Contents
Source: MDPI
<>
Optical Parametric Generators: A Detailed Overview
Introduction
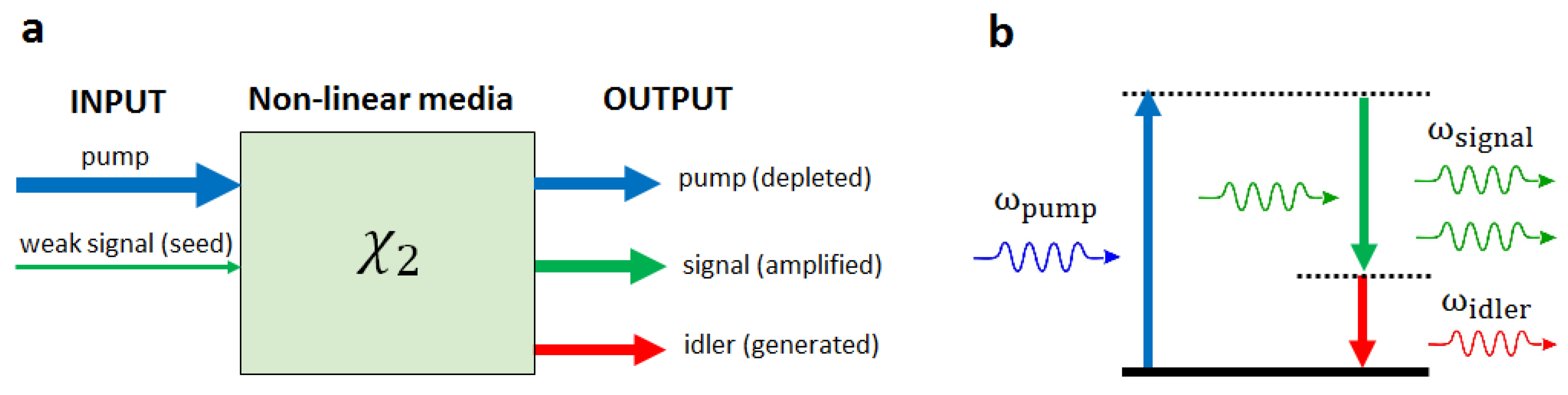
An optical parametric generator (OPG) is an optical device that generates high-power output without the need for an input signal. It operates based on the principle of parametric fluorescence, where quantum fluctuations are amplified to produce significant power levels.
Working Principle
OPGs require intense laser pulses for pumping to achieve high gain. They can utilize nanosecond, picosecond, or femtosecond pulses from lasers to initiate the parametric generation process. The gain in OPGs builds up and decays rapidly with the pump pulse.
Key Differences
Compared to optical parametric oscillators, OPGs are simpler in design as they do not require a resonator. The tuning of signal and idler wavelengths is achieved by adjusting phase-matching conditions, such as crystal temperature or rotation. While OPGs offer less control over pulse properties than some other devices, they can operate at high optical intensities near the material’s damage threshold.
Enhancements and Applications
Lowering the threshold and reducing linewidth can be achieved by injecting signal light into the OPG, effectively turning it into a parametric amplifier. These devices find applications in various fields requiring high-power optical outputs.
Conclusion
Optical parametric generators play a crucial role in generating high-power optical outputs without the need for an input signal. Their simple design and ability to operate at high intensities make them valuable tools in photonics research and applications.

Source: Gamdan Optics
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



