Contents
Source: Nature
Understanding Quasi-Three-Level Laser Gain Media
Introduction to Quasi-Three-Level Systems
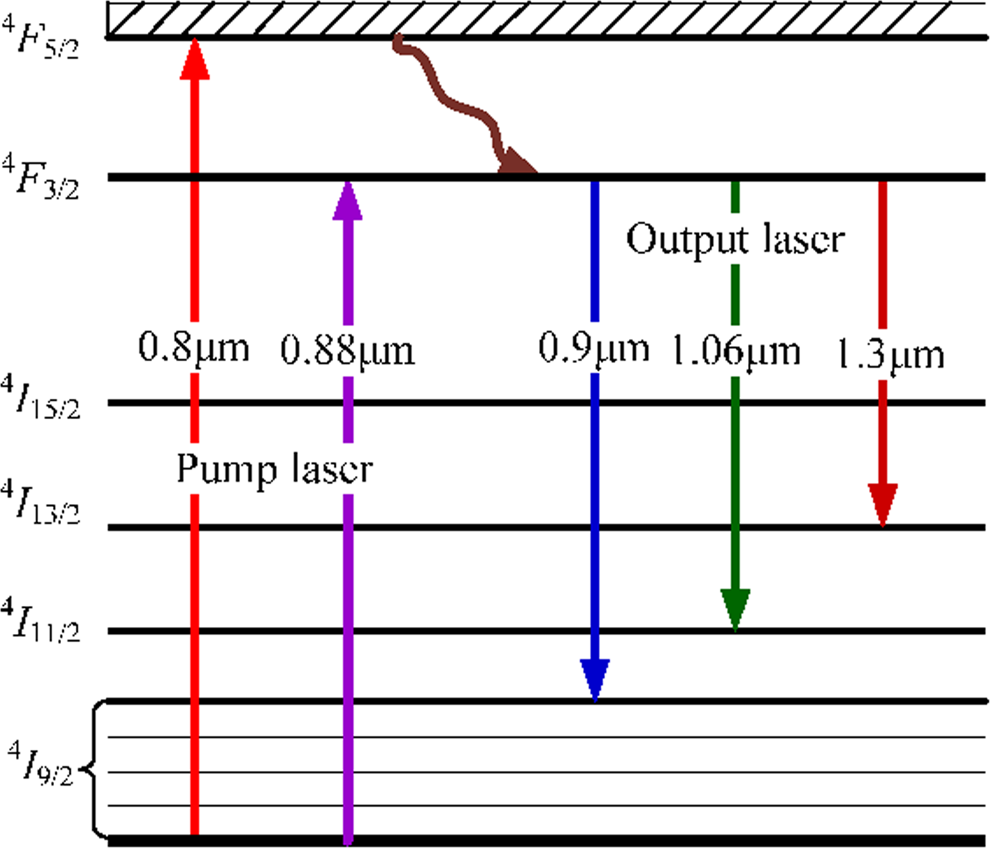
Quasi-three-level laser gain media exhibit characteristics that lie between traditional four-level and three-level systems. In these systems, there are four energy levels, but the second-lowest level is only slightly above the ground state, leading to unique behavior in terms of population distribution and gain.
Application in Solid-State Lasers
Quasi-three-level behavior is commonly observed in solid-state lasers, particularly in fiber lasers and amplifiers. For example, Yb3+:YAG crystals demonstrate quasi-three-level characteristics due to the specific energy level configurations of ytterbium ions.
Behavior in Different Wavelength Ranges
The behavior of quasi-three-level systems varies depending on the wavelength of operation. For instance, at longer wavelengths (e.g., 1060 nm), the system may exhibit characteristics closer to a four-level system, while at shorter wavelengths, the quasi-three-level behavior becomes more prominent.
Excitation-Dependent Gain Spectra
The spectral shape of the optical gain in quasi-three-level systems is influenced by the excitation level. At lower excitation levels, gain may be more prominent at longer wavelengths, while higher excitation levels lead to gain at shorter wavelengths. This dynamic behavior is crucial for optimizing laser performance.
Challenges and Efficiency Considerations
Despite their potential for high efficiency, quasi-three-level gain media face challenges such as incomplete pump absorption and losses due to fluorescence. These factors can impact the overall power efficiency of the laser system, requiring careful design considerations.
Common Misconceptions
Misunderstandings about reabsorption, transition cross-sections, and saturation fluence are common in the literature regarding three-level gain media. Clarifying these concepts is essential for a deeper understanding of laser physics and design.
Conclusion
Quasi-three-level laser gain media offer a unique set of characteristics that make them valuable for various laser applications. By understanding their behavior, challenges, and efficiency considerations, researchers and engineers can optimize the performance of laser systems utilizing these gain media.

Source: Fosco Connect
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



