Contents
Source: Nature
<>
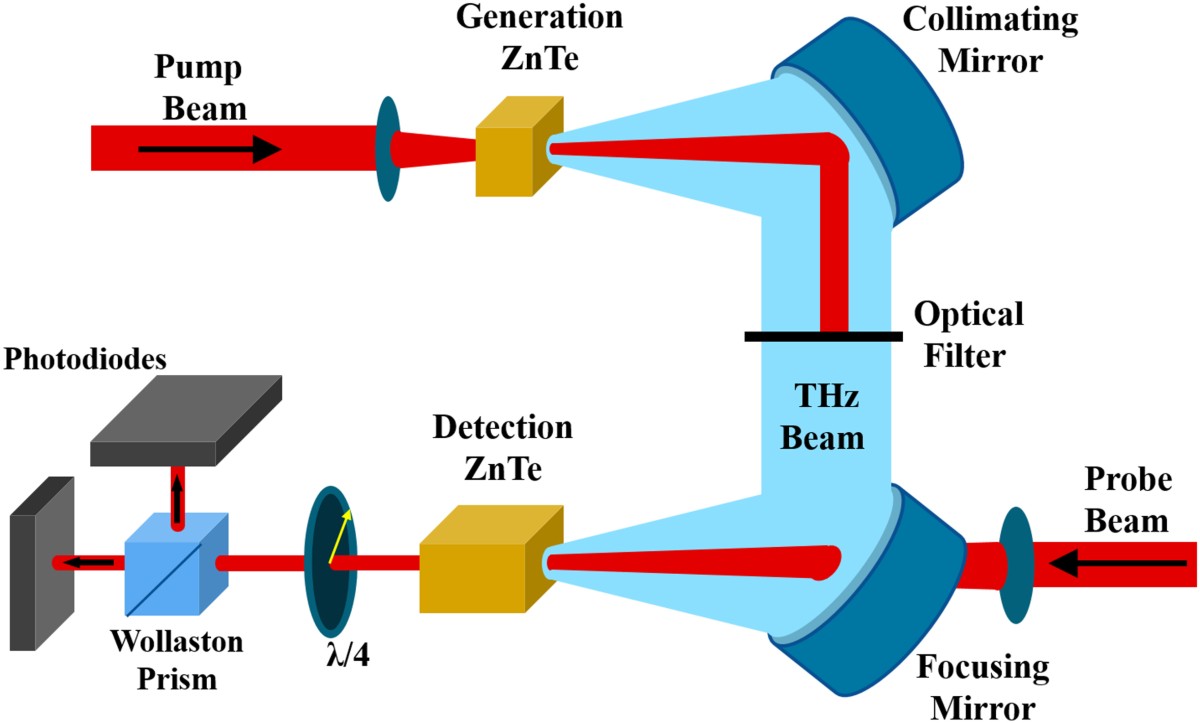
Optical Rectification for Terahertz Wave Generation
Introduction
When light passes through a material with nonlinearity, it generates a quasi-DC component in the nonlinear polarization. This component is significant when dealing with ultrashort pulses, leading to the emission of wide-spectrum electromagnetic pulses known as terahertz radiation.
Mechanism of Optical Rectification
The nonlinear polarization responsible for optical rectification is linked to the electro-optic tensor of the material. The effective electro-optic coefficient is often used to characterize the material’s nonlinearity for this process.
Comparison with Other Nonlinear Processes
Optical rectification differs from processes like frequency doubling in terms of generated radiation strength, conversion efficiencies, bandwidth, and absorption characteristics.
Materials and Phase Matching
Various materials, including inorganic crystals, organic crystals, and semiconductors, can be used for terahertz wave generation through optical rectification. Phase matching is crucial for achieving high power conversion efficiencies.
Terahertz Pulse Parameters
The energy of the generated terahertz pulse depends on the optical pulse energy, effective nonlinear coefficient, and pulse duration. Shorter pulses result in higher terahertz energy and larger bandwidth.
Dependencies and Calculations
Factors like free-carrier absorption, diffraction, pump depletion, and dispersion need to be considered in numerical models for accurate calculations of the nonlinear conversion process.
Conclusion
Optical rectification is a valuable technique for terahertz wave generation, with applications in various fields such as imaging, spectroscopy, and communications.
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



