Contents
Source: HZDR
Understanding Photocathodes
What is a Photocathode?
A photocathode is an electrode made from a material that emits electrons when exposed to light, a phenomenon known as the external photoelectric effect. These emitted electrons can be collected as a photocurrent by an anode held at a positive potential.
Applications of Photocathodes
Photocathodes are used in various photodetector devices such as photomultipliers, infrared viewers, streak cameras, image intensifiers, and image converters. They are essential components in devices that require the conversion of light signals into electrical signals.
Types of Photocathodes
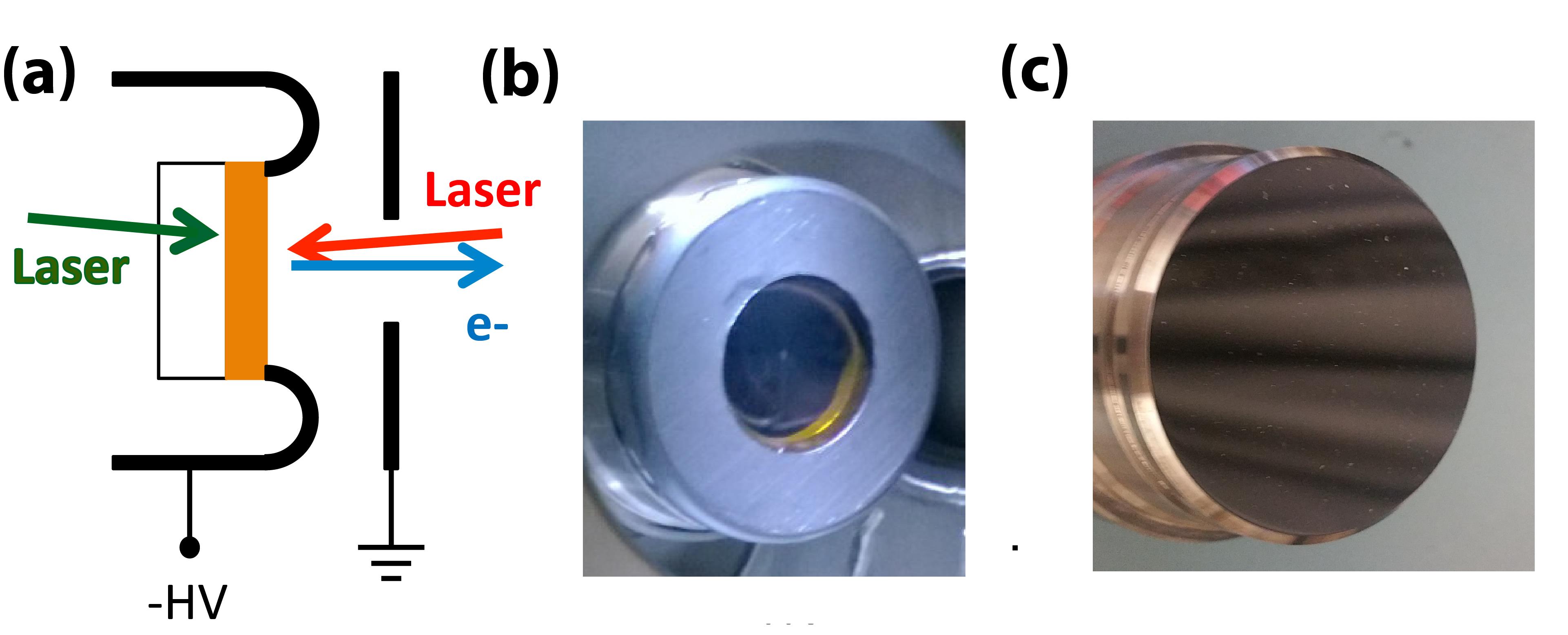
There are two main types of photocathodes: reflective and transmission-mode. Reflective photocathodes emit electrons on the side illuminated by light, while transmission-mode photocathodes allow electron extraction on the opposite side, often used in image intensifiers and photomultipliers.
Factors Affecting Performance
The performance of a photocathode is influenced by factors such as work function, spectral range, quantum efficiency, resistance, and dark current. The work function determines the maximum wavelength of light that can induce electron emission, while quantum efficiency represents the ratio of incident photons that generate electrons.
Materials Used in Photocathodes
Various materials are used in photocathodes, each with specific spectral responses and quantum efficiencies. Common materials include Sb-Cs for visible and ultraviolet regions, bialkali materials for wide spectral ranges, and semiconductors like GaAs and InGaAs for near-infrared to ultraviolet detection.
Challenges and Considerations
Photocathodes can experience aging, dark current from thermionic emission, and limitations in dynamic range and sensitivity. Proper storage, operation conditions, and material selection are crucial for optimizing the performance and lifespan of photocathodes.
Future Developments
Ongoing research aims to improve the efficiency, spectral range, and durability of photocathodes for diverse applications ranging from scientific instruments to industrial sensors.
Source: CLASSE: News and Events
Feel free to comment your thoughts.


