Contents
Source: LightTrans
Understanding Optical Apertures
Introduction to Optical Apertures
Optical apertures are structures that limit the propagation of light in various optical systems. They can be found in photographic objectives, telescopes, light sources, and other optical instruments. These apertures control the entry and exit of light, affecting the performance of the optical system.
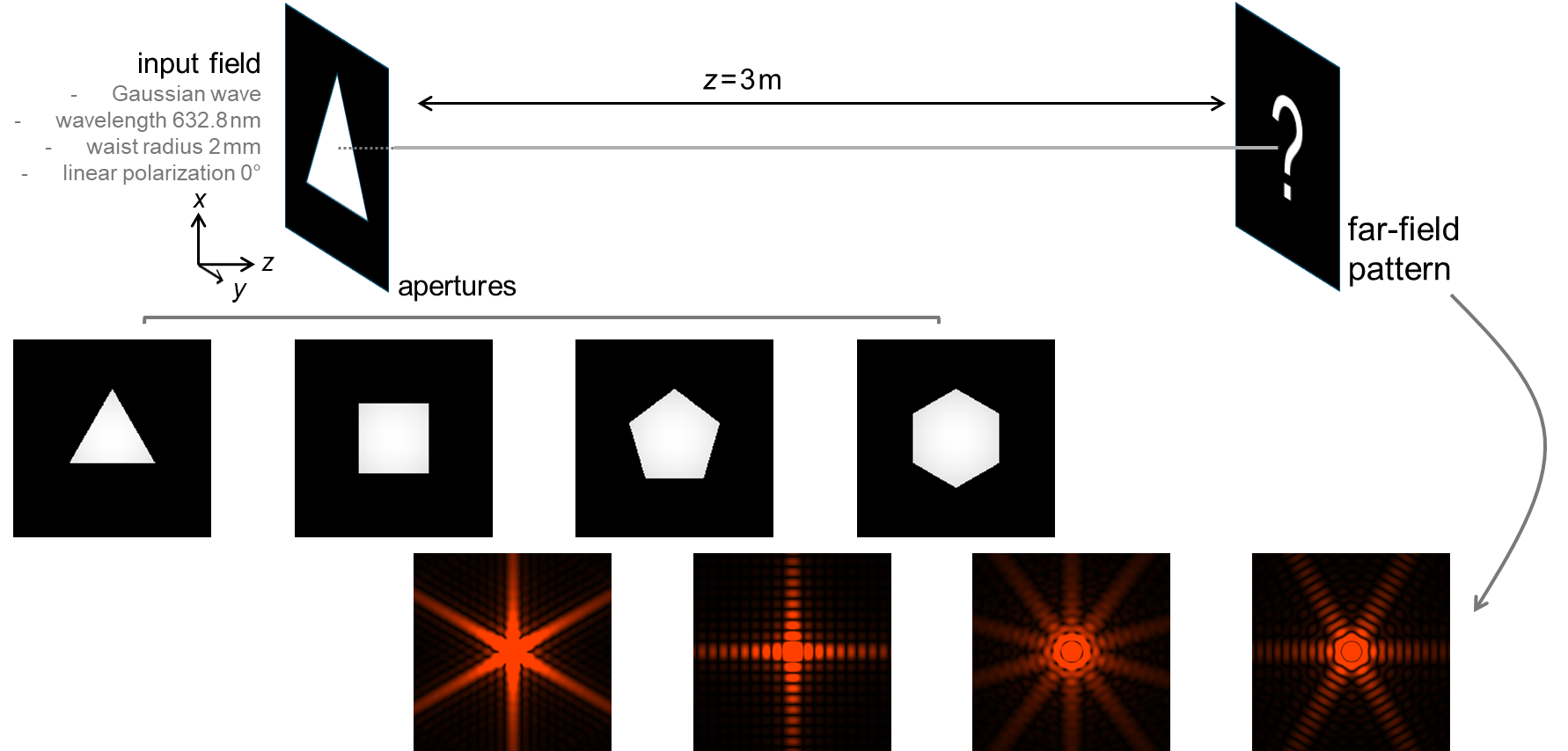
Types and Effects of Optical Apertures
Optical apertures come in different forms, such as diaphragms, pinholes, and slits, each with a specific geometric shape. These apertures can either enhance or degrade the image quality in optical instruments, depending on their design and placement within the system.
Applications of Optical Apertures
Apertures play a crucial role in various optical instruments. They are used in producing light with increased spatial coherence, filtering specific wavelengths in monochromators, and controlling the light transmission in photographic objectives. Apertures are also utilized in laser technologies for mode locking and beam shaping.
Aperture Sizes and Types
The size of an aperture is often specified by its diameter or f-number. Apertures can be categorized as hard or soft, with hard apertures being fully transmissive or blocking light, while soft apertures exhibit a gradual variation in transmissivity. Soft apertures, like Gaussian apertures, help mitigate diffraction effects.
Aperture Limitations in Optical Devices
In optical devices like telescopes and lasers, aperture sizes are critical for achieving high-resolution imaging and efficient laser operation. Large aperture sizes are necessary for devices operating at higher power levels to manage thermal effects, maintain beam quality, and limit nonlinearities caused by high optical intensities.
Conclusion
Understanding optical apertures is essential for optimizing the performance of optical instruments and devices. By controlling the entry and exit of light, apertures contribute to image quality, beam shaping, and overall efficiency in various optical applications.
Source: Knight Optical
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



