Contents
Source: www.batop.de
<>
Saturable Absorbers in Photonics
Introduction
A saturable absorber is an optical component that exhibits reduced absorption loss for light at high optical intensities. This nonlinear absorption phenomenon is crucial in various photonics applications, such as passive mode locking and Q switching of lasers.
Types of Saturable Absorbers
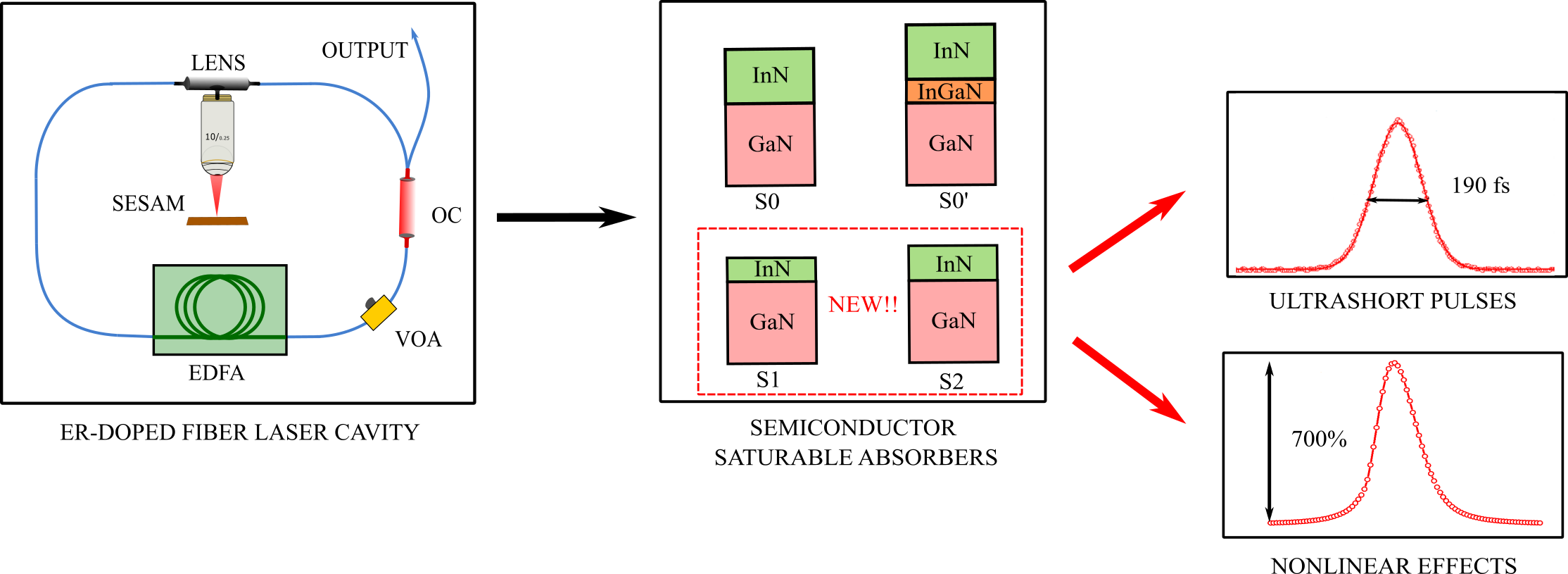
Saturable absorbers can be natural, like those found in certain materials, or artificial, designed to exhibit specific optical properties. One common type is the semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM), which is reflective and used in mode-locked lasers.
Artificial Saturable Absorbers
Artificial saturable absorbers do not rely on actual absorption but on optical loss that decreases with increasing optical power. These devices can be tailored for specific applications and offer flexibility in photonics systems.
Properties of Saturable Absorbers
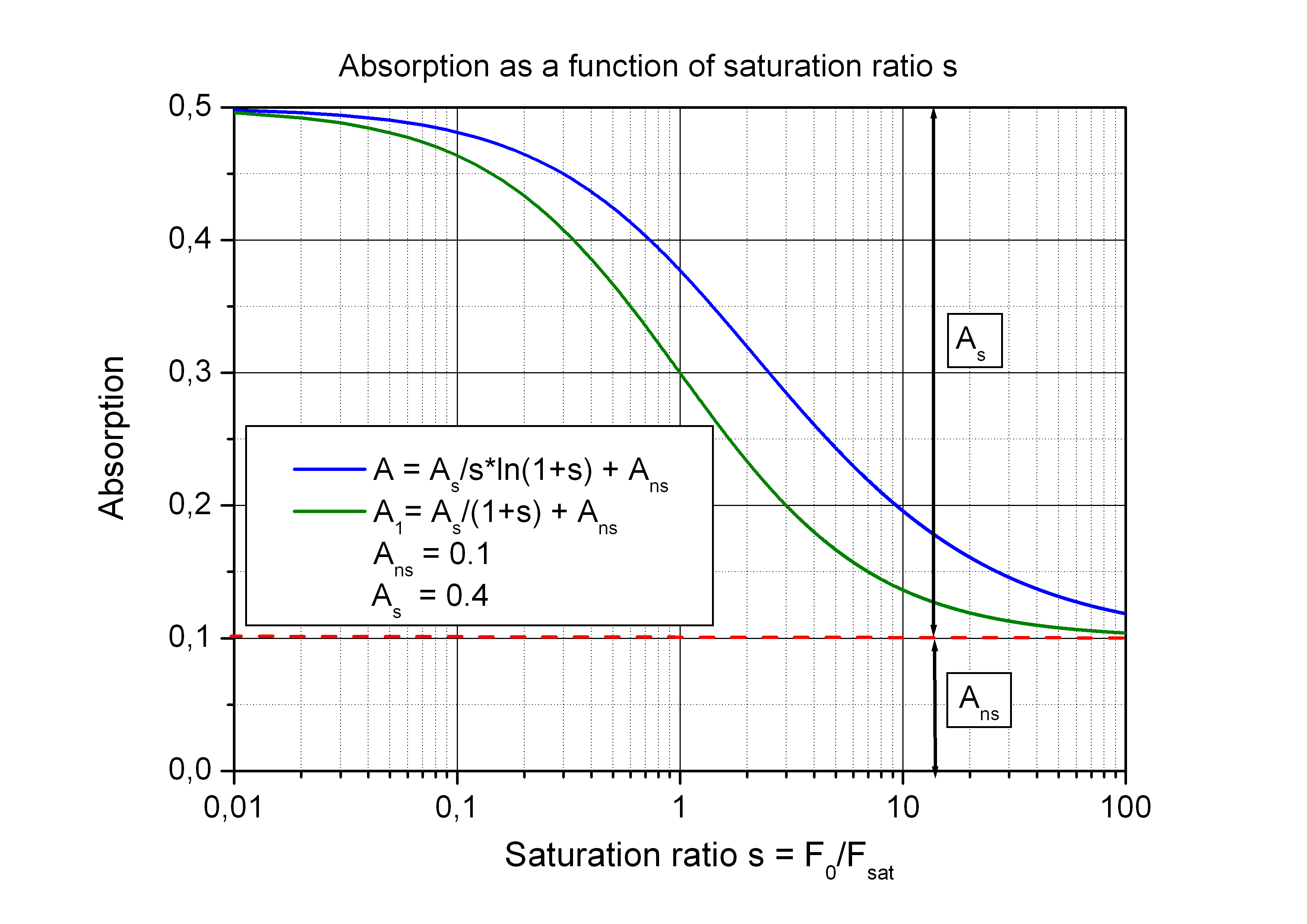
Key properties of saturable absorbers include modulation depth, non-saturable losses, recovery time, saturation fluence, saturation energy, saturation intensity, and damage threshold. These properties determine the performance and suitability of the absorber for different laser applications.
Selecting a Suitable Saturable Absorber
Choosing the right saturable absorber depends on the specific requirements of the laser system. For Q-switched lasers, factors like total absorption, saturation fluence, and recovery time are crucial. In contrast, mode-locked lasers prioritize modulation depth, saturation fluence, and recovery time for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Saturable absorbers play a vital role in laser technologies, enabling precise control over pulse generation and laser operation. Understanding the characteristics and selection criteria for saturable absorbers is essential for designing efficient and reliable photonics systems.
Source: MDPI
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



