Contents
Source: Wikipedia
<>
Understanding Optical Power in Photonics
Power as Energy per Time
Optical power can refer to the energy of light per unit time, such as that delivered by a laser beam. It is usually measured in watts or dBm (decibels relative to 1 mW). Radiometry uses the term radiant flux for a more general application.
Measurement of Optical Power
Optical powers of laser beams are often measured using optical power meters. These devices can handle a wide range of powers, from high-power lasers to very low optical powers. Optical power monitors are commonly integrated into optical systems, especially in optical fiber communications.
Power of Light Pulses
The power of an optical pulse varies with time, with the peak power representing its maximum. Average power is often specified for regular pulse trains. Even continuous-wave lasers exhibit some level of intensity noise.
Power and Intensity
The power of a laser beam can help estimate the maximum optical intensity within its profile. The total optical power of a beam is the integral of its intensity over the full beam area.
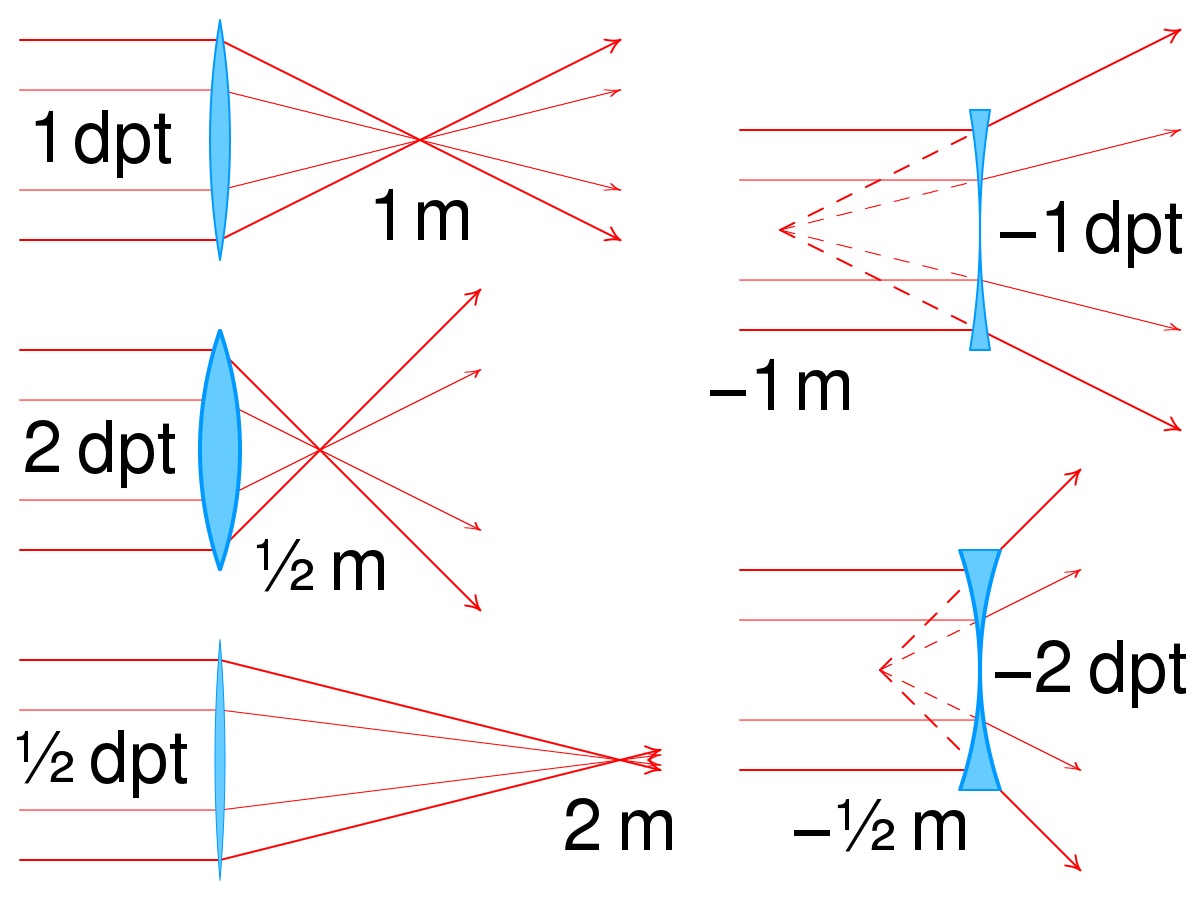
Focusing Power
Focusing power, also known as dioptric power, refers to the ability of optical elements like lenses to focus light. It is quantitatively the reciprocal of the focal length of the device, measured in inverse meters or diopters.
Conclusion
Understanding optical power is crucial in various photonics applications, from laser technology to optical communications. Whether measuring laser powers or analyzing light pulses, optical power plays a vital role in the field.

Source: Kaufland.de · Auf Lager
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



