Contents
- 1 Understanding Polarization Beat Length in Optical Fibers
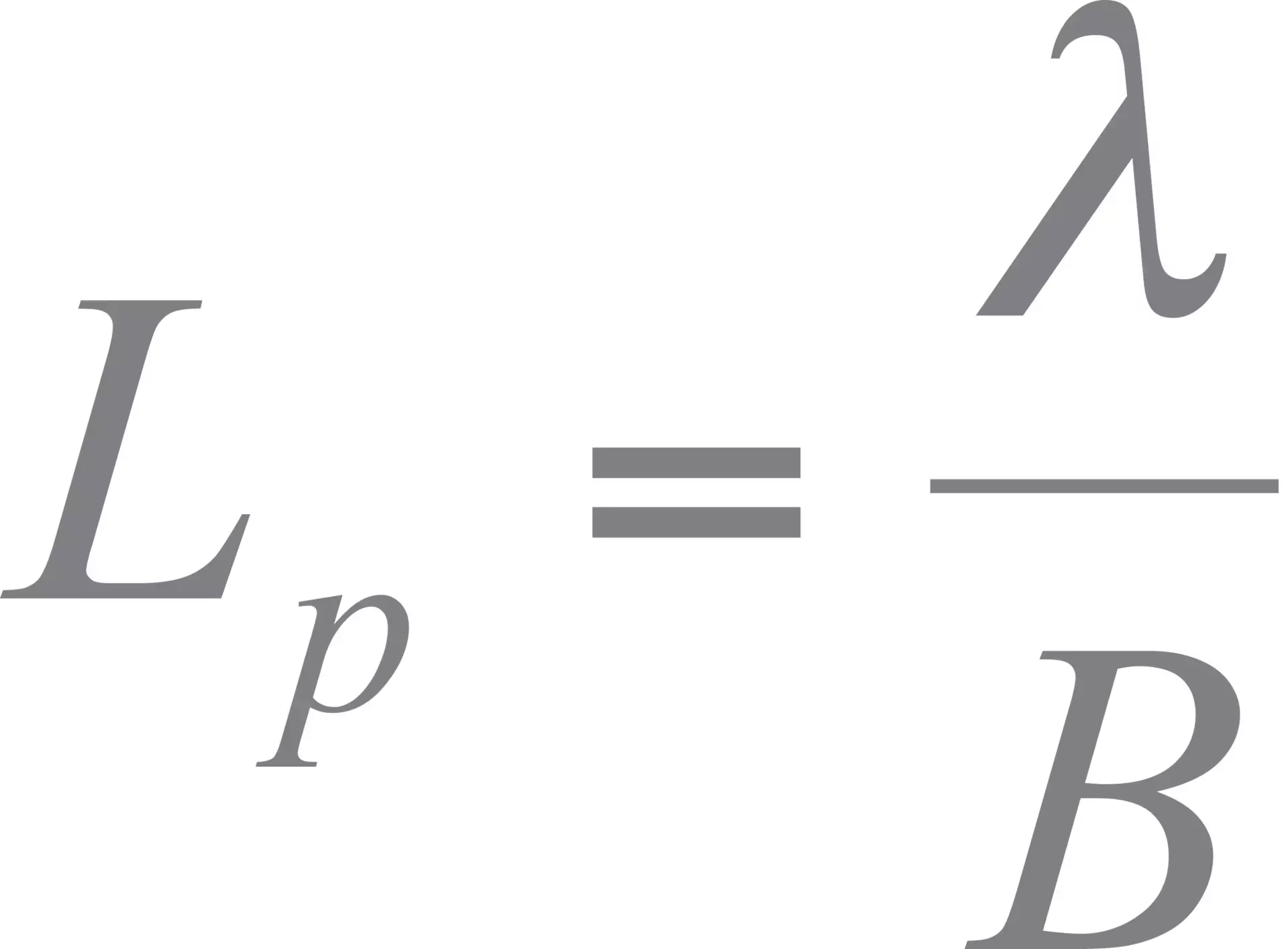
Source: Fibercore – Humanetics
Understanding Polarization Beat Length in Optical Fibers
Introduction to Polarization Beat Length
Polarization beat length is a fundamental concept in the study of optical fibers, particularly those that exhibit birefringence. This phenomenon occurs when two waves with different linear polarization states propagate through a birefringent medium, causing their phases to evolve at different rates. The polarization beat length is the distance over which these phase differences accumulate to a full cycle, effectively restoring the original phase relationship between the waves.

The Role of Birefringence
Birefringence is a property of certain materials where the refractive index varies depending on the polarization and propagation direction of light passing through it. In optical fibers, birefringence can arise from structural asymmetries or external stresses. This causes two orthogonally polarized waves to travel at different speeds, leading to a phase difference that varies linearly with the propagation distance.
Calculating Polarization Beat Length
The polarization beat length ( L_b ) can be calculated using the formula:
( L_b = frac{lambda_0}{n_x – n_y} )
where ( lambda_0 ) is the vacuum wavelength, and ( n_x ) and ( n_y ) are the refractive indices for the two orthogonal polarization states. The polarization beat length is essentially the period of the polarization evolution, marking the distance over which the polarization state of the light returns to its original configuration.
Significance in Polarization-Maintaining Fibers
In polarization-maintaining (PM) fibers, a short polarization beat length is often desirable as it indicates strong birefringence. This enhances the fiber’s ability to maintain the polarization state of light over long distances, reducing sensitivity to external perturbations such as mechanical stress or imperfections in the fiber.
Typical Beat Length Values
For PM fibers, polarization beat lengths can range from a few centimeters to even sub-millimeter scales in advanced photonic crystal fibers. Short beat lengths are advantageous as they minimize mode coupling effects, which can degrade the performance of the fiber.
Challenges in Non-Birefringent Fibers
In fibers designed to be non-birefringent, theoretically, the polarization beat length should be infinite. However, due to unavoidable imperfections and stresses, some residual birefringence is present, leading to a finite beat length that can vary significantly. This makes the characterization of such fibers more complex, often requiring statistical analysis to determine average properties.
Measurement Techniques
Several methods exist for measuring the polarization beat length of optical fibers. A common approach involves using linearly polarized broadband light and analyzing the resulting optical spectrum after it passes through the fiber. The spectral oscillations observed are directly related to the polarization beat length.
Relation to Polarization Mode Dispersion
Polarization mode dispersion (PMD) is related to the polarization-dependent group delay in optical fibers. While the polarization beat length provides insight into the birefringence of the fiber, it is not directly indicative of PMD, which depends on the derivative of the propagation constant difference with respect to optical frequency.
Conclusion
Understanding polarization beat length is crucial for optimizing the performance of optical fibers, especially in applications requiring precise control over polarization states. Advances in fiber technology continue to improve our ability to manage and exploit birefringence, leading to more efficient and reliable fiber optic systems.

Source: YouTube
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



