Contents

Source: Wikipedia
<>
Optical Isolators: Enhancing Light Control
Introduction
Optical isolators, also known as optical diodes, are crucial devices that allow light to pass in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They are essential components in various optical systems to prevent unwanted reflections and maintain signal integrity.
Essential Characteristics
Key features of optical isolators include insertion loss, degree of isolation, return loss, operation wavelength, requirements on input polarization, and maximum optical power transmission. These characteristics determine the effectiveness of an isolator in a specific optical setup.
Types of Optical Isolators
Faraday Isolators
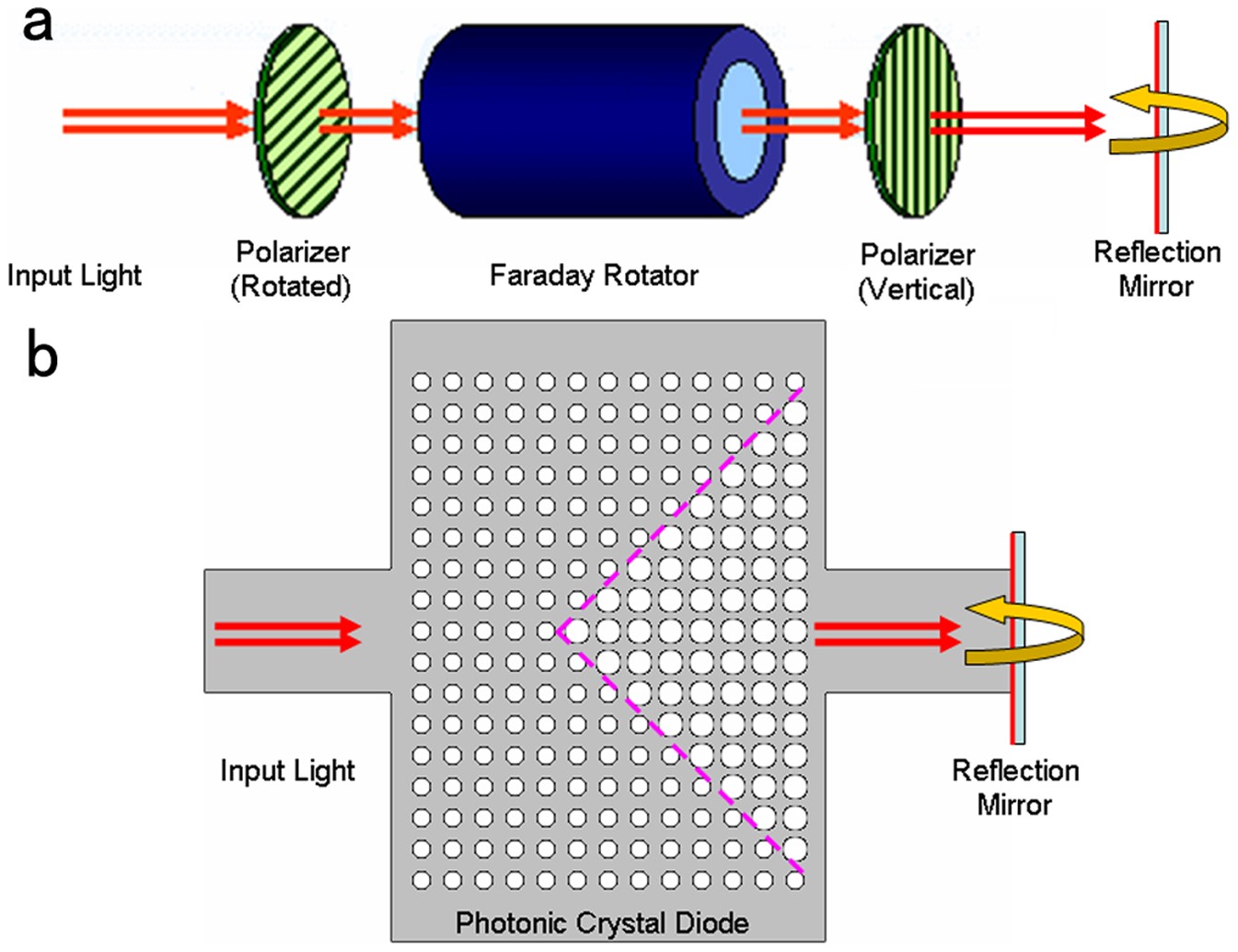
The most common type of optical isolators are Faraday isolators, which utilize the Faraday effect to achieve non-reciprocal light transmission. These isolators offer high optical isolation, low insertion loss, and can operate over a wide range of wavelengths.
Isolators Based on Waveplates
Another type of optical isolator uses waveplates instead of Faraday rotators. While these isolators can be more compact, they may have limitations related to sensitivity to polarization changes in reflected light.
Optical Isolators Based on Acoustic Effects
Emerging technologies are exploring optical isolators based on acoustic effects, offering a magnetic-field-free alternative for non-reciprocal light propagation. These isolators can be compact and suitable for integration into photonic chips, although they may have limitations in terms of optical bandwidth and power requirements.
Conclusion
Optical isolators play a critical role in controlling the flow of light in optical systems, ensuring efficient and reliable operation. Understanding the different types and operating principles of optical isolators is essential for designing and optimizing optical setups for various applications.
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



