Contents
Source: MDPI
Understanding Self-Terminating Lasers
Introduction
Self-terminating lasers are a type of solid-state gain media with laser transitions where the lower laser level has a longer lifetime than the upper-state lifetime. This unique characteristic poses challenges for continuous-wave operation, as lasing can only occur for a short period before the lower level becomes too populated for a population inversion to be sustained.
Examples of Self-Terminating Lasers
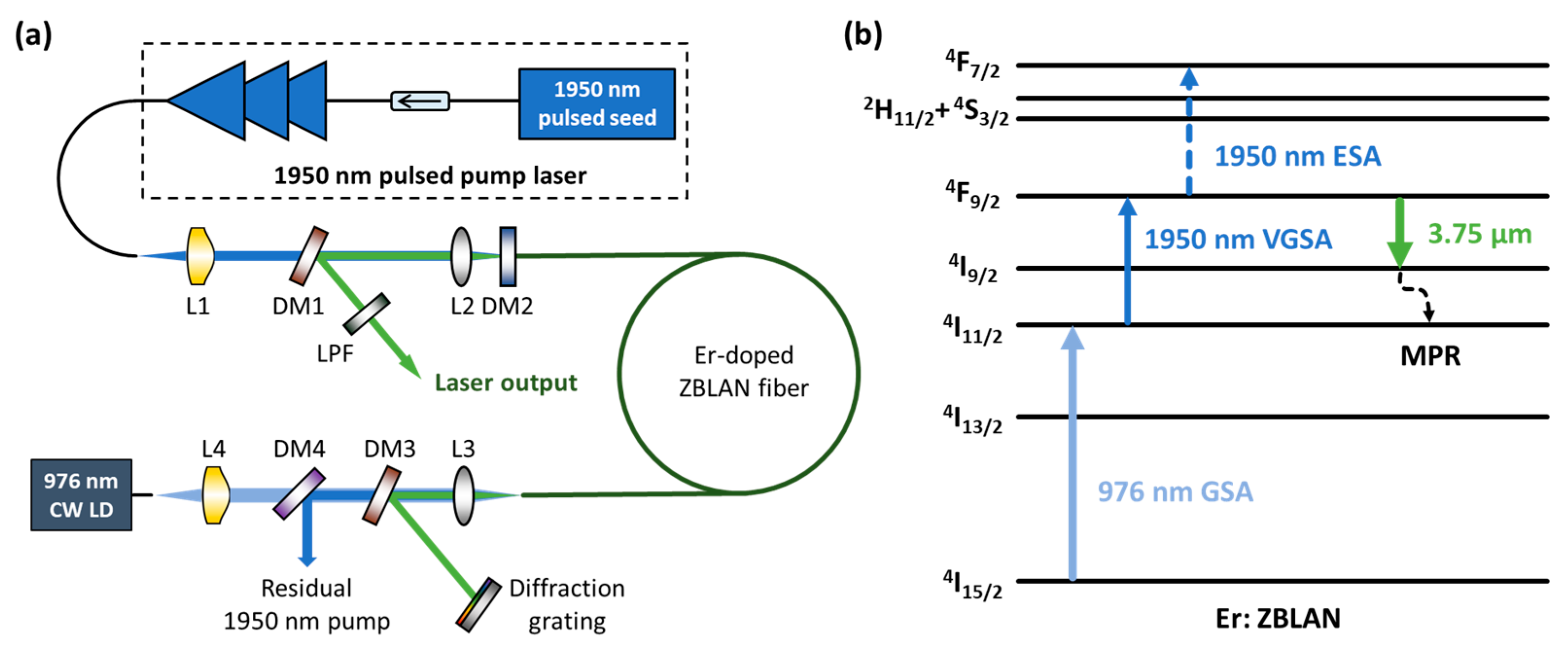
One example of a self-terminating laser is the 2.7-μm transition of erbium (Er3+) in fluoride fibers. Other examples include the copper vapor laser and nitrogen lasers.
Achieving Continuous Laser Operation
To achieve continuous-wave operation in self-terminating lasers, methods for depopulating the lower laser level effectively are required. One approach is to introduce an additional dopant that can quench the population in the lower laser level through energy transfer. Another method involves using cooperative lasing from the lower laser level to a lower energy level.
Conclusion
Self-terminating lasers present unique challenges for continuous operation due to the long lifetime of the lower laser level. By implementing techniques to depopulate the lower level effectively, continuous-wave operation can be achieved in these lasers. Further research and development in this area are essential for advancing laser technology.
Source: Nature
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



