Contents

Source: Tara Energy
<>
Radiant Energy in Radiometry
Understanding Radiant Energy
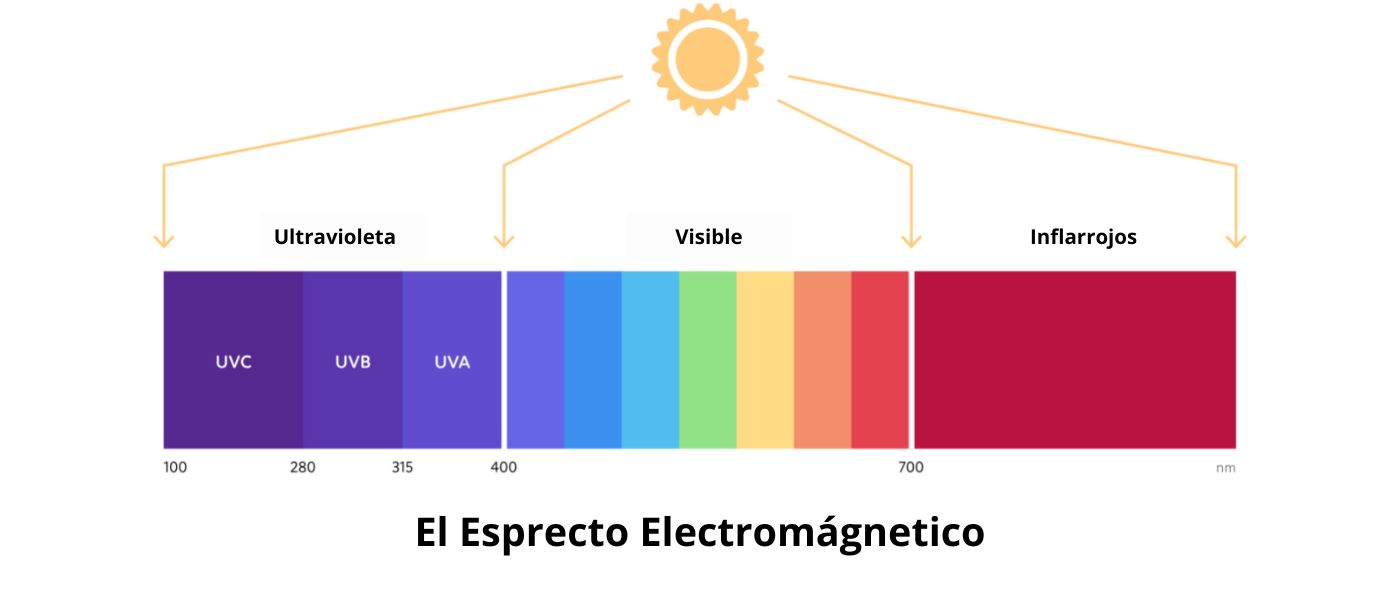
Radiant energy refers to the energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, which can be emitted, transmitted, or absorbed over a specific period. In radiometry, this concept plays a crucial role in various applications.
Relation to Luminous Energy
In the realm of radiometry, the counterpart of radiant energy is luminous energy. While radiant energy deals with the total energy of electromagnetic radiation, luminous energy focuses on the energy perceived by the human eye, taking into account the sensitivity of the human eye to different wavelengths of light.
Applications in Different Fields
Radiant energy finds applications in fields such as illumination and radiative heating, particularly with infrared radiation. In laser technology, however, the term “pulse energy” is more commonly used to describe the energy within an optical pulse.
Derived Quantities
Various radiometric quantities are derived from radiant energy. For instance, radiant flux represents the radiant energy per unit time, which is equivalent to optical power in optics. Additionally, radiant exposure quantifies the amount of radiant energy received per unit area.
Further Exploration
Radiant energy serves as a foundational concept in radiometry, influencing the measurement and understanding of light and other forms of electromagnetic radiation. Exploring this topic can lead to a deeper comprehension of energy transfer and interactions in diverse scientific and technological domains.
Source: Repsol
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



