Contents

Source: YouTube
<>
Understanding Return Loss in Optics
What is Return Loss?
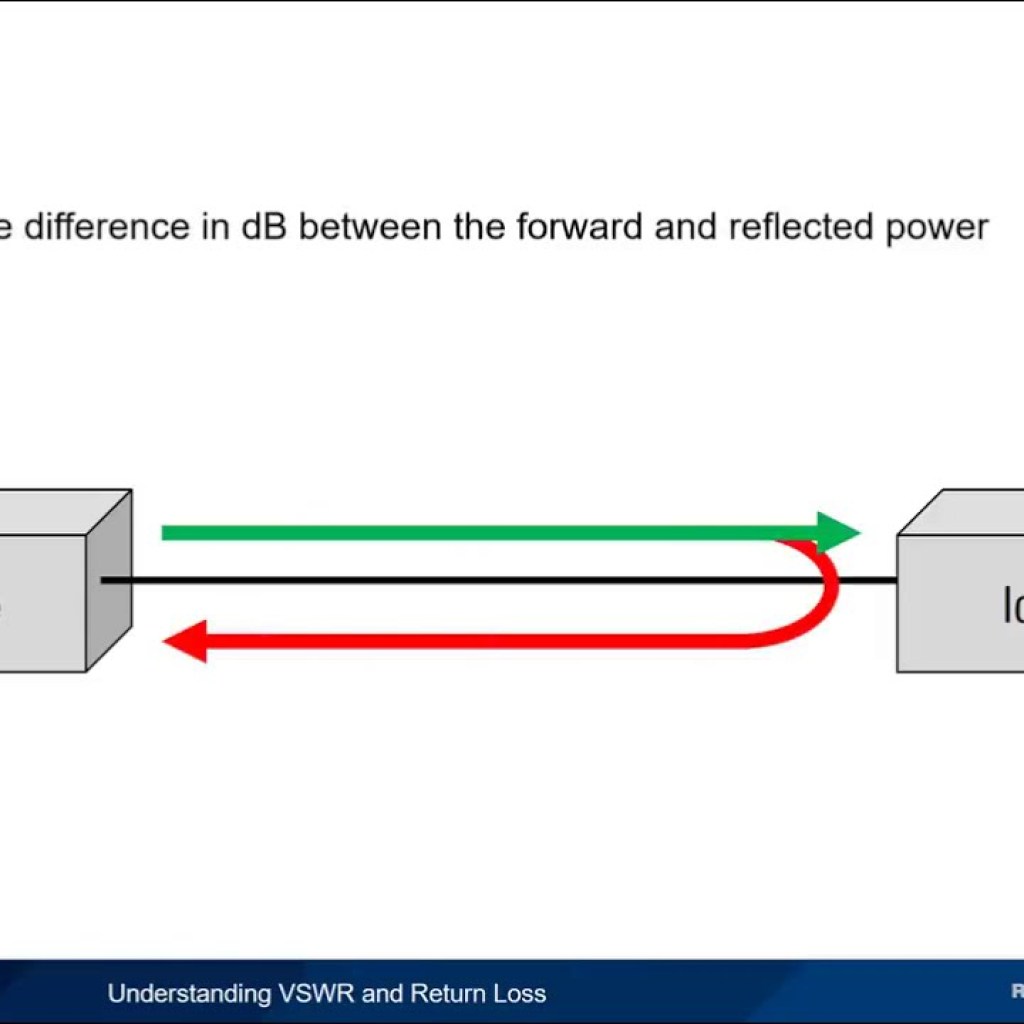
Return loss, also known as reflection loss, measures the reduction in optical power of reflected light compared to the incident light. It is typically expressed in decibels (dB), where a higher value indicates lower reflected power. Return loss only considers directly reflected light and not light redirected at an angle.
Factors Affecting Return Loss
Various factors can impact return loss in optical devices. For instance, differences in guiding properties of optical fibers or poor splices can lead to increased return loss. Quality splices should have a return loss of at least 45 dB, with angle-cleaved splices achieving even higher values.
Applications of Return Loss
Return loss plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency of optical components. For example, in fiber-optic communication systems, high return loss is essential for minimizing signal loss and maintaining signal integrity.
Importance of High Return Loss
High return loss is vital in various optical setups to prevent signal degradation, ensure signal fidelity, and minimize reflections that can interfere with system performance.
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing return loss in optical systems is essential for achieving reliable and efficient performance in various applications, from telecommunications to fiber-optic sensing.

Source: YouTube
Feel free to comment your thoughts.