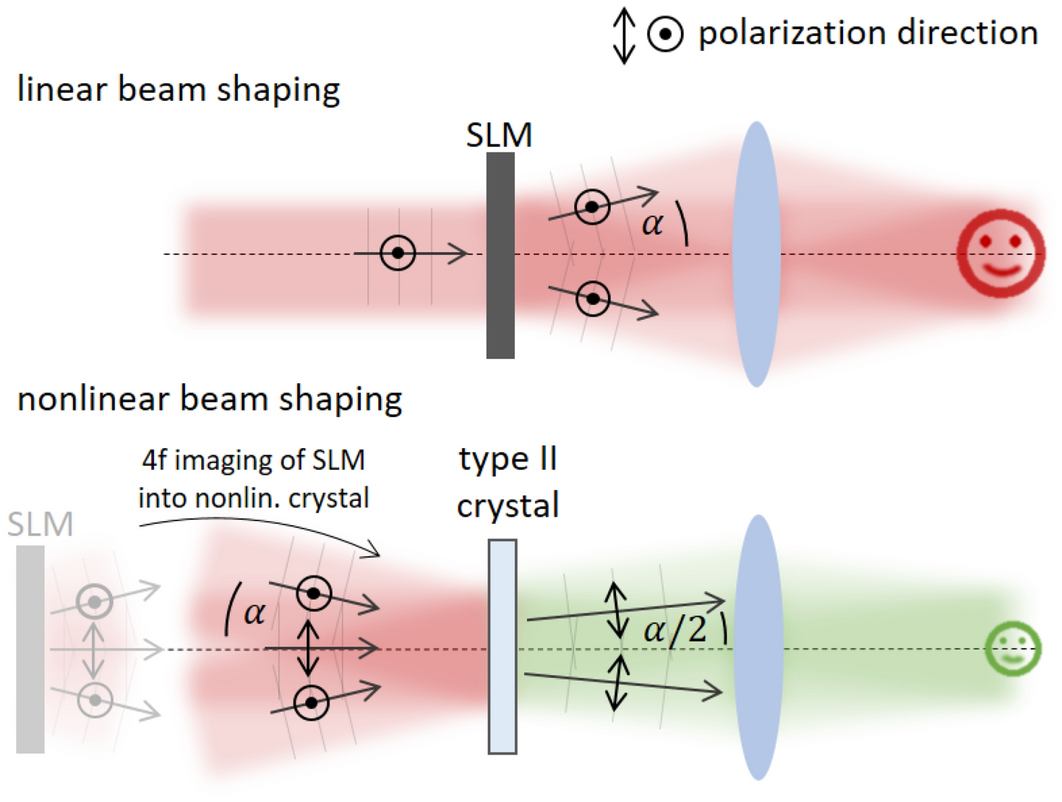
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



